03rd October 2025
1. Biostimulants: Recently, the Union Agriculture Ministry withdrew approval for 11 animal protein-based
biostimulants due to religious and dietary concerns.
- Key Highlights: Crops affected: These products were used for paddy, tomato, potato, cucumber, chilli, cotton, soybean, grapes, and green gram.
- Animal sources: The banned biostimulants were derived from bovine hide, hair, tanned skin, chicken feathers, pig tissue, cod skin/bones/scales, and sardine.
- Reason for withdrawal: Complaints from Hindu and Jain communities citing ethical, religious, and dietary restrictions.
- About Biostimulants: Substances or microorganisms (like beneficial bacteria, fungi, or plant extracts) applied to seeds, plants, or soil to stimulate natural plant processes. They help improve nutrient use efficiency, tolerance to abiotic stress, and overall crop quality.
- Different from fertilisers (which supply nutrients) and pesticides (which control pests).
- Often sold in liquid form and sprayed on crops.0
2. False Smut Disease: Recently, reports indicated that the paddy crop in Punjab, at the maturing and harvest stage, has been widely affected by
false smut disease, causing serious damage.
- · About False Smut Disease: False smut (also called haldi rog) is a major fungal disease of rice. Causal Agent: Caused by the fungus Ustilaginoidea virens.
- Other Names: Also known as Lakshmi disease or Oothupathi disease of rice.
- Infection Stage: Fungus infects during the flowering stage.
- Symptoms appear after the rice panicles emerge.
- Symptoms: Infected grains show black fungal mycelium growth, later covered with yellow fungal growth.
- Spores mature from orange to yellowish green or greenish black.
- Usually, only a few grains per panicle are infected; others remain normal.
- Impact: Leads to chalkiness of grains, reduced grain weight and seed germination.
- Yield loss depends on percentage of infected panicles and severity within each panicle.
- Disease affects grains only, not other plant parts.
3. India’s E-Waste Burden: Recently, India’s digital revolution has fuelled a surge in electronic waste, making the country the
world’s third-largest generator, posing serious environmental and health challenges.
- Key highlights: India generated 2 million metric tonnes of e-waste in 2025, ranking third globally (after China and the U.S.).
- This marks a 150% increase since 2017–18 (0.71 million MT).
- At current growth, India’s e-waste volume may double by 2030.
- Over 60% of e-waste comes from 65 major cities (hotspots: Seelampur, Mustafabad, Moradabad, Bhiwandi).
·
Health Impacts: Chronic bronchitis, asthma, and severe lung issues; 76–80% of Indian informal workers show symptoms.
- Lead, mercury, and cadmium exposure linked to cognitive impairment, low IQ, attention deficits, delayed neurobehavioral development in children.
- Rashes, burns, dermatitis, eye irritation due to direct contact with toxic substances.
- DNA damage, oxidative stress, immune system alterations; increased risks for children.
- Higher rates of miscarriages and preterm births in recycling zones.
4. Pandit Chhannulal Mishra: Recently, Padma Vibhushan vocalist and
thumri exponent
Pandit Chhannulal Mishra, a towering figure in Hindustani classical music, passed away.
- About Pt. Chhannulal Mishra: Born in Azamgarh in 1936.
- Musical Contribution: He became a doyen of Hindustani classical music, excelling in Khayal, Thumri, Dadra, Chaiti, Kajri, and Bhajan.
- Awards: Honoured with the Padma Bhushan in 2010 and the Padma Vibhushan in 2020.
- Hindustani music, from northern India, is a classical tradition known for intricate melodies, improvisation, and emotive expression.
- Origins: Evolved from ancient Vedic chants and later enriched by Persian influences.
- Indian Classical Music: Two main schools: Hindustani Music (North India) and Carnatic Music (South India – Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala)
- Key Features of Hindustani Music: Based on Shudha Swara Saptaka (Octave of Natural Notes).
- Transmitted through the Guru-Shishya Parampara.
- Common instruments: Tabla, Sarangi, Sitar, Flute, Violin, Santoor.
- Ten primary vocal styles: Dhrupad, Khayal, Tappa, Chaturanga, Tarana, Sargam, Thumri, Ragasagar, Hori, Dhamar.
5. India’s First Private Helicopter Assembly Line: Recently, Tata Advanced Systems Limited announced
India’s first private helicopter assembly line in Karnataka to build Airbus H125, with delivery set for early 2027.
- Key Highlights: The first ‘Made in India’ H125 is expected by early 2027.
- Usage: Will serve civil and para-public markets.
- Will also meet Indian armed forces’ light multi-role helicopter needs, especially in Himalayan frontiers.
- Military Variant: Plans include an H125M military version, to be built with high levels of indigenised components and technologies.
- Exports: The helicopters will also be available for South Asian regional export.
- Significance: Airbus called India an “ideal helicopter country”, highlighting helicopters as a tool for nation-building.
- Second Airbus-Tata Plant: This is TASL’s second final assembly line with Airbus, after the C295 military aircraft facility in Vadodara.
- TASL Role: Tata Advanced Systems becomes the first private sector company in India to build helicopters, strengthening both civil and defence aerospace capacity.
6. Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses: Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the
Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses to boost production and ensure self-sufficiency.
- About Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses: Covers research, seed systems, area expansion, procurement, and price stability.
- Quality Seeds Focus: Develop and distribute high-yielding, pest-resistant, climate-resilient varieties.
- Multi-location trials in major pulse-growing states to ensure regional suitability.
- Seed Production System: States to prepare five-year rolling seed production plans.
- ICAR to oversee breeder seed production.
- Foundation and certified seeds to be produced by central and state agencies.
- Tracking via SATHI portal (Seed Authentication, Traceability & Holistic Inventory).
- Capacity Building: Structured training programmes for farmers and seed growers.
- Promotion of sustainable practices and modern technologies.
- Post-Harvest Infrastructure: Establishment of 1,000 processing units to reduce losses and improve value addition.
- Subsidy of up to ₹25 lakhs for setting up processing and packaging units.
- Farmer Safeguards: Mechanism to monitor global pulse prices to protect farmer confidence.
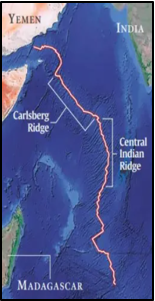
7. Polymetallic Sulphides: Recently, India secured its second exploration contract from the International Seabed Authority for
polymetallic sulphides in the Indian Ocean’s Carlsberg Ridge.
- ·About Polymetallic Sulphides: Mineral deposits formed near hydrothermal vents on ocean floors.
- Process: Seawater interacts with magma, releases hot mineral-rich fluids, deposits solids on seabed.
- Occurrence: Found along mid-ocean ridges at depths of 2,000–5,000 m.
- Composition: Rich in copper, zinc, lead, silver, gold, with traces of rare/precious metals.
- Applications: Electronics & high-tech industries (copper, rare metals).
- Green energy (zinc, silver for solar panels & batteries).
- Strategic use in aerospace, defence, and clean-tech manufacturing.
·
About Carlsberg Ridge: A
mid-ocean ridge system formed by
seafloor spreading.
- Location: Extends from the triple junction of African, Indian & Australian plates (near 2°N, 66°E) to the Gulf of Aden.
- Separates Arabian Sea (NE) from Somali Basin (SW).
8. Snow Leopard: Recently, Himachal Pradesh reported an increase in its
snow leopard population to 83, up from 51 in 2021, according to the
state’s Forest and Wildlife Wing.
- Key Highlights: Conducted across 26,000 sq. km of high-altitude habitats — Spiti Valley, Kinnaur, Pangi, Lahaul, and Great Himalayan National Park (GNHP).
- Methods Used: 271 camera traps
- 44 unique snow leopards detected 262 times.
- Estimated density: 16 to 0.53 leopards per 100 sq. km.
- Key Findings: Highest densities recorded in Spiti, Pin Valley, Upper Kinnaur, and Tabo. Many detections outside protected areas like Kibber WLS, GNHP, Sechu Tuan Nala WLS, Asrang WLS.
- New Discoveries: First official sighting of Pallas’s cat (Otocolobus manul) in Kinnaur.
- Rediscovery of woolly flying squirrel (Eupetaurus cinereus) in Lahaul.
- Significance: Himachal Pradesh is the first state in India to conduct a state-wide snow leopard population estimation. Provides a blueprint for other Himalayan states in snow leopard conservation.
9. Trichloroethylene (TCE): Recently, a study found that long-term outdoor exposure to
trichloroethylene (TCE) may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
- About Trichloroethylene: A volatile, colorless liquid organic chemical.
- Does not occur naturally; produced through chemical synthesis.
- Applications: Mainly used in making refrigerants and other hydrofluorocarbons.
- Serves as a degreasing solvent for metal equipment.
- Found in some household products: cleaning wipes, aerosol cleaners, tool cleaners, paint removers, spray adhesives, carpet cleaners, and spot removers.
- Used in commercial dry cleaning as a spot remover.
o
Pathways of Human Exposure: Present in
air, water, and soil at production or usage sites.
- Health Impacts: Prolonged exposure may lead to liver damage and increased risk of liver and kidney cancer.
- Has genotoxic and immunotoxic properties; may act as a teratogen.
- Studies link it to: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Reproductive and developmental toxicity (infertility in men & women, impaired fetal growth, cardiac teratogenesis).