1. Changes in Periodic Labour Force Survey 2025 | Key Updates & Coverage
For Prelims:
-
PLFS 2025 revamp
-
National Statistical Office (NSO)
-
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
-
Labour market estimates improvement
-
Frequency, coverage, accuracy enhancement
-
Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR)
-
Worker Population Ratio (WPR)
For Mains:
-
First Stage Units (FSUs) increase 12,800 → 22,692
-
Households surveyed per FSU increase 8 → 12
-
First Stage Unit definition
-
2011 census village
-
Urban Frame Survey (UFS) block
-
Usual activity status
Context
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) has revamped the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) methodology from January 2025 to improve frequency, coverage, and accuracy of labour market estimates.
About PLFS
- It is a survey conducted by the National Statistics Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) to estimate key employment and unemployment indicators in India. PLFS releases both monthly and annual data.
- Monthly bulletins provide estimates of labor market indicators like Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR), Worker Population Ratio (WPR), and Unemployment Rate (UR) in Current Weekly Status (CWS) separately for males and females.
- Annual report providing estimates in both usual status and CWS.
Key Changes
Monthly Estimate Introduced
- It will enable the generation of the monthly estimates of key labour market indicators viz. LFPR, WPR, and UR at the all-India level following the Current Weekly Status (CWS) approach.
Quarterly Estimates Extended to Rural Areas
- Upto December 2024, PLFS provided quarterly labour market indicators for the urban areas only.
- Now available for the entire country, improving rural employment data.
Enhanced Sample Size & Coverage
- First Stage Units (FSUs) increased from 12,800 to 22,692 annually.
- The number of households to be surveyed within a selected geographical unit (FSU) has been increased from 8 to 12 households.
About First Stage Unit
- First Stage Units (FSUs) are the basic geographical units used for sample selection.
- In rural areas, the FSU is typically the 2011 census village (or Panchayat ward in Kerala). In urban areas, it’s the Urban Frame Survey (UFS) block.
- The FSUs are the initial units from which households are then selected for the survey.
Conceptual Framework
- Activity status of a person is determined on the basis of the activities pursued by the person during the specified reference period.
- Current weekly status (CWS): Activity status determined on the basis of a reference period of last 7 days preceding the date of survey.
- Usual activity status: Activity status determined on the basis of the reference period of last 365 days preceding the date of survey
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): LFPR is defined as the percentage of persons in the labour force (i.e. working or seeking or available for work) in the population.
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): WPR is defined as the percentage of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): UR is defined as the percentage of persons unemployed among the persons in the labour force.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION
With reference to the ‘National Statistical Office (NSO)’, consider the following statements:
- It is an attached office under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- It is responsible for conducting large-scale sample surveys in various fields, including employment and unemployment.
- The data it collects is used for calculating GDP and other macroeconomic indicators.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
Mains:
Q. MAINS QUESTION 2020, GS 3
Account for the changes in the employment pattern in India over the last few decades.
Ans:
2. Groundwater Contamination in India: Public Health Crisis & Solutions
For Prelims:
-
Groundwater contamination India
-
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) 2024 report
-
Public health emergencySkin lesions and cancers
-
Joint pain and skeletal deformities
-
Kidney damage and neurological issues
-
Regulatory framework strengthening
For Mains:
-
Rural drinking water dependence 85%
-
Irrigation dependence 65%
-
Nitrate contamination (>20% samples)
-
Fluoride contamination (>9% samples)
-
Arsenic in Punjab, Bihar, Gangetic belt
-
Uranium contamination >100 ppb (Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan)
-
Iron and heavy metals excess (>13% samples)Sustainable agriculture, organic farming, IPM
-
Public awareness on groundwater protection
-
Regular monitoring and research
-
Community-led groundwater management
Context
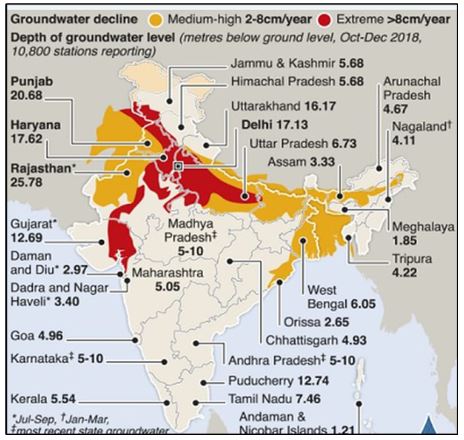
- India’s worsening groundwater contamination crisis has emerged as a major public health threat, with toxic pollutants linked to chronic illnesses across several states.
About
- Groundwater is the lifeline of India, meeting over 85% of rural drinking water and 65% of irrigation needs.
- Once considered pure, it is now increasingly tainted by nitrates, heavy metals, industrial pollutants, and pathogenic microbes.
- The 2024 Annual Groundwater Quality Report by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) has revealed alarming contamination levels across the country, underscoring the urgent need for systemic reform.
- This crisis is no longer limited to environmental concerns; it is a nationwide public health emergency.
Scale and Nature of Groundwater Contamination
Groundwater samples from over 440 districts show dangerous levels of contaminants
- Nitrates: Found in more than 20% of samples, mainly due to excessive fertiliser use and septic tank leakage.
- Fluoride: Excess levels in over 9% of samples, causing dental and skeletal fluorosis in states like Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic: Detected at unsafe levels in parts of Punjab, Bihar, and the Gangetic belt, posing severe cancer and neurological risks.
- Uranium: Recorded above 100 ppb in districts of Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, and Rajasthan, linked to phosphate fertilisers and over-extraction.
- Iron and Heavy Metals: Over 13% of samples exceeded safe iron limits; lead, cadmium, and mercury have been traced to industrial discharges..
Causes of Groundwater Contamination
- Industrial Discharges: Rapid industrialisation has led to the unregulated disposal of hazardous waste into water bodies. Industries such as textiles, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals often release toxic substances seeping into groundwater.
- Agricultural Practices: The excessive use of fertilisers and pesticides in agriculture contributes significantly to groundwater contamination. Nutrients like nitrates and phosphates leach into the soil, eventually reaching the water table. Additionally, improper irrigation and over-extraction of water further exacerbate the issue.
- Urbanisation: The rapid growth of urban areas often results in inadequate waste management systems. Sewage and solid waste are frequently dumped untreated, leading to leachate contaminating groundwater.
- Deforestation and Land Use Changes: Deforestation and changes in land use disrupt the soil’s natural filtration processes. This can lead to increased runoff and the subsequent entry of pollutants into groundwater systems.
- Mining Activities: Mining operations can introduce heavy metals and other harmful substances into the environment. When these contaminants reach groundwater sources, they pose serious health risks.
Health Impacts
- Fluorosis: Affecting over 66 million people in 230 districts; leads to joint pain, deformities, and stunted growth in children.
- Arsenicosis: Causes skin lesions, cancers, gangrene, and respiratory illnesses; prevalent in West Bengal, Bihar, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Nitrate Poisoning: Responsible for “blue baby syndrome” in infants; 56% of districts exceed safe nitrate limits.
- Uranium Toxicity: Causes chronic organ damage and kidney disorders; children are particularly at risk.
- Waterborne Diseases: Outbreaks of cholera, dysentery, and hepatitis due to sewage infiltration into aquifers.
Solution to the Crisis
- Regulatory Framework: Strengthening laws and regulations related to industrial discharges, agricultural practices, and waste management is essential. Implementing stricter penalties for non-compliance can deter polluters.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Promoting organic farming and integrated pest management can reduce the reliance on harmful chemicals. Training farmers in sustainable practices can help minimise the leaching of pollutants into groundwater.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: It is vital to educate communities about the importance of groundwater conservation and contamination prevention. Awareness programs can encourage responsible water use and pollution prevention practices.
- Research and Monitoring: Investing in research to understand the extent and nature of groundwater contamination can inform effective policy-making. Regular monitoring of groundwater quality can help in the early detection of contaminants and prompt remediation actions.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in groundwater management can enhance the effectiveness of conservation efforts. Community-led initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards protecting water resources.
Mains:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION 2013
Which of the following can be a source of groundwater contamination?
- Pesticide and fertiliser application in agriculture
- Industrial effluents
- Urban sewage
- Leachate from solid waste
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans:
Q. MAINS GS PAPER 2, 2019
Discuss the challenges of ensuring safe drinking water in urban and rural areas of India and suggest suitable policy measures.
Ans:
3. India's Soft Power Diplomacy: Challenges, Opportunities & Global Influence
For Prelims:
-
Cultural diplomacy
-
Bollywood global influence
-
Yoga & Ayurveda promotion
-
Indian cuisine diplomacy
-
Classical & folk arts global outreach
-
Indian diaspora as informal ambassadors
-
Remittances & knowledge transfer
-
Development partnership & humanitarian aid
-
Vaccine Maitri initiative
For Mains:
-
Non-Aligned Movement legacy
-
Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC)
-
Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
-
BRICS, SCO, Quad participation
-
Global South leadership
-
UNSC reform advocacy, Promotion of Indian languages abroad
-
Strategic diaspora engagement
-
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas
-
Digital diplomacy initiatives
Context
- With India's gradual rise in the international system, the issue of influence, perception and cultural diplomacy have gained significant attention amongst policymakers.
More Facets
- Beginning with the liberalisation of the economy, opening to foreign investments and the growth of modern media and communication technologies, soft power moved from being an academic concept to a political buzzword.
- Moreover, active use of public diplomacy by other rising powers such as China's "charm offensive" also drove India to up its ante further.
Key Elements of India's Soft Power Arsenal
Cultural Exports
- Bollywood & Regional Cinema: Massive global reach, especially in Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and the diaspora. Shapes perceptions of India and builds cultural familiarity.
- Yoga & Ayurveda: Universally recognized symbols of wellness and ancient Indian knowledge. Yoga Day celebrations are a major soft power success.
- Cuisine: Indian food is globally popular, serving as an accessible entry point to Indian culture.
- Dance, Music & Arts: Classical and folk traditions attract global interest and foster cultural exchange.
- Spiritual Traditions: Hinduism, Buddhism (as an export), Sikhism, and others attract seekers and promote values of peace and tolerance
Indian Diaspora
- Highly successful professionals (tech, academia, business, politics) in the West enhance India's image and act as informal ambassadors.
- Remittances and knowledge transfer contribute significantly.
Development Partnership & Humanitarian Aid
- Provides assistance to neighbours and developing nations (e.g. vaccines during COVID - "Vaccine Maitri"), building goodwill.
India's Soft Power Diplomacy in Action
- Historical Context: The article traces India's soft power roots to its non-aligned movement during the Cold War, which positioned it as a leader of the Global South. This legacy continues through India's advocacy for developing nations.
- Modern Initiatives: Programs like the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) and cultural exchanges through the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) promote India's influence. For example, ITEC has trained over 200,000 professionals from developing countries.
- Global Leadership: India's role in forums like BRICS, SCO, and the Quad, as well as its push for reforms in global institutions like the UN Security Council, enhances its soft power by projecting leadership and inclusivity.
- Vaccine Diplomacy: India's supply of affordable vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly to African and South Asian nations, earned goodwill and strengthened bilateral ties.
Major Challenges
- Tourism: Potential hampered by poor sanitation, transportation, safety concerns (especially for women), bureaucratic hassles (visas), and inadequate tourist infrastructure despite incredible heritage sites.
- Cultural Institutes: Underfunding and lack of strategic focus for institutions like the ICCR compared to competitors (e.g.,China's Confucius Institutes).
- Limited Global Media Presence: India's international media outreach (e.g.,through platforms like DD India) is weak compared to global giants like BBC or Al Jazeera.
- Inconsistent Branding: Unlike countries like the U.S. or Japan, India lacks a cohesive soft power strategy.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Cultural Diplomacy: Expanding ICCR's network of cultural centers and promoting Indian languages (e.g., Hindi, Sanskrit) can deepen global engagement.
- Leveraging the Diaspora Engaging the diaspora more strategically, through events like Pravasi Bharatiya Divas, can amplify India's influence.
- Digital Diplomacy: Investing in digital platforms and social media to promote India's culture and achievements can counter negative narratives and reach younger audiences.
- Educational Exchanges: Expanding scholarships for foreign students and promoting Indian universities as global education hubs can build long-term goodwill.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION
With reference to India’s cultural diplomacy, consider the following:
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India.
- It is responsible for India's participation in the SAARC Cultural Year activities.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?*
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2"
Ans:
Mains:
Q. MAINS 2019, GS PAPER 1
Highlight the significance of India’s cultural heritage in strengthening the country’s soft power in international relations."
Ans:
4. India’s NSA Ajit Doval Visit to Russia Amid US Trade Tensions: Defence & Strategic Ties
For Prelims:
-
IRIGC-MTC
-
UNSC permanent membership support
-
BRICS
-
SCO
-
G20
-
Act Far East policy
-
Indo-Pacific engagement
-
Russia-China alignment concerns
-
US-India strategic partnership
-
sanctions payment issues
-
delayed S-400
For Mains:
-
India-Russia defence ties
-
industrial cooperation
-
S-400 missile systems
-
Su-57 fighter jets
-
S-400 MRO facility India
-
Operation Sindoor
-
Pahalgam terror attack
-
BrahMos missile
-
Vladimir Putin India visit
-
US-India trade tensions
-
Russia-Ukraine war
-
Russia-China alignment concerns
-
US-India strategic partnership
-
sanctions payment issues
Context
- Amid tensions with the United States, Indian National Security Adviser Ajit Doval headed to Moscow in a bid to expand defence and industrial ties between India and Russia.
About the Visit
- The visit will focus on strengthening Defence as well as Industrial Ties.
- NSA Ajit Doval’s visit would also focus on the purchase of additional S-400 missile defence systems and dialogue on Su-57 fighter jets.
- As per reports, the two sides would discuss the possibility of the purchase of additional S-400 missile systems and the talks could include setting up S-400 MRO facilities in India.
- NSA Ajit Doval also thanked Russia for its Support for Operation Sindoor and condemning of Pahalgam Terrorist Attack
Current Geopolitical Ties Demands Greater Cooperation
- It is also pertinent to note that the Russian S-400 System played a crucial role in Operation Sindoor that targeted nine terror camps located in Pakistan and Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir.
- At the same time Brahmos Missile, a joint venture between India and Russia played a significant role during operation Sindoor.
Importance of the Visit
- NSA Ajit Doval also confirmed the upcoming Visit of Russian President Vladimir Putin to India at End of the Year.
- The Visit comes amid escalating trade relations between the USA and India.
- The visit comes at a crucial time, as Russian President Vladimir Putin and American President Donald Trump can meet in UAE for the Russian-Ukraine War.
About India - Russia Relations
- Historical Overview:
- 1947: India and the USSR established diplomatic relations just months before India gained independence in August 1947.
- Cold War Period (1947-1991): The USSR emerged as a reliable ally for India, especially during times of Western hostility.
- Both signed the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation (1971) that laid the foundation for a strategic partnership.
- 1991: India recognised the Russian Federation after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
- 1993: Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation
- 2000: Declaration of Strategic Partnership
- Multi-Dimensional Cooperation Framework: India and Russia are bound by a Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership (2010).
- Over the years, it has expanded far beyond traditional military ties, integrating economic, energy, space, and educational cooperation.
Trade and Economic Relations
- Bilateral Trade: Over US$60 Billion in 2024-25; ($50 Billion in 2023–24).
- Main Imports from Russia: Crude oil, coal, fertilizers, and defense equipment.
- Main Exports to Russia: Pharmaceuticals, electronics, iron & steel, tea, and coffee.
- Strategic and Defense Cooperation: It includes INS TUSHIL, S-400 Triumf missile systems, INS Vikramaditya, production of AK-203 Rifle, BrahMos Missile, submarines, tanks, and aircraft.
- India-Russia Inter-Governmental Commission on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-MTC): It continues to coordinate procurement, servicing, and joint R&D programs.
Political and Multilateral forums
- Support on Global Platforms: Russia reiterated its support for India’s permanent membership in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- Both countries coordinate in BRICS, SCO, and G20 to push for a multipolar global order.
- Russia is supportive of India’s Act Far East Policy and Indo-Pacific engagement.
Challenges in Relations
- Geopolitical Pressures: Russia’s growing alignment with China, India’s regional rival, has raised concerns in India.
- India’s strategic partnerships with Western nations, particularly the US, have added layers of complexity to its ties with Russia.
- Payment mechanisms are a challenge due to Western sanctions on Russia, which restrict banking channels.
- Delay in Defense Equipment: Russia’s delayed delivery of the S-400 Triumf air defense system, largely due to the Ukraine conflict and related sanctions, has raised concerns in Indian defence circles.
- India’s efforts to diversify its defense procurement sources could impact its reliance on Russian arms.
- Ukraine Conflict: India’s neutral stance on the Ukraine war has been criticized by Western allies, while Russia expects stronger support from India.
- The conflict has also disrupted global supply chains, affecting bilateral trade.
Conclusion
- As India and Russia mark 78 years of diplomatic engagement, their relationship stands as a resilient example of strategic pragmatism.
- From being Cold War-era allies to 21st-century strategic partners, the journey reflects adaptability, trust, and mutual benefit.
- Despite shifting global dynamics, India-Russia ties are poised to remain strong, with new frontiers in trade, technology, and defense cooperation.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION
With reference to India’s foreign relations, consider the following statements:
- BrahMos missile is a joint venture between India and Russia.
- INS Vikramaditya was originally a Russian-built aircraft carrier.
- The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant is being built with Russian assistance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
Mains:
Q. MAINS GS PAPER 2
Discuss India’s policy of balancing its relations with the United States and Russia. Highlight the strategic significance of this approach for India’s foreign policy."
Ans:
5. Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms & Rare Intrahepatic Case in India
For Prelims:
-
Ectopic pregnancy
-
Bulandshahr rare intrahepatic case
-
Foetus growing in liver
-
Fertilized egg outside uterus
-
Tubal pregnancy
-
Ovary implantation
-
Abdominal cavity implantation
For Mains:
-
Vaginal bleeding
-
Lower abdominal pain
-
Pelvic pain
-
Back pain
-
Dizziness
-
Fainting
-
Shoulder pain
-
Bowel movement discomfort
-
Low blood pressure
Context
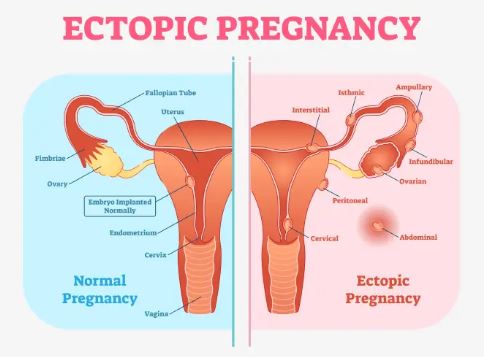
- Recently, in Bulandshahr, Uttar Pradesh, doctors identified an extremely rare case of intrahepatic ectopic pregnancy, where a foetus was growing in a woman’s liver.
About Ectopic Pregnancy
- Occurs when a fertilised egg implants outside the uterus, most often in the fallopian tube (tubal pregnancy).
- It can also occur in other locations such as: Ovary, Abdominal cavity and Cervix (lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina)
- In such cases, the fertilised egg attaches to a structure other than the uterus, making it non-viable.
Causes
Blockage in the movement of the fertilised egg towards the uterus due to :
- Inflammation or scarring of the fallopian tubes.
- Damage to the fallopian tubes from previous surgeries or infections.
- Irregular shape or structural abnormalities of the fallopian tube.
Symptoms
Missed period, Nausea and Breast tenderness
- Later or Severe Symptoms: Vaginal bleeding, Lower abdominal pain, Pelvic and back pain, Dizziness or fainting, Shoulder pain, Discomfort during bowel movements and Low blood pressure (in severe cases)
Prelims:
Q. UPSC Prelims 2021
With reference to female reproductive system, consider the following statements:
- The ovum is released from the ovary and moves to the uterus through the fallopian tube.
- Fertilisation of the ovum usually takes place in the uterus.
- In ectopic pregnancies, the fertilised egg implants outside the uterus.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
6. Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN): Boosting Rural Telecom & 5G Connectivity in India
For Prelims:
-
Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN)
-
Telecom infrastructure
-
Rural & semi-urban India
-
Minister of State for Communications & Rural Development
-
Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan (CTDP)
-
Mobile connectivity
For Mains:
-
Aspirational Districts
-
4G Saturation Campaign
-
High-speed 4G
-
Uncovered villages
-
Revamped BharatNet Project
-
Broadband
-
Gram Panchayats
-
Villages
-
5G spectrum auctions
-
Telecommunications Act 2023
-
Affordable telecom projects
-
Replaced Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF)
-
Indian Telegraph Act 1885
Context
- Recently, the Minister of State for Communications & Rural Development stated that the government is actively strengthening telecom infrastructure in rural and semi-urban India under the Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN) initiative.
Key Initiatives Funded by DBN
- Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan (CTDP) – Mobile connectivity in the North Eastern Region, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, and Lakshadweep.
- Mobile Services Expansion – Coverage in Left Wing Extremism (LWE)–affected areas and Aspirational Districts.
- 4G Saturation Campaign – High-speed 4G in uncovered villages.
- Revamped BharatNet Project – Broadband to Gram Panchayats and villages.
- 5G & Infrastructure Push – Spectrum auctions for 5G services.
About DBN
Established under the Telecommunications Act, 2023 to fund telecom projects in underserved rural/remote areas at affordable rates.
- Replaced the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) set up under the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885.
Prelims:
Q. Prelims Question, 2020
With reference to the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF), consider the following statements:
- The fund was established with the objective of providing financial support for the provision of telecom services in commercially unviable rural and remote areas.
- The fund is maintained under the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885.
- The fund is fully financed through the grants given by the Union Government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
7. Vegetable Oil Products Regulation Order 2011 | Key Amendments & Benefits
For Prelims:
-
Essential Commodities Act 1955
-
Food Safety and Standards Act 2006
-
Vegetable Oil Products Production and Availability (Regulation) Order 2011
-
Collection of Statistics Act 2008
-
Department of Food and Public Distribution
For Mains:
-
Regulation of edible oil sector in India
-
Policy interventions for edible oil supply-demand balance
-
Data-driven governance in food security
-
Impact of institutional restructuring on commodity regulation
-
Role of Essential Commodities Act in agricultural commodities
-
Edible oil imports and self-reliance strategies
-
Government measures for inflation control in edible oil prices.
Context
- Recently, the Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD) under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution notified amendments to the Vegetable Oil Products, Production and Availability (Regulation) Order, 2011 (VOPPA Regulation Order, 2011).
Key Highlights
- Legal Basis: Order originally framed under the Essential Commodities Act, 1955 after repeal of older regulations by the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
Key Objectives
- Align provisions with institutional changes after the 2014 merger of two key directorates. Strengthen edible oil data collection using the Collection of Statistics Act, 2008.
Benefits
Better visibility on domestic production, imports, and stock levels.
- Timely policy interventions (e.g., import duty changes, facilitating imports) to balance supply-demand.
- Improved interface, simplified return submission forms for ease of compliance.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION, 2020 GS PAPER 1
Under the Essential Commodities Act, 1955, which of the following commodities can be declared as essential by the Government of India?
- Drugs
- Fertilizers
- Pulses
- Edible oils and seeds
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans:
8. Notary Portal India | Digital Services for Notaries Under Notaries Act 1952
For Prelims:
-
Notary Portal
-
Notaries Act 1952
-
Notaries Rules 1956
-
Ministry of Law and Justice
-
Faceless paperless transparent service delivery
For Mains:
-
Legal reforms and digitisation
-
E-governance in justice delivery system
-
Ease of Doing Legal Services
-
Transparency and efficiency in notarial work
-
Paperless legal administration
-
Centralised digital platforms for legal professionals
-
Service delivery reforms under Ministry of Law and Justice
-
Digital transformation of statutory functions
-
Integration of legal services with Digital India
-
Impact of technology on public service delivery in legal sector
Context
- Recently, the Government of India launched the Notary Portal — a dedicated online platform aimed at streamlining services under the Notaries Act, 1952 and the Notaries Rules, 1956.
About Notary Portal
- The portal aims to provide a faceless, paperless, and transparent system, reducing manual processes and enhancing efficiency in notarial work.
Key Features
- The portal serves as an online interface between Notaries appointed by the Central Government and the Ministry of Law and Justice. It offers multiple digital services, including:
- Submission of applications for appointment as a Notary
- Eligibility verification for new appointments
- Issuance of digitally signed Certificates of Practice
- Renewal of Certificates of Practice
- Request for change of practice area
- Submission of annual returns
- As of July, 2025, more than 34,900 digitally signed Certificates of Practice have been issued to newly appointed Notaries across various States and Union Territories through the portal.
Prelims:
Q. Prelims (2018)
With reference to ‘Digital India’, consider the following statements:
- Digital India is a programme to prepare India for a knowledge future.
- Digital India is an umbrella programme that covers multiple departments.
- The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is an important component of Digital India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
9. IUCN and TRAFFIC Report: India-Nepal Success in Rhino Conservation 2025
For Prelims:
-
IUCN Red List status – Greater one-horned rhino (Vulnerable)
-
CITES Appendix I
-
Habitat – Alluvial grasslands, riverine forests (India: Assam, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh; Nepal: Chitwan, Bardia)
-
Poaching threats – Horn trade, habitat loss, human–wildlife conflict
-
TRAFFIC – Wildlife trade monitoring network
-
Transboundary conservation – India–Nepal cooperation
For Mains:
-
Bilateral cooperation in wildlife conservation
-
Role of intelligence gathering in anti-poaching
-
Community participation in rhino protection
-
Cross-border conservation diplomacy
-
Role of global organisations (IUCN, TRAFFIC, WWF) in species recovery
-
Challenges – habitat encroachment, climate change, illegal trade
-
Success stories as conservation models for other endangered species
Context
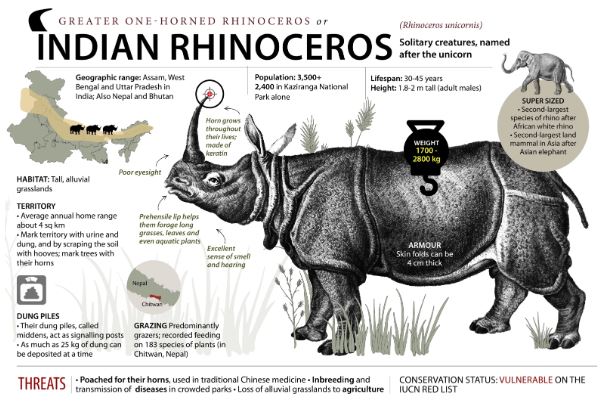
- Recently, a report by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and TRAFFIC praised India and Nepal for strengthening monitoring and surveillance measures, which have significantly reduced poaching of the greater one-horned rhino (Rhinoceros unicornis).
Key Findings
India and Nepal’s strengthened anti-poaching measures have significantly curbed rhino poaching.
- Effective field monitoring, patrolling, and intelligence gathering credited for success.
- Total estimated population (March 2025): 4,075 (India: 3,323; Nepal: 752).
- Increase of 61 rhinos since CoP19 report (2022).
- Steady rise since 2007: India: 2,150 (2007) → 3,323 (2024) and Nepal: 413 (2007) → 752 (2024).
Prelims:
Q. Prelims PYQs 1. (2020)
Consider the following statements:
- The Indian wild ass is found in the wild only in India.
- The one-horned rhinoceros is naturally found only in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans:
10. TRISO Nuclear Fuel: US Advances Next-Gen Safe & Efficient Reactor Fuel
For Prelims:
-
TRISO – TRi-structural ISOtropic particle fuel
-
US Department of Energy (DOE)
-
Standard Nuclear
-
BWX Technologies
-
Core fuel kernel – uranium, carbon, oxygen
-
Three-layer carbon–ceramic coating
-
Seed-sized particles → pellets / pebbles
For Mains:
-
Nuclear energy supply chain diversification
-
Nuclear non-proliferation & safety
-
Small modular reactor (SMR) applications
-
Gen-IV reactor fuel innovations
-
High-temperature gas-cooled reactor advantages
-
Molten salt reactor fuel requirements
-
Energy security & strategic autonomy
-
Decarbonisation role of advanced nuclear
-
US–Russia nuclear fuel geopolitics
-
Public–private partnerships in nuclear R&D
Context
- Recently, the US Department of Energy (DOE) named Standard Nuclear as the first company to develop next-generation TRISO nuclear fuel, a move intended to cut dependence on Russian uranium and enhance domestic supply chains.
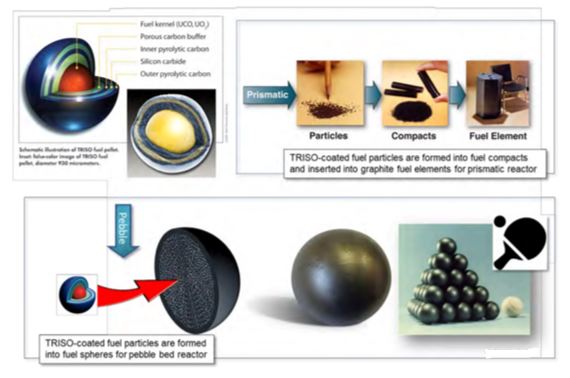
About TRISO Nuclear Fuel
Stands for TRi-structural ISOtropic Particle Fuel
- A high-performance nuclear fuel designed for advanced reactors, offering greater safety and efficiency.
- Developed through collaboration between the US Department of Energy (DOE) and private companies such as BWX Technologies.
How it is Formed
Core fuel kernel made of uranium, carbon, and oxygen.
- Encased in three protective carbon–ceramic layers to prevent radiation leakage.
- Particles are seed-sized but can be shaped into pellets or pebbles for reactor use.
Key Features
Extreme Durability – Resistant to neutron irradiation, corrosion, oxidation, and very high temperatures.
- Self-Contained Safety – Each particle acts as its own containment, reducing radiation risk.
- Versatile Application – Suitable for molten salt and high-temperature gas-cooled reactors.
Significance
Supports next-generation small modular reactors (SMRs) and Gen-IV reactors.
- Reduces US reliance on Russian uranium.
- Boosts clean energy security and promotes nuclear innovation.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS 2023
With reference to India’s nuclear power, consider the following statements:
- Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) in India use enriched uranium as fuel.
- Light Water Reactors (LWRs) in India use imported enriched uranium.
- Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) in India use a mixed oxide of uranium and plutonium as fuel.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
11. SheLeads II: Empowering Women Leaders for Inclusive Political Leadership
For Prelims:
-
SheLeads II
-
UN Women India Country Office
-
Capacity-building initiative
-
Gender equality in leadership
-
Lok Sabha elections
-
State Assembly elections
For Mains:
-
Women’s political representation
-
Capacity building for women leaders
-
Gender-inclusive policy-making
-
Public and political leadership
-
Role of UN agencies in governance reform
-
Women empowerment in decision-making
-
Inclusive and representative development agenda
-
Barriers to women’s political participation
-
Leadership training for elections
Context
- Recently, the Union Minister for Women and Child Development launched the second edition of SheLeads II: Workshop for Women Leaders, the flagship capacity-building initiative of UN Women.
- About SheLeads Programme: Organiser: UN Women India Country Office
Objective
- To promote gender equality in public and political leadership by empowering women to contest upcoming Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections.
Approach
- Providing women with the platforms, skills, and networks needed for impactful leadership.
- Preparing them to take up roles in policy-making and governance that reflect the aspirations of all citizens.
Significance
- Strengthens women’s capacity to lead from the front in political and public spheres.
- Contributes to making the development agenda more inclusive and representative.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC Prelims 2020
Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
- Women’s Political Participation — 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments
- Reservation of one-third seats in Panchayats — Constitution (Seventy-third Amendment) Act, 1992
- Reservation of one-third seats in Municipalities — Constitution (Seventy-fourth Amendment) Act, 1992
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
12. Haemophilia Care Advances: From Bleed Management to Proactive Prevention
For Prelims:
-
Rare inherited bleeding disorder
-
clotting factor deficiency
-
Haemophilia A
-
Factor VIII deficiency
-
reduced blood clotting
-
excessive bleeding
-
spontaneous internal bleeding
For Mains:
-
1 in 10,000 births prevalence
-
India diagnosis gap
-
estimated 1–1.5 lakh cases
-
29,000 diagnosed
-
20% identified
-
low awareness
-
limited diagnostics
-
socio-economic barriers
-
restricted testing and treatment access
Context
- Recently, haemophilia care has been transforming — moving from reactive bleed management to proactive prevention through prophylaxis, with new therapies aiming to not only rebalance the body’s clotting system but also restore it, bringing the long-sought goal of “zero bleeds” closer to reality.
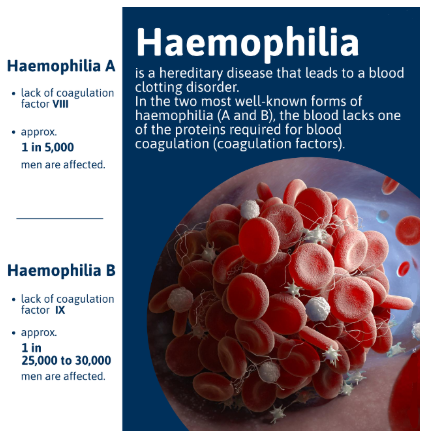
About Haemophilia
A rare inherited bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency of clotting factors, most commonly Factor VIII in Haemophilia A.
- Leads to severely reduced blood clotting ability, where even minor injuries can result in excessive bleeding.
- Can cause spontaneous internal bleeding into joints and muscles, leading to pain, disability, and potentially life-threatening complications such as brain bleeds.
- Caused by a mutation in genes responsible for producing clotting factor proteins; these genes are located on the X chromosome, making men more vulnerable.
- Prevalence: Around 1 in 10,000 births
- India’s Diagnosis Gap: Estimated cases: 1–1.5 lakh (based on global prevalence).
- Diagnosed cases: ~29,000 (only about 20% identified).
- Key barriers to diagnosis: Low public and medical awareness.
- Limited diagnostic facilities.
- Socio-economic constraints restricting access to testing and treatment.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS, 2020
With reference to genetic disorders, consider the following:
- A person with a single X chromosome has Turner syndrome.
- A person with an extra copy of chromosome 21 has Down syndrome.
- A male with an extra X chromosome has Klinefelter syndrome.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
13. Rare Albino Indian Flapshell Turtle Spotted in Gujarat | Vulnerable Species
For Prelims:
-
Shallow stagnant waters
-
rivers, streams
-
marshes
-
ponds
-
lakes
-
irrigation canals
-
sand bottom
-
mud bottom
-
burrowing
-
femoral flaps
-
oval soft shell
-
evolutionary link
-
hard shell turtles
For Mains:
-
370 mm length
-
20 years lifespan
-
omnivorous
-
solitary
-
diurnal
-
drought survival 120–160 days
-
IUCN Vulnerable
-
CITES Appendix I
-
Wildlife Protection Act Schedule I
-
albinism
-
melanin deficiency
-
genetic mutation
-
recessive trait
Context
- Recently, a rare albino Indian flapshell turtle, distinguished by its bright yellow shell and skin, was spotted in a freshwater lake at Chikodra village, Gujarat.
About
Scientific Name: Lissemys punctata
- Type: Freshwater turtle, common in tropical South Asia.
- Distribution: Found in Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Myanmar.
Habitat
- Prefers shallow, quiet, often stagnant waters such as rivers, streams, marshes, ponds, lakes, irrigation canals, and tanks.
- Favors sand or mud-bottom waters due to burrowing habits.
Key Features
Possesses femoral flaps extending from the shell to cover limbs when withdrawn.
- Oval soft shell shows evolutionary link to hardshell turtles.
- Size: Can grow up to 370 mm in length.
- Lifespan: Around 20 years.
- Diet: Omnivorous.
- Behaviour: Generally solitary, active during the day.
- Adaptability: Can survive extreme droughts for 120–160 days.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Albinism: A rare genetic condition affecting melanin production, influencing pigmentation in skin, hair, and eyes across species.Caused by a mutation inherited from both parents (recessive trait)
Prelims:
Q. UPSC Prelims 2020
Consider the following pairs:
- Olive Ridley Turtle — Gahirmatha Beach
- Leatherback Turtle — Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Hawksbill Turtle — Gulf of Mannar
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: