Explore the Cold War era—from causes and major events to global impact and the fall of the Soviet Union. Learn how this ideological conflict shaped world history.

The Cold War was a prolonged period of political and ideological conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union, lasting from the end of World War II in 1945 until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. Unlike traditional wars, the Cold War was not fought through direct large-scale battles between the two superpowers. Instead, it manifested through an arms race, proxy wars, espionage, propaganda, and competition for global influence.
President George H.W. Bush described it as the "great ideological struggle of the twentieth century between Communism and Freedom," which ultimately ended in a decisive victory for democratic and capitalist forces.
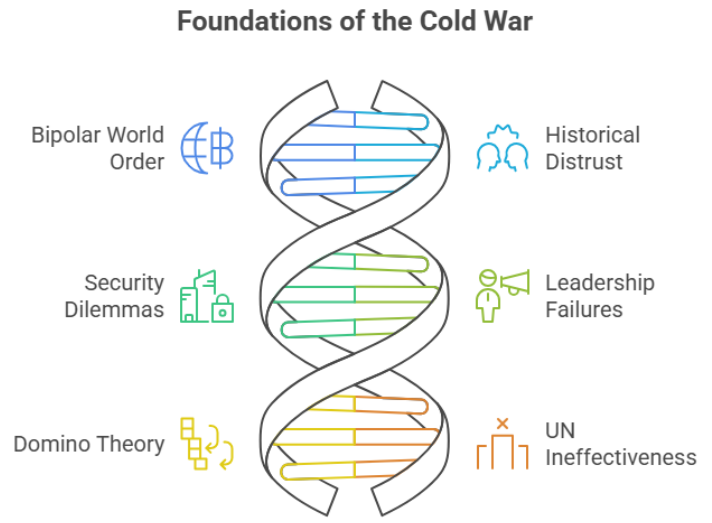
Understanding the Cold War requires examining the deep-rooted causes that led to this global standoff.
After World War II, the world was essentially divided into two major spheres of influence: the capitalist bloc led by the United States and the communist bloc led by the Soviet Union. This bipolar division set the stage for the Cold War.
Old suspicions between the West and the USSR grew due to their incompatible ideologies—capitalism vs communism. This mistrust was reinforced by wartime decisions and post-war actions, including Soviet control over Eastern Europe.
The Soviet Union sought buffer states to protect itself from future Western invasions, while the U.S. pursued containment policies to stop the spread of communism. These actions further escalated Cold War tensions.
Statements and policies by key leaders like Joseph Stalin and Harry Truman hardened positions. Initiatives like the Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan were seen by the Soviets as aggressive strategies against communism.
The U.S. feared the "domino effect," where if one country fell to communism, others would follow. This fear influenced American interventions in regions like Southeast Asia, intensifying the Cold War.
The inability of the UN to resolve or prevent global crises also contributed to the longevity of the Cold War. Veto powers used by the U.S. and USSR often paralyzed international decision-making.
The Cold War was not a traditional war but involved distinct features that defined global politics for nearly five decades.
Both superpowers tried to expand their spheres of influence globally through alliances, economic aid, and military interventions.
One of the defining features of the Cold War was the nuclear arms race. The development of weapons of mass destruction created a tense atmosphere of Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD).
The Cold War led to the establishment of two major military alliances:
Numerous global incidents during the Cold War era kept the world on edge and reflected the intense rivalry between the two blocs.
Perhaps the most dangerous moment of the Cold War, the Cuban Missile Crisis brought the U.S. and USSR to the brink of nuclear war. The Soviets placed nuclear missiles in Cuba, prompting a tense 13-day standoff.
The Berlin Wall became a physical and ideological symbol of the Cold War, dividing East Berlin (communist) from West Berlin (capitalist). Its fall in 1989 marked the beginning of the end for the Cold War.
One of the earliest Cold War proxy wars, the Korean conflict involved the U.S. and UN forces supporting South Korea, while China and the USSR backed North Korea.
Another proxy conflict, the Vietnam War saw American efforts to prevent a communist takeover, with disastrous consequences and growing domestic opposition.
The Cold War rivalry extended to space, resulting in landmark achievements like the Soviet launch of Sputnik in 1957 and the U.S. moon landing in 1969.
The Cold War had a lasting influence on international politics, economics, technology, and society.
The race for nuclear superiority created a global atmosphere of fear. Countries lived under the constant threat of annihilation.
Nations were divided into the Western bloc or Eastern bloc. Numerous proxy wars broke out in Asia, Africa, and Latin America where superpowers supported opposing sides.
The competitive environment of the Cold War spurred significant progress in space research, military technology, and science.
The constant propaganda and suspicion impacted education, media, and public perception. In the U.S., the fear of communism led to McCarthyism and civil liberty suppression.
The enormous military spending and systemic inefficiencies of the Soviet economy contributed to the USSR’s collapse in 1991, effectively ending the Cold War.
NATO is a political and military alliance established in 1949. Its primary goal was collective security: an attack on one member would be considered an attack on all.
Created by the Soviet Union in 1955 as a direct response to NATO, the Warsaw Pact aligned Eastern bloc countries under Soviet military leadership.
Both NATO and the Warsaw Pact symbolised the militarization of the Cold War and the global alignment of nations based on ideology.
The Cold War gradually ended as communist regimes across Eastern Europe fell during the late 1980s. The most significant event was the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, resulting from economic stagnation, failed reforms, and public dissatisfaction.
Key events leading to the end:
The end of the Cold War marked the beginning of a unipolar world dominated by the United States and paved the way for new global challenges.
The Cold War was more than just a rivalry between two nations—it was a battle of ideologies, economics, and global influence that shaped the modern world. From nuclear threats and proxy wars to space exploration and political revolutions, its effects continue to resonate in international relations today.
The legacy of the Cold War reminds us of the dangers of global divisions and the importance of diplomacy, cooperation, and peace.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.