India unveils a roadmap for achieving net zero emissions by 2050 through increased reliance on bioenergy sources.
Introduction to Bioenergy
- What is it? Bioenergy refers to the energy derived from biomass, which includes organic materials such as agricultural residues, wood, and dedicated energy crops.
- A Renewable Powerhouse: It is a renewable energy source that can be converted into various forms of energy, including heat, electricity, and liquid fuels.
The Potential of Bioenergy in India
- Biomass potential: India has an estimated biomass potential of around 18,000 MW.
- Biomass-based power capacity: Currently, India has approximately 9,868 MW of biomass-based power capacity.
- Ethanol blending target: India aims to achieve a 20% blending of ethanol with petrol (gasoline) by 2030.
- Biodiesel blending target: India targets a 20% blending of biodiesel with diesel by 2030.
Types of Bioenergy
- Biofuels
- Biomass Power
- Biogas
- Biochar
Advantages of Bioenergy
- Renewable: Bioenergy sources can be continuously replenished, making them sustainable in the long run.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Bioenergy has the potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions when compared to fossil fuels.
- Waste management: Bioenergy production can utilize organic waste materials, contributing to waste management and reducing landfill volumes.
- Rural development: Bioenergy projects can stimulate rural economies by creating job opportunities and providing energy access to remote areas.
Challenges and Concerns in Bioenergy Development

|
Measures:
Sustainable Feedstock Selection: Promote the use of non-food crops and agricultural residues as feedstock for bioenergy production to minimize competition with food production.Technological Advancements: Explore emerging technologies like algae-based biofuels and genetically engineered energy crops for enhanced bioenergy production.Integrated Approach: Promote the concept of biorefineries that integrate the production of various bioenergy products, such as biofuels. |
Policy and Initiatives in India:
- National Biofuel Policy: The Indian government has launched the National Biofuel Policy to promote the use of biofuels and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Ethanol blending program: India has implemented an ethanol blending program to blend ethanol with gasoline, aiming to reduce fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biomass power initiatives: Various schemes and incentives are in place to encourage the establishment of biomass power plants in India.
- Waste-to-energy projects: The government is promoting waste-to-energy projects to convert organic waste into biogas or electricity.
|
Conclusion
Bioenergy presents a promising avenue for meeting energy demands while reducing environmental
impacts. However, careful planning, sustainable practices, and technological advancements are essential for maximizing the benefits of bioenergy and minimizing potential drawbacks.
National Bioenergy Programme
The National Bioenergy Program is a government initiative aimed at promoting the production and utilization of bioenergy in the country. It focuses on harnessing the potential of renewable biomass resources for meeting energy needs, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
Objectives of the National Bioenergy Programme
- The program aims to establish a robust bioenergy sector that contributes to national energy security, rural development, and environmental sustainability.
- It seeks to enhance the share of bioenergy in the overall energy mix, diversifying the sources of energy generation.
Key Components of the Bioenergy Programme
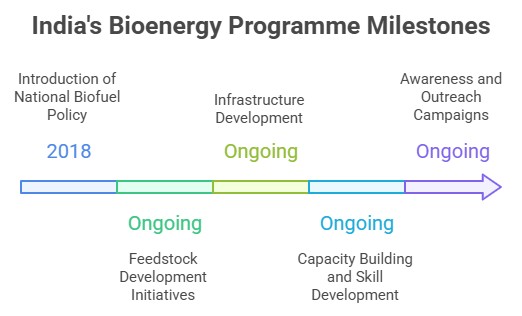
- Policy Framework: The Indian government introduced the National Biofuel Policy in 2018, which sets targets for blending biofuels in transportation fuels and provides incentives for bio energy projects.
- Feedstock Development: For instance, energy crops such as sugarcane, maize, and Jatropha are being cultivated on marginal lands and wastelands to serve as feed stocks for biofuel production.
- Infrastructure Development: Dedicated biomass processing facilities, bio refineries, and bio fuel blending facilities are being established across the country to support the scaling up of bio energy production.
- Capacity Building and Skill Development: Training programs, workshops, and collaborations with educational institutions and research centers are being conducted to enhance the capabilities of stakeholders involved in bioenergy production and research.
- Awareness and Outreach: Campaigns, seminars, and exhibitions are conducted to disseminate information, showcase successful bioenergy projects, and encourage the adoption of bioenergy technologies.
|
Impacts and Achievements of Bioenergy Programmes
- The National Biofuel Policy aims to achieve a 20% ethanol blending rate in gasoline and 5% biodiesel blending rate in diesel by 2030, which will significantly reduce fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- In 2020, India achieved an ethanol blending rate of around 8.5% in gasoline, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and increased energy security.
- The establishment of biomass power plants and biogas plants under the program has provided decentralized energy access to rural communities, improving livelihoods and reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels.
|
Conclusion
India's National Bioenergy Program drives sustainable bioenergy production and utilization through policies, feedstock development, technology advancements, infrastructure, capacity building, and awareness, ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Ethanol Blending Programme
"Prime Minister Narendra Modi takes a major step towards a greener future by introducing 20% ethanol-blended petrol in 11 States/UTs, bolstering renewable energy adoption and combating carbon emissions."
Current Status and Future Targets of Ethanol Blending
- The initial blending target was set at 5% (E5), which has been gradually increased over the years.
- As of 2021, the government has set a target of achieving 20% ethanol blending (E20) by 2025.
- Several states and regions in India have already achieved significant blending levels, with some reaching E10 and E15.
|
|
Objectives:
- Reduce dependency on imported fossil fuel.
Enhance energy security.
- Promote the use of renewable and eco-friendly fuels.
- Boost the income of farmers by creating a market for ethanol produced from agricultural crops.
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impact of vehicular pollution on the environment.
|
Benefits of Ethanol Blending:
- Environmental Benefits: Ethanol is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to petrol, leading to reduced emissions of carbon monoxide, particulate matter, and greenhouse gases.
- Energy Security
- Economic Benefits: opportunities for investment in ethanol production, generating income for farmers and promoting rural development.
- Engine Performance: Ethanol blending can enhance octane rating, which improves engine performance and reduces knocking in vehicles.
|
Ethanol Production and Supply:
- Primary production: Ethanol is primarily produced from sugarcane molasses, a by-product of sugar manufacturing, through the fermentation process.
- Other: Other feedstocks used for ethanol production include corn, grains, and agricultural residues.
- Supply: Ethanol is supplied to oil marketing companies (OMCs) for blending with petrol, and OMCs procure ethanol from domestic manufacturers and through imports.
|
Challenges in Expanding Bioenergy via Ethanol Blending
Availability and Supply, Technical Compatibility Problem, Infrastructure Development, Limited availability of ethanol-blended fuels at fuel stations, Feedstock Dependence, Economic Viability.
Way forward
- Advanced Ethanol Production Technologies: such as cellulosic ethanol production using agricultural residues, waste biomass, or algae
- Decentralized Ethanol Production: Reduce transportation costs, encourage local job creation, and boost rural economies.
- Integrated Biorefineries:
- Technological Innovations for Blending: such as inline blending systems and automated blending processes.
- Sustainable Feedstock Production: To minimize the environmental impact of feedstock cultivation, promote efficient land use, and ensure long-term availability of biomass for ethanol production.
- Carbon Capture and Utilization: Create additional revenue streams by utilizing captured CO2 for various applications.
Conclusion
The Ethanol Blending Programme plays a crucial role in India's energy transition and sustainable development through offering multiple benefits, including reduced environmental impact, enhanced energy security, and economic opportunities for farmers and industries. Continued efforts and investments are required to overcome challenges and achieve higher blending targets, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable transport sector in India.
Transition to Clean Economy: Prospects and Challenges
- Definition: The shift from fossil fuel-based systems to sustainable and low-carbon alternatives, involving the adoption of renewable energy sources, implementation of energy-efficient measures, and promotion of sustainable practices across sectors.
- This transition aims to mitigate climate change, reduce pollution, enhance energy security, and foster long-term economic growth.
Components of Transition and Benefits/Prospects

Challenges
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment required for clean energy infrastructure and technologies can be a challenge for widespread adoption.
- Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Effective policies and regulations are necessary to support the transition and overcome barriers.
- Market Barriers: Existing fossil fuel subsidies and market distortions can hinder the competitiveness of clean technologies.
- Workforce Transition: Ensuring a smooth transition for workers in industries affected by the shift, providing training and new job opportunities.
- Social Equity: Addressing equity concerns and ensuring access to clean energy and its benefits for marginalized communities.
Solutions
- Green Financing: Establish financial mechanisms and incentives for clean energy projects, such as green bonds and renewable energy investment funds. An example is the UK's Green Investment Group, which provides funding for renewable energy projects.
- Technology Innovation: Invest in research and development of advanced clean technologies, including energy storage systems and smart grids. Tesla's development of affordable electric vehicles and energy storage solutions serves as an example.
- Carbon Pricing: Implement carbon pricing mechanisms like carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems to create economic incentives for reducing emissions. The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is an example.
Conclusion
The transition to a clean economy holds vast potential for a sustainable future. By embracing innovation, investing in renewable energy, and fostering collaboration, we can create a greener world, ensuring long-term environmental protection, economic growth, and an improved quality of life for future generations.
Green Hydrogen
- Meaning: Green hydrogen is hydrogen gas produced through electrolysis using renewable energy sources, making it a sustainable and zero-emission fuel.
Key Benefits and Objectives of Green Hydrogen
- Carbon Neutrality and Climate Change Mitigation
- According to the Hydrogen Council, green hydrogen could meet 18% of the world's energy demand, potentially reducing CO2 emissions by 6 gigatons by 2050.
- Energy Independence and Security: Green hydrogen reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy independence and security.
Impacts of Green Hydrogen
- Decarbonization of Hard-to-Abate Sectors: Green hydrogen enables decarbonization in sectors such as steel, chemicals, and heavy transportation, which are challenging to electrify. For example, in Europe, hydrogen is being explored for steel production, with initiatives like the H2 Green Steel project in Sweden.
- Energy Transition Synergies: Green hydrogen is complementing other renewable energy sources, facilitating an integrated and sustainable energy system.
- The Western Australia Renewable Hydrogen Strategy aims to create a hydrogen export industry, capitalizing on the region's abundant wind and solar resources.
- Scalability and Long-Term Potential: With advancements and cost reductions, green hydrogen has the potential to become a scalable and cost-competitive energy solution.
- The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimates that green hydrogen costs could fall by 64-71% by 2050.
Concerns and Challenges
- Cost and Economic Viability: Green hydrogen production currently has higher costs compared to conventional hydrogen methods.
- Infrastructure Development: unavailable comprehensive infrastructure
- Energy Intensity and Efficiency: The electrolysis process used to produce green hydrogen requires a substantial amount of electricity.
- Scaling Up Renewable Energy Sources: In 2020, renewable energy accounted for 29.9% of global electricity generation.
Way Forward
- Scientific Advancements: Foster research and development to enhance electrolysis efficiency and lower the cost of green hydrogen production.
- Ecological Synergy: Integrate green hydrogen projects with renewable energy installations, such as wind and solar farms, to optimize resource utilization and reduce environmental impact.
- Circular Economy Approach: Promote the use of green hydrogen in sectors like agriculture, where it can replace fossil fuel-based fertilizers, reducing emissions and enhancing sustainability.
- International Collaboration: Strengthen international partnerships for knowledge-sharing, joint research, and technology transfer to accelerate the development and deployment of green hydrogen.
- Investment Incentives: Provide financial incentives, subsidies, and tax benefits to attract private investments in green hydrogen projects and infrastructure development.
Conclusion
Effective air pollution policies are vital for mitigating the adverse impacts on human health, the environment, and sustainable development. By integrating scientific research, robust policy frameworks, technological advancements, and community participation, governments can address air pollution challenges and strive for cleaner air and a healthier planet.
|
Extra Marks Fetching component by theIAShub
- Ahmedabad: Janmarg BRTS improved public transportation and reduced emissions.
- Indore: "Sutra Seva" bicycle-sharing system encourages cycling, reducing vehicle dependence.
- Kochi, India: Kochi Metro Rail promotes sustainable and efficient transport, reducing congestion.
|
Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022
The Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022 is a recent legislative amendment to the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
Features and Highlights

Criticism
- Lack of Clarity: The Act lacks clarity on the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, causing uncertainty and leaving stakeholders unaware of its scope and operation.
- Ambiguity in Penalties: The Act does not provide clear guidelines for calculating and imposing penalties, resulting in inconsistencies and confusion during enforcement.
- Unrealistic Targets: The Act sets ambitious non-fossil energy consumption targets, Inadequate Support Mechanisms: The Act lacks sufficient incentives and subsidies to encourage energy conservation practices, potentially hindering industry and consumer adoption.
- Implementation Challenges: The Act requires robust monitoring, enforcement, and capacity-building mechanisms for effective implementation, raising concerns about resource allocation and compliance oversight.
Way Forward
- Clear Guidelines: Provide detailed and transparent guidelines for the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, ensuring clarity and understanding among stakeholders.
- Transparent Penalties: Establish a transparent framework for penalties, ensuring consistency and fairness in their calculation and imposition.
- Realistic Targets: Set achievable non-fossil energy consumption targets, considering the diverse energy needs of industries and sectors.
- Incentives and Support: Introduce effective incentives, subsidies, and grants to encourage energy conservation practices
- Strong Implementation: Allocate sufficient resources for monitoring, enforcement.
Key differences between the Energy conservation act, 2001 and Energy conservation (amendment) act, 2022:
|
Aspect
|
Energy Conservation Act, 2001
|
Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022
|
|
Focus
|
Energy conservation
|
Energy conservation and sustainability
|
|
Key Objectives
|
Efficient energy use
|
Energy efficiency, renewable energy, and reduction of carbon emissions
|
|
Carbon Credit Trading
|
Not specified
|
Empowers the government to specify a carbon credit trading scheme
|
|
Use of Non-fossil Sources
|
Not specified
|
Empowers the government to specify minimum share of consumption of non-fossil sources by designated consumers
|
|
Energy Conservation Codes
|
Energy conservation building codes
|
Energy conservation and sustainable building codes
|
|
Vehicle and Vessel Standards
|
Limited to equipment and appliances
|
Includes vehicles and vessels, along with existing compliance standards
|
|
Penalty Provisions
|
Existing penalties for non-compliance
|
Enhanced penalties for various violations, including equipment standards, non-fossil source consumption, and deceptive practices
|
|
Governing Council Composition
|
Not specified
|
Expanded composition of the governing council for the Bureau of Energy Efficiency
|
Conclusion
The Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022 signifies a positive step towards a sustainable future by promoting renewable energy, carbon credit trading, and energy-efficient practices. Its implementation and enforcement, along with a focus on innovation and collaboration, will be essential in realizing a cleaner and greener India.
|