Explore the French Revolution (1789–1799): causes, timeline, key events, impacts on France, women, and India. A turning point in world history.

The French Revolution (1789–1799) was one of the most influential events in world history. It signaled the collapse of centuries-old monarchy and the rise of republicanism. Driven by the motto "Liberty, Equality, Fraternity," the French Revolution sparked massive political, social, and economic changes—not just in France, but globally.
It brought an end to feudal privileges, promoted secularism, introduced modern concepts of citizenship, and gave birth to human rights discourses that continue to shape democratic societies. While the revolution led to violence and instability, it laid the foundation for many modern institutions and ideas.
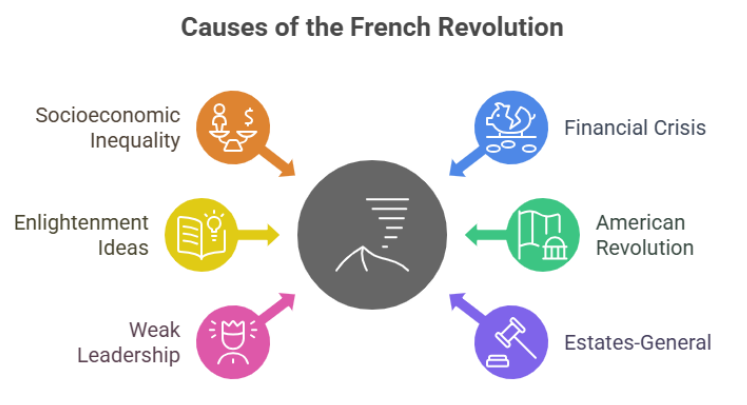
French society was deeply divided into three estates. The First Estate (clergy) and Second Estate (nobility) enjoyed privileges and paid little to no taxes, while the Third Estate—which included peasants, workers, and bourgeoisie—bore the tax burden and lived in hardship. This vast inequality fueled discontent.
Decades of royal extravagance, along with the financial burden of wars such as the American War of Independence and Seven Years' War, left France nearly bankrupt. The tax system was regressive, placing more pressure on the already struggling Third Estate.
Enlightenment philosophers like Voltaire, Rousseau, and Montesquieu questioned the divine right of kings and promoted values such as liberty, equality, reason, and democratic governance. Their ideas inspired the revolutionaries to challenge autocratic rule.
The success of the American Revolution served as a powerful example. It proved that it was possible to overthrow an unjust monarchy and establish a nation based on democratic principles.
King Louis XVI was seen as indecisive and ineffective. His inability to initiate meaningful reforms and control rising debt led to growing unrest. His lavish lifestyle only widened the gap between the monarchy and the masses.
In 1789, the calling of the Estates-General gave the Third Estate a political voice. When voting inequalities surfaced, the Third Estate broke away and declared itself the National Assembly, setting the revolution in motion.
On July 14, 1789, Parisians stormed the Bastille prison, symbolizing the beginning of the French Revolution and the fall of absolute monarchy.
The National Assembly passed this revolutionary document affirming that “men are born and remain free and equal in rights.”
France adopted its first constitution, turning the monarchy into a limited one, though unrest continued.
The monarchy was officially abolished, and France was declared a republic.
Led by Robespierre, the revolution entered a radical phase. Thousands were executed, including King Louis XVI and Queen Marie Antoinette.
The revolution ended when Napoleon Bonaparte took power through a coup, beginning a new authoritarian era.
The French Revolution successfully dismantled the feudal system, ending privileges for the nobility and clergy.
The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen became a cornerstone for modern human rights and legal systems worldwide.
Religion was separated from the state. The law now treated citizens equally, regardless of birth or class.
The revolution’s ideals sparked movements in Latin America, Europe, and even India, promoting liberty, justice, and democratic governance.
Mass executions during this phase of the French Revolution led to fear and repression. Political rivals and common citizens were not spared.
The revolutionary government kept changing. Economic instability and civil unrest plagued the country for years.
Though based on liberty, the revolution eventually led to Napoleon’s dictatorship, which curtailed many democratic freedoms.
Thousands of women marched to Versailles demanding bread and reforms. Their protest forced the King to move to Paris and acknowledge the Assembly.
Women formed clubs like the Society of Revolutionary Republican Women to demand political rights and justice.
They took part in riots and protests, worked in support roles during wars, and engaged in debates about women’s rights.
She authored the Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen (1791), challenging the male-centric view of citizenship and demanding equality.
Indian thinkers and reformers were inspired by the principles of liberty and equality.
The French Revolution encouraged resistance against British rule and promoted the idea of self-rule.
The intellectual ripple effects led to religious and social reform movements in 19th-century India, such as the Brahmo Samaj and Arya Samaj.
Leaders like Gandhi, Nehru, and others drew inspiration from revolutionary ideals for India’s independence movement.
The French Revolution remains a defining chapter in world history. It challenged monarchy, feudalism, and absolute power, replacing them with ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity. Though accompanied by violence and political turmoil, its long-term impacts reshaped global politics, law, and social structures.
Its legacy lives on—not just in modern France, but in every democracy that values freedom, rights, and equality. The French Revolution reminds us of the power of collective action and the enduring strength of revolutionary ideas.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.