Explore the major pre and post-independence regional movements in India, including Telangana, Dravidian, Bodoland, Gorkhaland, and more in historical detail.

India’s unity in diversity is both its strength and its challenge. Across the country’s vast landscape, different regions have expressed unique cultural, linguistic, and political identities. This has given rise to several regional movements throughout Indian history. These movements have shaped not just state boundaries but also national policies and democratic representation.
From the early 20th century demands for Dravidian and tribal identity to post-independence struggles like Telangana and Gorkhaland, regional movements reflect the country’s dynamic sociopolitical evolution. This article provides a detailed analysis of both pre-independence regional movements and post-independence regional movements to understand their origins, goals, and outcomes.
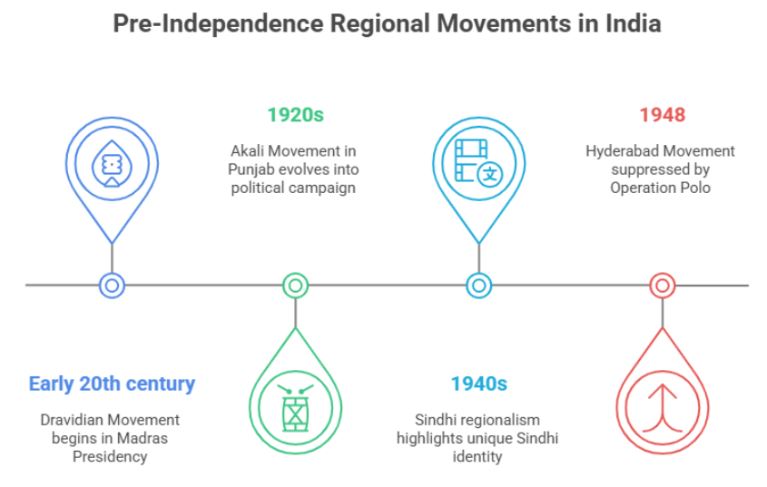
Before India gained independence in 1947, several regional movements emerged that were rooted in linguistic, cultural, religious, and ethnic identities. These movements played a vital role in shaping the early political landscape of modern India.
The Dravidian Movement originated in the early 20th century, primarily in the Madras Presidency (now Tamil Nadu). It emphasized South Indian identity and sought to resist the dominance of North Indian, especially Aryan and Brahminical culture.
The Akali Movement was a Sikh-led movement in Punjab during the 1920s. Though it began as a religious reform movement to free gurdwaras from corrupt mahants, it soon evolved into a political campaign for autonomy.
During British rule, Assamese identity faced erosion due to the migration of Bengali-speaking populations. The early Assam Movement resisted British policies that marginalized the native Assamese language and culture.
Before partition, Sindhi regionalism highlighted the unique identity of Sindhi people who felt culturally and linguistically distinct from the larger Indian population.
The Hyderabad Movement gained momentum as the princely state of Hyderabad, ruled by the Nizam, resisted integration into independent India.
Several princely states like Travancore, Junagadh, and Kashmir expressed reluctance or conditions for joining the Indian Union, leading to localized regional movements demanding autonomy or outright independence.
Tribal communities in regions like Chhota Nagpur, Jharkhand, and Bastar began organizing movements during the British era, demanding recognition of their rights and resisting exploitation.
After 1947, India's federal structure allowed room for accommodating regional identities. However, unresolved issues, economic disparity, and ethnic assertions gave rise to several significant regional movements.
The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 was a turning point in addressing regional movements.
Strong regional movements in these areas emphasized cultural uniqueness and administrative neglect.
One of the most intense regional movements post-independence has been in the North-East.
The Khalistan Movement in the 1980s sought an independent Sikh state.
The Dravidian Movement transformed into political organizations like DMK and AIADMK, which have dominated Tamil Nadu politics.
The Bodoland Movement in Assam is driven by the Bodo ethnic group seeking a separate state.
One of the most successful regional movements in recent Indian history.
This ongoing movement demands a separate Gorkhaland state carved out of West Bengal.
Several lesser-known but significant regional movements continue to shape Indian politics.
The history of regional movements in India shows that they are neither inherently divisive nor always unifying. They can be tools for social justice, decentralization, and cultural preservation if handled wisely. However, they also have the potential to incite division and violence if exploited politically.
India’s strength lies in accommodating its diversity. Understanding and addressing the root causes of regional movements—whether they arise from neglect, identity assertion, or inequality—is key to maintaining national unity and fostering inclusive development.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.