Explore the recommendations and impact of the Radhakrishnan Commission (1948–49), the pioneer in reshaping university education in post-independence India.

The Radhakrishnan Commission, formally known as the University Education Commission (1948–49), was established by the Government of India to assess and reform the university education system of newly independent India. Headed by Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, a renowned philosopher, educationist, and future President of India, the commission laid the groundwork for India's modern higher education structure.
At a time when India had just achieved independence, there was an urgent need to redefine the goals, structure, and relevance of higher education. The Radhakrishnan Commission not only addressed these concerns but also made visionary recommendations that have shaped India's university system for decades.
The main objective of the Radhakrishnan Commission was to examine the state of university education in India and recommend measures to align it with national development, individual growth, and global standards. It aimed to produce responsible citizens, skilled professionals, and enlightened individuals through a robust and inclusive higher education system.
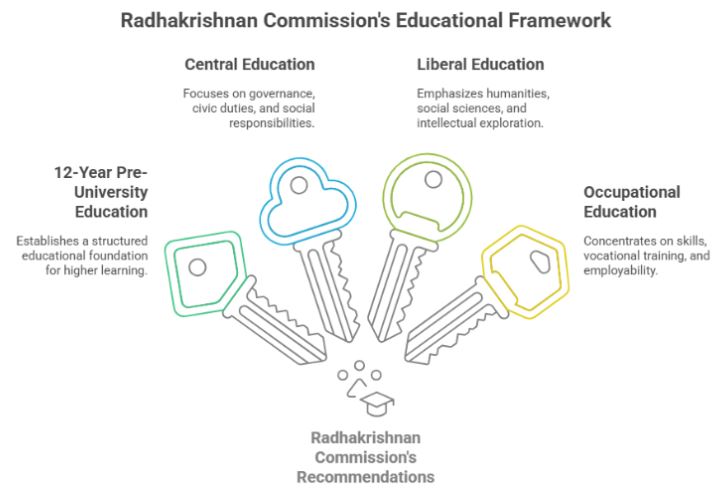
The Radhakrishnan Commission recommended a 12-year pre-university education system, replacing the previous fragmented structure. This recommendation laid the foundation for the 10+2+3 educational model, which later became the standard format in India’s academic structure.
The commission advocated for a well-rounded university education, combining:
This integrated model envisioned by the Radhakrishnan Commission aimed to develop students holistically, balancing knowledge, character, and competence.
A pioneering recommendation of the Radhakrishnan Commission was the establishment of rural universities, inspired by Shantiniketan (founded by Rabindranath Tagore) and Jamia Millia Islamia. These institutions were envisioned to address the needs of India’s rural population by:
The idea was to integrate academic knowledge with grassroots challenges, making education more meaningful and inclusive.
Recognizing the importance of global communication and research access, the Radhakrishnan Commission emphasized retaining English as a medium of instruction in higher education. It considered English crucial for academic excellence, especially in science, law, and technology.
Simultaneously, the commission recommended that:
The Radhakrishnan Commission advocated for a multilingual education model, respecting India’s linguistic diversity while ensuring academic competitiveness.
One of the critical constitutional recommendations of the Radhakrishnan Commission was to include university education in the Concurrent List of the Indian Constitution. This would allow both the central and state governments to legislate on higher education, ensuring uniform standards and national coordination.
Perhaps the most transformative suggestion of the Radhakrishnan Commission was the creation of a national body to coordinate and regulate higher education. This led to the establishment of the University Grants Commission (UGC):
The UGC became the backbone of higher education governance in India, a direct result of the Radhakrishnan Commission’s vision.
The University Grants Commission has since played a central role in implementing the Radhakrishnan Commission’s recommendations. Key developments include:
The Radhakrishnan Commission also laid the ideological foundation for NEP 1968, NEP 1986, and the National Education Policy 2020, all of which borrowed its principles of holistic education and national integration.
The Radhakrishnan Commission transformed India’s higher education landscape in several ways:
Even today, the Radhakrishnan Commission is considered the most influential and visionary document in India’s educational history.
As India moves towards becoming a knowledge economy, the recommendations of the Radhakrishnan Commission remain highly relevant. Its emphasis on:
…continues to shape educational policies in 21st-century India.
The Radhakrishnan Commission (1948–49) was a milestone in India’s educational evolution. It laid the blueprint for a robust, inclusive, and globally competitive university education system. Its emphasis on quality, language diversity, rural inclusion, and institutional governance helped transform India’s higher education from colonial remnants into a modern, progressive system. Even after seven decades, the principles of the Radhakrishnan Commission remain deeply embedded in India’s academic and administrative structures, guiding its future with wisdom from the past.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.