Explore the Civil Disobedience Movement launched by Mahatma Gandhi in 1930 through the iconic Salt March, and compare it with the Khilafat and Non-Cooperation Movements.

|
PARAMETERS |
KHILAFAT MOVEMENT |
NON-COOPERATION MOVEMENT (NCM) |
CIVIL DISOBEDIENCE MOVEMENT (CDM) |
|
Causes for Emergence |
Dissatisfaction with the Treaty of Sèvres, which dismembered the Ottoman Empire. |
Reaction to the Rowlatt Act, Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, and dissatisfaction with the Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms. |
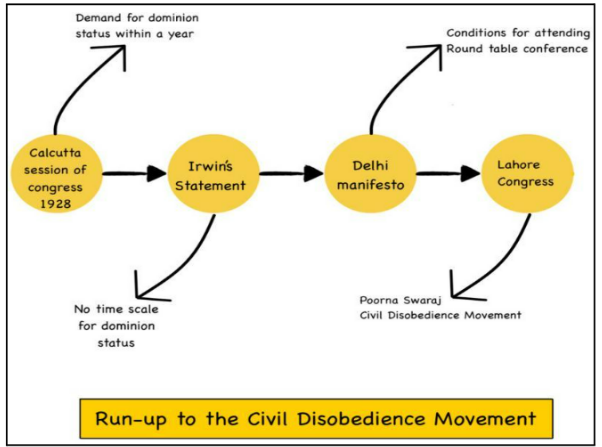
The failure of the Simon Commission and subsequent Round Table Conferences to offer substantial constitutional reforms; imposition of the salt tax and economic hardships. |
|
Leaders Associated |
Ali Brothers (Muhammad Ali and Shaukat Ali), Maulana Abul Kalam Azad |
Mahatma Gandhi, Motilal Nehru, C.R. Das, Lala Lajpat Rai |
Mahatma Gandhi, Sarojini Naidu, B.R. Ambedkar (Poona Pact negotiation), Vallabhbhai Patel |
|
Role of Mahatma Gandhi |
Supported the movement to foster Hindu-Muslim unity and press the British for concessions. |
Central figure, strategized and led the movement advocating for Swaraj and boycott of British institutions and goods. |
Key leader, initiated the Salt March, negotiated with the British (Gandhi-Irwin Pact), and led the movement for complete independence. |
|
Various Events/Incidents |
Formation of the All-India Khilafat Committee, Non-cooperation with the British. |
Boycott of British goods, educational institutions, and courts; return of British honors; Swaraj was declared the goal. |
Salt March, Dandi, breaking the salt laws, boycott of foreign goods, refusal to pay taxes, widespread arrests, and protests. |
|
Section of Population Participated |
Predominantly Muslims, with significant support from Hindus to promote unity. |
Cross-section of Indian society including students, teachers, peasants, workers, and the middle class. |
Broad participation, including peasants, workers, women, and a significant number of the urban and rural poor. |
|
Hindu-Muslim Angle |
Aimed at Hindu-Muslim unity by addressing a Muslim cause. |
Achieved significant Hindu-Muslim unity, although it began to wane towards the end. |
Hindu-Muslim unity was less pronounced due to rising communal tensions and separate electoral demands by Muslims. |
|
Movement Included Which Type of Boycotts? |
Boycott of British goods and institutions was endorsed as part of the wider non-cooperation movement. |
Comprehensive boycott of British goods, services, institutions, and schools; included non-payment of taxes. |
Focused on the boycott of the salt tax, foreign goods, refusal to pay taxes, and violation of forest laws in some areas. |
|
Significance |
Fostered short-lived Hindu-Muslim unity, increased political awareness among Muslims. |
Marked a significant escalation in the Indian independence struggle; mass participation and the concept of Swaraj gained prominence. |
Demonstrated the power of nonviolent civil disobedience, brought the issue of Indian independence to international attention, and led to the Gandhi-Irwin Pact. |
|
Impact |
Contributed to the collapse of Hindu-Muslim unity after the movement's decline. |
Energized the national movement, laid the groundwork for future mass movements, though it was withdrawn after the Chauri Chaura incident. |
Led to the Government of India Act 1935; increased divisions on communal lines but also paved the way for the Quit India Movement. |
|
British Suppression/Decline |
Suppressed by the British; decline after the abolition of the Caliphate. |
Severely repressed by the British; ended after the Chauri Chaura incident led Gandhi to call off the movement. |
Intense government repression; ended with Gandhi's withdrawal of the movement and subsequent negotiations in the Second Round Table Conference. |


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.