Strait Of Hormuz 2025: Explore its location, map, bordering countries like Iran and Oman, strategic importance, oil and LNG flow, closure threats, and global impact. Understand why this maritime chokepoint is vital for global energy and security.
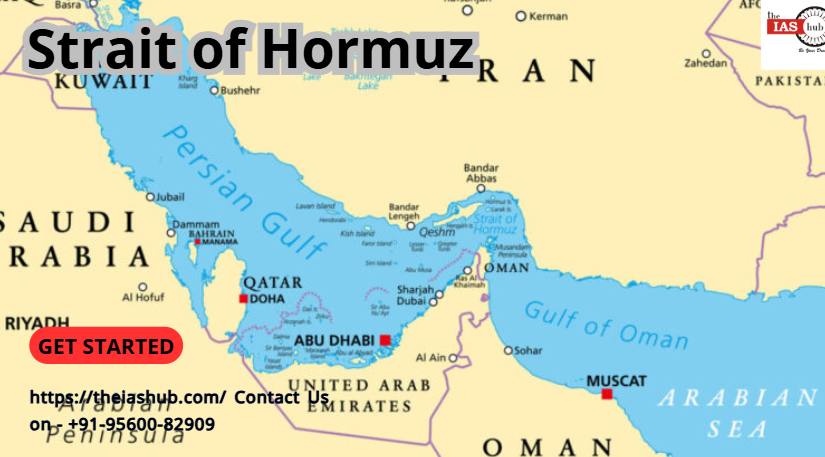


The Strait of Hormuz is one of the most geopolitically sensitive waterways in the world. Located between Iran and Oman, this narrow passage connects the oil-rich Persian Gulf to the open seas of the Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea. Every day, millions of barrels of crude oil and large volumes of liquefied natural gas (LNG) pass through this maritime corridor, making it central to global energy markets. The strait’s strategic importance is not just economic but deeply intertwined with regional politics and global security.
Also Read: Bharat Forecast System

The Strait of Hormuz is approximately 167 km long and at its narrowest point, it is just 33 km wide. It separates Iran on the north from the Musandam Peninsula of Oman on the south. It serves as the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean, making it a crucial maritime artery. On the world map, it is located between latitudes 26°N and longitudes 56°E.
| Feature | Detail |
| Length | ~167 km |
| Narrowest width | ~33 km |
| Adjacent countries | Iran (north), Oman (south) |
| Connected bodies | Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman |
| Strategic lanes | Two 3-km shipping lanes (inbound/outbound) |
Also Read: Padma Awards 2025

Courtesy: Map of World
The strait is clearly visible on any political world map and is situated between the southern coast of Iran and the northern tip of Oman. It connects the landlocked Persian Gulf with the Arabian Sea, making it the only maritime route for Persian Gulf nations to export oil and gas to the rest of the world.
Also Read: Chief Justice of India
The Strait of Hormuz is bordered by two key countries: Iran to the north and Oman and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to the south.
| Country | Position Relative to Strait of Hormuz | Key Areas or Strategic Points | Geopolitical Role |
| Iran | North of the strait | Qeshm Island, Bandar Abbas | Controls northern access; strong naval presence; key player in regional security |
| Oman | South (Musandam Peninsula exclave) | Khasab, Musandam Peninsula | Controls part of southern entrance; neutral diplomatic stance; monitors maritime traffic |
| United Arab Emirates (UAE) | South and west of the strait | Fujairah (eastern coast), oil export terminals | Major oil exporter; supports international maritime security; aligned with GCC policies |
In 2025, tensions flared in the region when Iran’s parliament approved a motion authorizing the potential closure of the Strait of Hormuz. This move was a reaction to international military developments and perceived economic pressures. Although this decision is pending final executive clearance, it caused immediate reactions in oil markets, with prices jumping temporarily due to fears of disruption.
While Iran has threatened closure multiple times in history, such as during the Iran–Iraq War or in response to sanctions, the strait has never been fully closed. Any such action would not only damage global economies but also hurt Iran’s own exports. As a result, full closure remains a highly unlikely but severe scenario.
Also Read: UPSC Chairman List
The Strait of Hormuz holds immense importance due to the volume of oil and gas that flows through it. As of 2024–2025, about 20 million barrels of crude oil pass through the strait daily, accounting for nearly one-quarter of the world’s seaborne oil trade and about one-fifth of total global oil consumption. It also handles nearly 20% of the global LNG trade, primarily from Qatar.
| Commodity | Daily Flow Through Hormuz | Global Share |
| Crude Oil | ~20 million barrels | ~25% seaborne oil |
| LNG | Significant volumes | ~20% global LNG |
The strait’s role is irreplaceable for many economies, especially in Asia. Around 84% of the oil passing through Hormuz goes to markets in China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
Impacts of a Closure Scenario:
| Sector | Potential Consequences |
| Global Oil Market | Oil prices may surge due to supply disruption |
| Asian Economies | Major energy importers face shortages |
| Shipping Industry | Higher insurance premiums and rerouting costs |
| Military Tensions | Risk of conflict escalation |
Even short-term disruption can significantly impact oil supply chains, especially for energy-dependent countries. The presence of international naval forces in the region, including fleets from major powers, is a deterrent to any permanent closure.
Several Gulf countries have attempted to reduce their dependence on the Strait of Hormuz by constructing alternate oil and gas pipelines. However, these alternatives cannot fully replace the strait’s role.
Major Bypass Routes for State of Hormuz:
| Country | Pipeline | Capacity (mbpd) | Destination |
| Saudi Arabia | East–West (Petroline) | ~5.0 | Red Sea (Yanbu Port) |
| UAE | Habshan–Fujairah Pipeline | ~1.8 | Gulf of Oman (Fujairah) |
| Iran | Goreh–Jask Pipeline | Partial use | Jask Terminal (Gulf of Oman) |
Despite these efforts, over two-thirds of Gulf energy exports must still pass through Hormuz. Thus, the strait remains indispensable.
India imports over 85% of its crude oil, and nearly half of this comes via the Strait of Hormuz. A disruption here would not only raise energy prices domestically but could lead to broader economic impacts such as inflation, trade deficits, and strategic vulnerability.
India has taken some steps to mitigate this risk through:
Nevertheless, in the short to medium term, the security of the Strait of Hormuz remains crucial for India’s energy and economic stability.
Are you preparing for UPSC Mains 2025? Join IAShub’s UPSC coaching batches to boost your preparation. Enroll now!
The Strait of Hormuz is far more than a geographic feature — it is a strategic artery that sustains the global economy. Despite frequent threats of closure, it has remained open, largely due to its indispensable role and the risks involved in disrupting global oil and gas flows. As recent events have shown, even the possibility of closure triggers immediate economic and political ripple effects. For countries like India and for UPSC aspirants, understanding the geography, economics, and geopolitics of the Strait of Hormuz is essential. With global energy security hanging in balance, the world continues to watch this narrow stretch of water with intense focus.
The Strait of Hormuz lies between Iran to the north and Oman to the south, linking the Persian Gulf with the Arabian Sea. It appears as a narrow waterway on the world map, strategically situated in West Asia. It is one of the most vital geographic features for global trade and security.
While Iran has frequently threatened to close the Strait of Hormuz in response to sanctions or military pressure, it has never actually done so. Closure would harm Iran’s own exports and provoke international response. However, such threats do raise oil prices and regional tensions.
A closure of the Strait of Hormuz would disrupt global oil and gas flows, cause a spike in energy prices, and increase geopolitical instability. Countries heavily reliant on Gulf energy exports, like India and China, would face economic stress. Global markets would also react swiftly to such an event.
The Strait of Hormuz features frequently in UPSC exams under international relations, geography, and current affairs. Its strategic location, energy relevance, and role in global security make it a key topic. UPSC aspirants should understand its geopolitical significance and recent developments.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.
