Explore the European policy in India by Portuguese, Dutch, and French powers. Learn about their administrative, social, and economic impact on Indian society.

The arrival of European powers in India marked a significant turning point in Indian history. Each power—Portuguese, Dutch, French, and later the British—brought its own systems of administration, trade practices, legal structures, and cultural influence. The European policy in India was not uniform, but it shared one common feature: the pursuit of political dominance and economic exploitation. Over time, these policies reshaped India’s social, political, cultural, and economic structures.
In this article, we will discuss the major European policy in India, focusing on the Portuguese, Dutch, and French, and analyze their lasting impact on Indian society and governance.
The French were among the most prominent European powers to establish their presence in India. Their administrative and legal practices reflected a centralized and modern approach to governance.
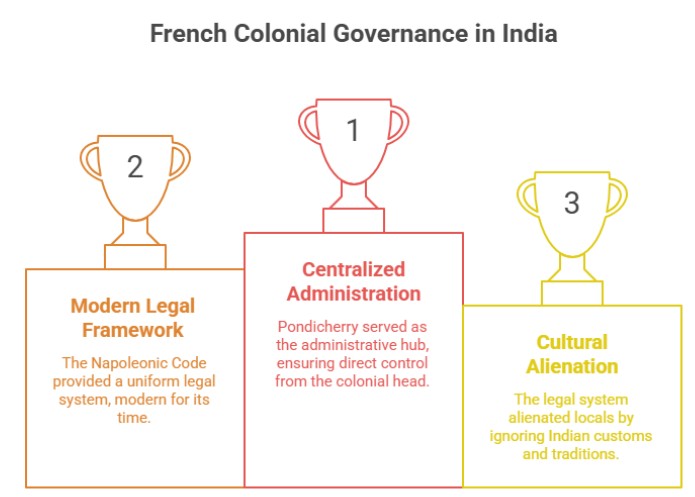
The French organized their territories with Pondicherry as the administrative centre. Their governance followed a centralized model where decisions flowed directly from the colonial head. Unlike the British, who often involved local rulers, the French believed in direct control, reflecting their European policy in India that was rigid and highly centralized.
The French introduced the Code Civil, also known as the Napoleonic Code, in their colonies. This system provided a uniform legal framework that was modern for its time. However, it also alienated local populations, as it did not take into account the customs and traditions of Indian communities. The French legal system symbolized the broader European policy in India, which often prioritized Western structures over indigenous systems.
The Portuguese were the first Europeans to establish long-term colonies in India, and their policies were deeply intertwined with religion and central authority.
The Portuguese governed their territories, especially Goa, through a centralized administration led by the Viceroy of India. This top-down system reflected a strict model of governance. Their colonial administration highlighted how the European policy in India undermined local rulers and autonomy.
The Portuguese were highly active in spreading Christianity. They undertook forced conversions and established the Inquisition in Goa, which became notorious for its harsh treatment of non-Christians. Their European policy in India went beyond economic and political motives, extending deeply into cultural and religious transformation.
The Dutch presence in India was primarily motivated by trade rather than political dominance. Their approach reflected a commercial dimension of the European policy in India.
The Dutch East India Company (VOC) concentrated on establishing trading posts and factories along the Indian coast. Their aim was to control spice trade routes and maximize profits rather than impose direct political rule.
Unlike the French and Portuguese, the Dutch exercised limited direct control over territories. Instead, they relied on alliances with local rulers and trade agreements. This was a unique aspect of the European policy in India, where commercial interests outweighed governance and cultural imposition.
The policies of Europeans had a deep and long-lasting impact on India’s economic, cultural, political, and social fabric. The European policy in India created profound transformations, many of which shaped modern India.
One of the most visible effects of the European policy in India was economic exploitation. European powers extracted resources, controlled trade routes, and monopolized local industries. Indian artisans and farmers were often forced into systems that benefited European traders, causing decline in local economies and industries.
The Europeans introduced Western education, legal systems, and lifestyles, which brought modernization but also cultural dislocation. Traditional practices, indigenous education, and local crafts declined as Western culture dominated. This cultural transformation, as part of the European policy in India, often weakened traditional structures.
The European policy in India contributed to widening social inequalities. Certain communities were favored for administrative or religious reasons, while others were marginalized. These divisions often exacerbated tensions and sowed seeds of conflict in Indian society.
Colonial powers introduced modern state structures, centralized administration, and legal codes. While this helped in laying the foundation for a modern state, it also eroded traditional political systems and autonomy of Indian rulers. The European policy in India created a dual legacy: modernization on one hand and political dependency on the other.
The collective European policy in India was a blend of political ambition, economic exploitation, and cultural influence. While Europeans brought modernization in administration and education, their exploitative practices weakened India’s self-sufficiency. The Portuguese emphasized religious dominance, the French centralized administration, and the Dutch prioritized trade. Each of these powers contributed to India’s transformation, often at the cost of its traditional systems.
The European policy in India was shaped by different powers with varying goals—religious, commercial, administrative, and political. Despite these differences, the overarching result was exploitation, cultural disruption, and structural change in Indian society. The Portuguese enforced religion, the Dutch pushed for commerce, and the French centralized governance, but together, their policies left behind a legacy of economic dependency, social division, and cultural transformation.
The long-term consequences of the European policy in India are still visible today, as India continues to balance its traditional heritage with the systems introduced during the colonial era. Understanding these policies is crucial for comprehending how colonialism shaped modern India.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.