Discover the history of tribal movements in India, their role in resisting colonialism, major rebellions, and their contribution to India’s freedom struggle.

The history of India’s independence is incomplete without acknowledging the role of tribal movements in India. Long before organized political parties and mass civil disobedience campaigns, tribal communities raised their voices against exploitation, injustice, and colonial rule. These uprisings were not isolated incidents; they represented some of the earliest organized resistances to British authority. The tribal movements in India reflected the struggles of indigenous communities to defend their land, culture, and livelihood against colonial exploitation and non-tribal encroachments.
One of the most significant features of tribal movements in India was that they began as early forms of resistance to colonialism. At a time when the British were consolidating their power, tribal communities revolted to safeguard their rights.
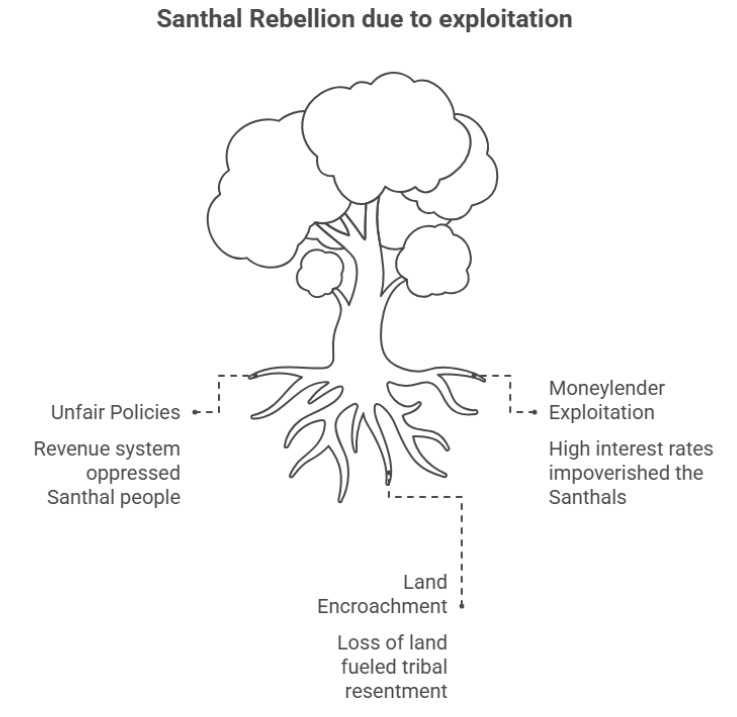
The Santhal Rebellion remains one of the most important tribal movements in India. The Santhals rose in protest against unfair revenue policies, exploitation by moneylenders, and the encroachment of their lands by non-tribal settlers. Led by Sidhu and Kanhu Murmu, this rebellion challenged British authority and highlighted the growing discontent among tribal communities.
The Santhal Rebellion is remembered not just as an uprising but as a symbol of courage, showing how tribal movements in India laid the foundation for larger anti-colonial struggles.
Another major feature of tribal movements in India was the fight to defend traditional rights and ancestral lands. For tribal communities, land was not just a resource but a cultural and spiritual identity. British policies and non-tribal intrusion threatened this connection, sparking widespread rebellions.
The Munda Rebellion, also known as the Ulgulan (The Great Tumult), was led by Birsa Munda. This became one of the most influential tribal movements in India, demanding an end to the ‘zamindari’ system and exploitation by landlords and British officials. Birsa Munda also emphasized social reforms, urging his people to return to their traditional practices and reject exploitative structures.
The rebellion brought to light the determination of tribal movements in India to resist cultural erosion and economic exploitation, and it remains a milestone in India’s freedom struggle.
The courage displayed by tribal communities inspired later uprisings across India. The tribal movements in India showed that organized resistance was possible, motivating peasants, workers, and other marginalized groups to challenge colonial exploitation.
The Bhil Revolt in the Western Ghats was among the earliest tribal movements in India against colonial authority. The Bhils opposed British interference in their socio-political structure and resisted heavy taxation. Their struggle not only disrupted British expansion but also influenced later peasant movements in the region.
This revolt demonstrated how tribal movements in India were precursors to larger nationalistic movements, inspiring broader resistance against colonialism.
While often localized, the tribal movements in India played a critical role in the larger national struggle for independence. By challenging British authority, tribal rebellions weakened colonial control and created conditions that facilitated the growth of the nationalist movement.
The Rampa Rebellion, led by Alluri Sitarama Raju in the Andhra region, was one of the most powerful tribal movements in India during the 20th century. Raju united tribal communities against oppressive forest laws that restricted their rights to use forests for livelihood.
Although it was brutally suppressed, the Rampa Rebellion showed how tribal movements in India directly contributed to weakening British authority and aligning with the broader freedom struggle.
Another crucial dimension of tribal movements in India was their ability to bring socio-economic injustices into the national spotlight. Tribal uprisings highlighted forced labor, unfair taxation, and exploitation by landlords and moneylenders, issues that resonated with peasants and common people across the country.
The Khonds of Odisha launched one of the most significant tribal movements in India against British revenue policies and suppression of their cultural practices. The rebellion also exposed how colonial authorities tried to manipulate traditional customs for their own benefit.
This uprising emphasized that tribal movements in India were not just about land but also about dignity, identity, and social justice.
The tribal movements in India shared some common features that make them unique in the history of resistance:
The legacy of tribal movements in India extends far beyond the colonial period. They highlighted the need for protecting indigenous rights, recognizing cultural identities, and addressing socio-economic inequalities. After independence, many provisions in the Constitution, such as the Fifth and Sixth Schedules, were designed to safeguard tribal rights, drawing inspiration from historical uprisings.
Today, the memory of tribal movements in India serves as a reminder of how marginalized communities contributed to national freedom and how their sacrifices laid the groundwork for a more inclusive India.
The story of India’s independence is not complete without acknowledging the bravery of tribal movements in India. From the Santhal Rebellion to the Rampa Rebellion, from the Bhil Revolt to the Munda Ulgulan, these uprisings showed the determination of tribal communities to fight exploitation and defend their rights.
Although many of these revolts were suppressed, they weakened colonial authority and inspired broader nationalist movements. The tribal movements in India not only defended land and culture but also contributed to the larger goal of freedom, leaving a legacy of courage, resilience, and resistance that continues to inspire generations.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.