1. Fears About Ethanol-Blended Petrol in India: Concerns, Impact & Government Response
Context
- As India pushes ahead with its ethanol-blended petrol programme—a key measure to cut emissions and reliance on energy imports, apprehensions have been raised particularly by owners of older vehicles.
They fear ethanol-blended petrol may
- Lower fuel economy
- Damage the engine
- Reduce vehicle lifespan
- Lead to expensive repairs
Response By the Government
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG) has dismissed most concerns as:
- Largely unfounded”(groundless)
- Not backed by scientific evidence or expert analysis.
The government stated
- Ethanol blending is technically sound
- It is a forward-looking, environmentally responsible measure.
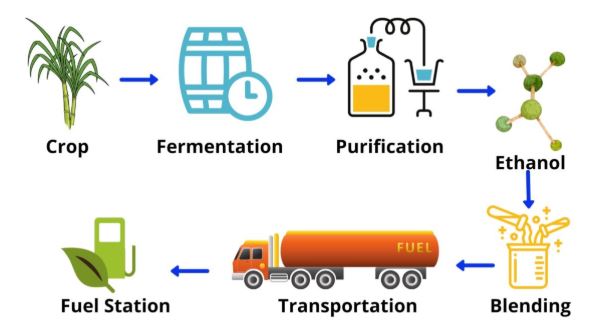
Ethanol Blending and its Policy Context
- Ethanol is an alcohol-based biofuel typically derived from sugarcane, maize, or other biomass sources.
- It’s blending with petrol reduces carbon emissions and helps India reduce dependency on imported fossil fuels.
- The government’s Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme, launched in 2003 and accelerated over the past decade, first achieved a 10% ethanol blending (E10) milestone in 2022.
- In 2025, the E20 rollout was declared complete nationwide.
- The achievement aligns with India’s broader renewable energy and energy security ambitions under the National Bio-Energy Programme.
Concerns
Vehicle Compatibility Issues
- E20 fuel (20% ethanol + 80% petrol) was achieved in 2024, 5 years ahead of the 2030 target.
- Newer cars (post-April 2023) are built to handle E20.
- Older cars may not be tuned for E20, leading to:
- Potential engine corrosion
- Concerns in two-wheelers due to material compatibility.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency
- One of the most debated impacts of ethanol blending is the drop in mileage.
- Ethanol contains about 30% less energy per litre than petrol. This energy deficit translates into increased fuel consumption per kilometre driven.
- Central Govt’s View: The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG) has clarified that the mileage loss is “marginal”, around 1-2% for E10-designed vehicles calibrated for E20 and 3-6% for others. With proper engine tuning, the Ministry says efficiency losses can be minimised.
- Expert Opinion: Independent automotive experts, however, estimate that real-world mileage loss could be as high as 6-7%, particularly for vehicles not optimised for E20. This would mean more frequent refuelling and higher running costs for users.
Response From Industry
- Major automobile manufacturers have responded by:
- Hero MotoCorp stated that vehicles manufactured before April 2023 may require engine modifications and replacement of rubber components to safely run on E20.
- TVS Motor Company acknowledges that ethanol’s corrosive nature requires re-engineered components to prevent premature wear and compatibility issues..
Support Measured by Government
- Interest Subvention Scheme (2018) to enhance production capacity.
- GST on ethanol reduced from 18% to 5%.
- Industries (Development and Regulation) or IDR Act amended (2016) to clarify CentreState roles in ethanol supply.
- Maize approved as a feedstock by NBCC(National Biofuels Coordination Committee) in 2020.
- National Policy on Biofuels, notified in 2018, aims to promote the production and use of biofuels to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, enhance energy security, and mitigate climate change.
Prelims:
Q. Prelims Question 2022, GS Paper 1
With reference to “Biofuels”, consider the following statements: Biofuels can be manufactured from cellulose-containing plant materials. Second-generation biofuels can be produced from non-food crops. Third-generation biofuels can be derived from algae. Fourth-generation biofuels involve engineered bio-refineries that do not use biomass. Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans:
Mains:
Q. Mains Question UPSC MAINS, 2020, GS PAPER 3
What are the major factors responsible for the making and unmaking of the groundwater crisis in India? Discuss food security implications of the same."
Ans:
2. Cloudburst in Uttarkashi: Causes, Impact, and Disaster Management Measures
Context
- A devastating cloudburst in Uttarkashi’s Dharali region triggered flash floods and landslides, killing at least four people and sweeping away homes.
About the News
- At least four people died as flash floods and mudslides struck Dharali village in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand, damaging several buildings, shops, and hotels.
- While cloudbursts are common triggers of flash floods in Uttarakhand’s hilly regions, the recent incident was not due to a technical cloudburst but rather sustained heavy rainfall over the past three days.
Factors Behind Uttrakashi Flash Floods
- Continuous rainfall over the past few days, combined with Uttarkashi’s fragile topography, triggered mudslides, debris flows, and flash floods.
- Climate change-induced intense rainfall and accelerated glacier melting further worsened the situation.
- Rainfall of any intensity, if continuous, recorded over such high altitudes where Uttarkashi is located, can be disastrous.
- That is because this region is built on layers of mudslides over the past several centuries.
- Uttarkashi district is situated along the southern Himalayan slope, where there is limited vegetation and no significant obstruction.
- Link to Climate Change: Global warming increases atmospheric moisture-holding capacity. This leads to more intense, erratic, and sudden rainfall, making cloudbursts more frequent and severe.
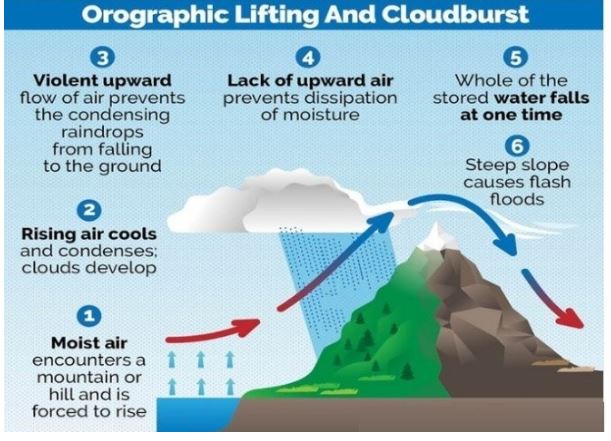
About Cloudburst
- A cloudburst is defined by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) as rainfall exceeding 100 mm/hour over a small area (20–30 sq km).
- These events are often associated with cumulonimbus clouds in mountainous regions, caused by orographic lift and convection Currents that rapidly accumulate moisture before collapsing violently.
How Cloudbursts Happen
- Orographic Lift: In hilly regions, warm air currents push moisture-laden clouds upward. This upward movement (orographic lift) is a key reason cloudbursts are more frequent in mountainous terrain.
- Growth of Droplets: As clouds rise higher, water droplets grow larger and more form. Lightning within these clouds often delays rainfall, increasing moisture load.
- Sudden Downpour: When clouds can no longer hold the excess moisture, they burst, releasing intense rainfall over a small area.
Hilly Reasons are more Prone
- Due to Topography, steep slopes accelerate water runoff and debris flow.
- Moist monsoon air is rapidly lifted over hills, intensifying precipitation due to Orographic Lifting.
- Rocky Terrain causes poor water absorption and rapid accumulation on the surface.
Impact of Cloudburst
- Flash Flood: A flash flood happens quickly, when a lot of rain suddenly enters into the drainage systems (waterbodies, drains), and water overflows.
- Flash floods are more common in hills, because rocky terrain does not absorb water very well.
- Example: The 2013 Kedarnath Disaster involved a cloudburst followed by massive flash floods.
- Landslide: Landslides are a geological phenomenon that involves the sudden and rapid movement of a mass of rock, soil, or debris down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- Loss of Life and Livelihood: Sudden nature of cloudbursts leaves little time for evacuation. Destruction of homes, agricultural fields, and livestock affects livelihoods, especially in rural and tribal communities.
- Damage to Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, power lines, and communication networks are often washed away.
- Social Impact: Frequent disasters create trauma, displacement, and migration pressures. Affects education, healthcare, and access to essential services in remote regions.
Why Prediction is Difficult
- Cloudbursts occur in limited areas (10–30 sq km), making them hard to detect with standard radar systems.
- The event lasts under an hour, offering little time for forecasting and issuing effective alerts.
- Installing advanced radar and AI-based forecasting models in remote areas remains expensive and underfunded.
Measures Taken In India
- The Disaster Management Act, of 2005 provides a comprehensive legal and institutional framework for the management of various disasters in India.
- The National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) has been providing capacity building and other support to various national and state-level disaster management authorities.
- Early Warning system:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD), implements the Ensemble Prediction System (EPS), which uses multiple models to improve the accuracy of rainfall predictions.
- Doppler Weather Radars (DWRs): Installed in hilly and vulnerable regions to detect intense rainfall events in real-time.
- Flash Flood Guidance System (FFGS): Developed with WMO support to provide early warning for flash floods across South Asia, including India.
- Mobile-based Alert Systems: IMD and NDMA use SMS and app-based alerts to inform people in real-time.
Way Ahead
- To effectively mitigate the impact of cloudbursts, India must adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach that combines scientific forecasting, infrastructural resilience, and community-based preparedness.
- Land use planning and zoning regulations must be strictly enforced to prevent construction in high-risk zones.
- Urban and rural infrastructure should be designed to handle sudden surges in water flow, with emphasis on stormwater drainage systems, slope stabilization, and rainwater harvesting.
- Also there is a need to integrate climate change adaptation into disaster management planning as intensity of such extreme weather events has increased.
Prelims:
Q. Prelims Question 2016 GS PAPER 1 With reference to ‘cloudbursts’ consider the following statements:
1. Cloudbursts occur only during daytime.
2. Cloudbursts occur only in hilly areas.
3. Cloudbursts occur only when there is orographic uplift
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) None of the above
Ans:
Mains:
Q. Mains Question 2024, MAINS, GS PAPER 1 What is a Phenomenon of CloudBurst, Explain?
Ans:
3. India Becomes 5th Largest Aviation Market with 241 Million Passengers in 2024
Context
- India has officially emerged as the world’s fifth largest aviation market, handling 241 million passengers in 2024, according to the latest World Air Transport Statistics (WATS) released by the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- Among the busiest flight routes, Mumbai-Delhi ranked 7th globally, marking India’s growing dominance in global air travel.
Key Highlights of the Report
- India recorded 241 million air passengers in 2024, a 11.1% increase from 2023, when the figure stood at 211 million
- The US remains the world’s biggest aviation market with 876 million passengers in 2024, growing 5.2 percent year-on-year.
- China was the second-biggest passenger market, with 741 million passengers, a growth of 18.7 per cent compared to 2023.
- While the UK was at the 3rd spot with 261 million passengers, Spain stood at the 4th position with 241 million.
- The figures include all international and domestic passengers departing or arriving in each country.
- Airport Pair Ranking:
- Asia-Pacific dominated the busiest airport-pair rankings.
- Jeju–Seoul (South Korea) was the busiest route globally with 13.2 million passengers.
- Mumbai–Delhi ranked 7th globally with 5.9 million passengers.
Pillars of Avian Transformation
- Legislative Reforms for Systemic Change:
- Protection of Interest in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025 aligns India’s aircraft leasing system with the Cape Town Convention, reducing leasing costs and improving investor confidence.
- Bharatiya Vayuyan Adhiniyam, 2024: Replaces the colonial-era Aircraft Act, 1934. It encourages Make in India, simplifies licensing, and aligns regulations with global standards like the Chicago Convention and ICAO norms.
- Infrastructure Expansion and Capacity Building:
- Terminal Upgrades: Foundation laid for new terminals at Varanasi, Agra, Darbhanga, and Bagdogra.
- Greenfield Airports: 12 operationalised since 2014 (e.g., Shirdi, Mopa, Shivamogga), with Navi Mumbai and Noida (Jewar) to be operational by early 2025–26.
- CAPEX Investment: ₹91,000 crore allocated under National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP); ₹82,600 crore spent by Nov 2024.
Government Initiatives
- UDAN Scheme: Enhances regional air connectivity by making air travel affordable for common citizens.
- National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP): Promotes MRO, airport development, and aircraft leasing in India.
- Green Airports Policy: Encourages use of renewable energy, waste reduction, and carbon-neutral targets.
- Development of Noida International Airport and expansion of existing metro and non-metro airports.
- Aircraft Leasing and Financing Ecosystem: GIFT City is being promoted as a global aircraft leasing hub.
Challenges
Air Turbine Fuel
- ATF accounts for almost 45% of the operational cost of an Indian airline.
- ATF prices rose over 50% in 2022. As per Boeing, fuel costs for Indian airlines are 90% higher compared to their global peers. Additionally, ATF fuel is subjected to VAT which can range from anywhere between 15-30%, depending on the states’ taxation rules. The civil aviation ministry plans to bring down this tax to 1-4%.
Elevated Debt Level and Losses
- Due to a temporary halt in all airline operations at the peak of the pandemic and the subsequent rise in ATF pricing, the finances of Indian airline companies have been in disarray.
- Losses to the tune of Rs. 23,000 crores were recorded in 2021. Investment Information and Credit Rating Agency (ICRA) projects these losses to be in the range of Rs 15,000-17,000 crore this fiscal, despite the opening up of the economy.
Indian Aviation Policy
- Some Indian States impose provincial taxes of as much as 30% on jet fuel.
- Indian aviation policy has also posed barriers to entry and growth while also not affecting players uniformly.
- From 2004 to 2016, new airlines in the country had to be in operation for at least five years and have a fleet of at least 20 aircraft to be able to fly internationally, which stabilizes the operations and viability of carriers.
Way Forward
- Fuel Pricing Reform: Rationalise Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) taxes across states to make air travel cost-effective.
- Sustainability Focus: Encourage Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), electric aircraft technology, and carbon offsetting mechanisms.
- Skilling and Training: Expand aviation skill development programs through institutions like the National Aviation University.
- International Hub Strategy: Develop select Indian airports into full-service international hubs competing with Dubai, Doha, and Singapore
Prelims:
Q. Prelims Questions GS Paper 1, 2020
In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of
(a) Digital security infrastructure
(b) Food security infrastructure
(c) Aviation safety infrastructure
(d) Telecommunication infrastructure.
Ans:
Mains:
Q. Mains Question MAINS, 2021
"‘Investment in infrastructure is essential for more rapid and inclusive economic growth.’ Discuss in the light of India’s experience."
Ans:
4. Israel-Iran Conflict: Impact on India’s Economy, Energy Security, and Diplomacy
Context
- Recent Conflict between Israel and Iran has put many effects on India as India is a major partner of both the Countries.
About the Issue
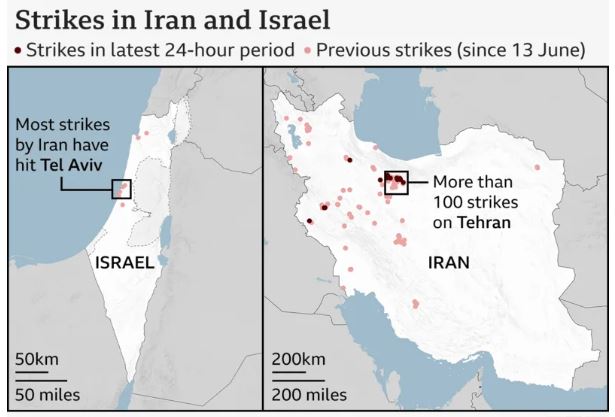
- In a sudden attack on June 13, Israel launched strikes on Iranian nuclear installations, assassinated top generals, and bombed several cities across the country. Iran's response has been more robust than expected, as it too has launched barrage after barrage of ballistic missiles on military targets and research facilities in Israel.
India Stance on the issue
- PM Modi expressed "concern" to Israeli PM Netanyahu, emphasizing the need for peace and stability.
- EAM Jaishankar conveyed "deep concern" to Iran's FM, urging against retaliation and for diplomacy.
- Similar concerns were conveyed to Israel. Official MEA statements called for dialogue and diplomacy, avoiding direct criticism of Israel.
- India abstained on a UN Gaza ceasefire resolution critical of Israel and dissociated itself from an SCO statement condemning Israeli "aggression," marking a departure from past positions.
Economic Impact
- Declining Trade: Trade with both Iran and Israel has significantly dropped due to regional tensions:
- Iran: Fell from ~$14 billion (2017) to $1.4 billion (last year) after India halted oil imports under US pressure.
- Israel: Fell from $11 billion (2022) to $3.75 billion (last year) due to Gaza conflict tensions.
- Exception: Indian defense imports from Israel surged from $5.6 million (2015) to $128 million (last year).
Strait of Hormuz Closure
- If Iran closes the Strait (as a pressure tactic or due to fighting), India faces severe consequences. 40-50% of India's energy imports transit the Strait.
- Sharp spike in oil & LNG prices, increased shipping costs/insurance premiums, costly imports, less competitive exports, and inflation.
Impact on Connectivity Projects
- IMEC (India-Middle East-Europe Corridor): Already stalled post-Oct7 attacks, requires cooperation through Arab states and Israel.
- Chabahar Port & INSTC: Investments critical for trade/connectivity to Afghanistan, Central Asia, and Eurasia are threatened by the conflict.
Geopolitical Impact
- Balancing ties: India faces a complex challenge maintaining strong ties with both Israel and Iran, who represent polarized global blocs (US/West vs. Global South/Russia/China).
- Global Division: US & G7 largely back Israel's "right to defend" and label Iran the "principal source of regional instability."Global South, critical of Israel's Gaza war, expressed sympathy for Iran.
- BRICS Challenge: India faces difficulty distancing itself from potential antiIsrael statements at the upcoming BRICS summit (July), which now includes Iran. India's SCO abstention sets a precedent being watched.
- Gulf Relations Risk: A perceived "pro-Israel shift" could damage India's vital ties with Gulf nations, crucial for 40% of India's remittances 54% of oil imports.
Way Forward
- Protect Remittances & Labour: Assure safety of the large Indian diaspora in the Gulf and maintain open channels for remittances.
- Diversify Energy Imports: Fast-track plans to reduce dependence on the Gulf/Hormuz route (LNG terminals, pipelines, renewables, strategic reserves).
- Chabahar & INSTC: Engage with Iran and Russia to insulate these projects as much as possible. Explore involving other Central Asian partners more deeply. Seek alternative routes within INSTC if Iran becomes untenable.
- Revive IMEC: Use diplomacy to keep the concept alive with Arab partners and Europe, even if implementation is delayed. Position it as a post-conflict stability project.
- Deepen Gulf Ties: Beyond energy/remittances, expand investments, technology partnerships, and security cooperation (maritime security, counter-terrorism) with key Gulf states.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS 2017, GS PAPER 1 "What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India?"
(a) India’s trade with African countries will increase enormously.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans:
Mains:
Q. UPSC MAINS GS PAPER 2, 2018 India’s relations with Israel have of late acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss.
Ans:
5. CLOVES Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Explained
Context
- Recently, CLOVES Syndrome has drawn renewed attention as an extremely rare genetic disorder, with fewer than 200 cases reported worldwide.
About CLOVES Syndrome
- Stands for Congenital, Lipomatous, Overgrowth, Vascular malformations, Epidermal nevi, and Spinal/skeletal anomalies (including scoliosis).
Cause
- Caused by mutations in the PIK3CA gene, which plays a critical role in producing the PI3K enzyme, involved in essential cellular functions. •
- These mutations can cause the enzyme to become overactive, leading to abnormal cell growth.
- PIK3CA mutations are also linked to several cancers, including breast, lung, ovarian, gastric, brain, colon, and rectal cancers.
- The mutation is sporadic and occurs spontaneously during fetal development. It is not hereditary and cannot be passed down genetically.
Symptoms
- Presence of soft fatty tissue masses on the abdomen, back, sides, and buttocks.
- Vascular anomalies, such as dilated veins in the chest, arms, and legs, increase the risk of blood clots.
- Limb overgrowth, large hands or feet with wide gaps between fingers or toes. Skin abnormalities, including port-wine stains and raised bumps.
- Spinal issues, including scoliosis or tethered cord.
- Possible kidney complications.
Treatment
- Currently, there is no known cure for CLOVES Syndrome.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC, 2020, GS PAPER 1 PRELIMS QUESTION
Consider the following statements:
1. Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent.
2. A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
3. Human-induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
6. Black Scorpion Venom: New Research Reveals Potent Sting Mechanism
Context
- Recently, Indian researchers uncovered the biochemical basis behind the potent sting of the glossy black scorpion, a species native to the forests of Eastern and Southern India.
- This discovery marks a significant step forward in addressing a long-neglected public health concern in tropical regions.
Key Highlights
- Species Studied: Heterometrus bengalensis (HB), a lesser-known species of glossy black scorpion, found in the forests of Eastern and Southern India.
Research Institute
- Study conducted by the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), Guwahati, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
Objective
- First-ever comprehensive biochemical, proteomic, and pharmacological profiling of HB venom to address the scientific gap in scorpion venom research.
Key Discovery
- The venom contains 25 distinct toxins from 8 different protein families, which are responsible for its potent sting.
Pharmacological Findings
- Tested on Swiss albino mice, the venom triggered:
- Systemic toxicity Elevated liver enzymes (indicating hepatic stress)
- Organ damage
- A pronounced proinflammatory immune response, pointing to risks like shock or severe allergic reactions in humans.
Significance
- Provides a basis for future research on venom toxicity and possible therapeutic interventions.
- Improved medical treatment for scorpion stings.
- Better understanding of venom biology.
- Enhanced public health preparedness in affected regions.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS GS PAPER 1, 2023
With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements:
1. Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
2. When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled for equal protection whether it is found in a protected area or outside.
3. Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient for capturing it from the wild. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
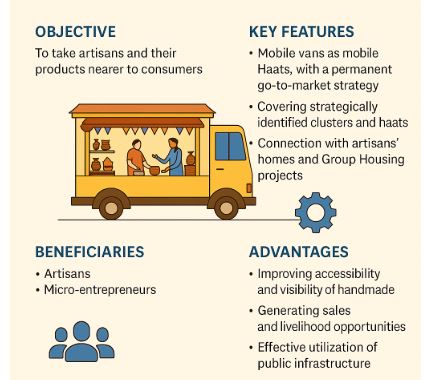
7. Haat on Wheels Initiative: Promoting Indian Handloom Directly to Consumers
Context
- Recently, on the occasion of the 11th National Handloom Day, the Ministry of Textiles, in collaboration with the National Handloom Development Corporation (NHDC), launched the innovative "Haat on Wheels" initiative. An Exclusive Handloom Expo was also inaugurated at Handloom Haat, Janpath.
About Haat on Wheels Initiative
- A mobile retail platform promoting direct-to-consumer handloom sales.
- Showcasing 116 distinct weaves from across India
- Will travel across Delhi NCR, including: Markets, Residential societies, Art and cultural zones.
Aim
- Bridge the gap between weavers and urban consumers
- Promote "Vocal for Local", sustainable fashion, and indigenous craft.
Theme of the Year
- "My Handloom, My Pride; My Product, My Pride"
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PYQ, 2023
With reference to handloom and handicraft products in India, consider the following statements:
1. In India, the Geographical Indication (GI) tag is mandatory for a product to be recognised as a handloom product.
2. In India, Handloom Mark is issued by the Textiles Committee under the Ministry of Textiles.
3. A product can be covered under both Handloom Mark and GI tag. Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
8. Environmental DNA (eDNA): A Revolutionary Tool for Biodiversity Monitoring
Context
- Recently, scientists have moved beyond traditional methods like catching animals or counting plants and are increasingly using environmental DNA (eDNA) to study biodiversity.
About eDNA
- Refers to genetic material that organisms shed into their surroundings during their life or after death. It originates from cellular material such as skin cells, feces, saliva, or decomposed tissue, which gets deposited in water, soil, or air.
Working
- Scientists collect a few litres of water (or soil/air samples) from the environment.
- The DNA fragments present are filtered and sequenced to detect the presence of different organisms.
- This method can identify a broad spectrum of life forms, including: Microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, archaea), Fungi, plants, insects, birds, fish, amphibians, and mammals.
Advantages
- Non-invasive and eliminates the need to capture or count organisms.
- Highly sensitive, detecting both rare and cryptic species that are hard to observe directly.
- Useful in early detection of invasive species and in forensic identification (e.g., detection of human remains). Faster, cheaper, and scalable to large marine and freshwater ecosystems.
Recent Study
- Kashi River Basin, China: eDNA metabarcoding in the Kashi River found fish species across 21 sites, far exceeding the 27 species recorded in earlier net surveys.
- The study also showed how seasonal changes and human interventions (like hydropower) affect biodiversity.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS, 2020
With reference to the "DNA Barcoding", which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. It is used for the identification of species using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes.
2. It can be used to assess biodiversity in a given area.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans:
9. India Cine Hub Portal: Boosting Film-Friendly Ecosystem in India
Context
- Recently, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting urged States to actively use the India Cine Hub portal to attract and facilitate global film productions at the local level. The Ministry also outlined a roadmap for promoting low-cost cinema infrastructure across the country.
About India Cine Hub portal
- Launched on June 28, 2024, designed to streamline the process of granting film-making permissions, disbursing incentives, and mapping resources across India.
- Aims to create a film-friendly ecosystem and ease of doing business in the media sector and promotes India as a global filming destination.
Key Features
- GIS-based location mapping to help filmmakers identify ideal shooting spots.
- A common application form to simplify permission processes.
- Single-window clearance mechanism for all necessary approvals.
Current Integration Status
- Fully Integrated: 7 States and 2 Union Territories
- Onboarded (In Progress): 21 States and 6 Union Territories
Extended Services
- Originally meant for foreign filmmakers, the portal's services have now been extended to Indian filmmakers as well.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC, 2018 GS PAPER 1
With reference to the National Digital Heritage Mission (NDHM), consider the following statements:
1. It is a mission to digitally preserve India’s cultural heritage.
2. It is implemented by the Ministry of Culture.
(a) 1 ONLY
(b) 2 ONLY
(c) BOTH 1 AND 2
(d) NEITHER 1 NOR 2
Ans:
10. Indri Lemur: Habitat, Characteristics, and Behavior of Madagascar's Largest Lemur
Context
- Recently, for the first time, a team of researchers successfully mapped the intestinal microbiome of the Indri lemur.
About Indri Lemur
- Common Name: Indri (locally known as babakoto)
- Scientific Name: Indri indri
- Distribution and Habitat: Endemic to the remote rainforests of northeastern Madagascar
- Inhabits both coastal and montane rainforests, ranging from sea level up to 1,800 metres in elevation.
Physical Characteristics
- Largest living lemur species, measuring 60-70 cm (24-28 inches) in length.
- Possesses a rudimentary tail, large hands and feet, and a round head with a pointed face and furry, rounded ears
- Covered in smooth, silky fur, typically black with white markings on the head, throat, forearms, and buttocks (color patterns vary by region)
Behaviour and Diet
- Diurnal and strictly arboreal
- Moves through the forest by clinging to and leaping between trees in an upright posture
- Herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, flowers, and other vegetation
- Life expectancy in the wild ranges from 15 to 18 years.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS 2017
Consider the following pairs:
Wildlife : Naturally found in
1. Blue-finned Mahseer : Cauvery River
2. Irrawaddy Dolphin : Chambal River
3. Rusty-spotted Cat : Eastern Ghats
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
11. WHO-IRCH Workshop 2025: India Leads Global Efforts in Herbal Medicine Regulation
Context
- Recently, India has been selected to host the WHO-International Regulatory Cooperation for Herbal Medicines (IRCH) Workshop, marking a significant milestone advancing global regulatory frameworks for traditional and herbal medicine.
Key Highlights
Objectives
- To promote a unified global framework for herbal medicine through collaboration, robust safety standards, regulatory alignment, capacity-building, and empowerment of traditional medicine systems.
Countries Participating Physically
- Bhutan, Brunei, Cuba, Ghana, Indonesia, Japan, Nepal, Paraguay, Poland, Sri Lanka, Uganda, Zimbabwe; Virtual Participants: Brazil, Egypt, USA
New Initiatives Introduced
- Ayush Suraksha (Pharmacovigilance) Programme: To improve safety monitoring and reporting of adverse effects in traditional medicines
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS, 2015
With reference to the World Health Organization (WHO), consider the following statements:
1. WHO is a specialized agency of the United Nations.
2. It publishes the World Health Report.
3. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: