23rd October 2025
1. GFRA 2025: Recently, India achieved a significant milestone in global environmental leadership by rising to the 9th position in total forest area worldwide, according to the
Global Forest Resources Assessment (GFRA).
- About GFRA: Released by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Bali.
- India’s Previous rank: 10th globally.
- Continues to rank 3rd in the world in annual forest area gain, showing sustained progress in afforestation and reforestation efforts.
- The Minister attributed the achievement to Government of India’s proactive forest protection and afforestation policies under the leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi.
- Initiatives such as “Ek Ped Ma Ke Naam” have encouraged mass public participation in tree planting and protection.
- Community-led environmental action and strong state-level plantation drives have contributed significantly to this success.
- The progress reflects India’s commitment to sustainable forest management, ecological balance, and climate resilience.
2. JAIMEX-25: Recently, the
Japan-India Maritime Exercise (JAIMEX-25) was conducted between the naval forces of India and Japan, with the Harbour Phase held at Yokosuka, Japan.
- Key Highlights: Participating Naval Units: India: INS Sahyadri – an indigenously built Shivalik-class Guided Missile Stealth Frigate.
- Japan: JMSDF ships Asahi, Oumi, and submarine Jinryu.
- Sea Phase Activities: Advanced Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) and missile defence drills.
- Flying operations and underway replenishment
- Aimed at enhancing interoperability and operational coordination.
- Harbour Phase Activities: Cross-deck visits, joint operational planning, and sharing of best practices.
- Cultural exchanges and a combined Yoga session to strengthen camaraderie.
- Strategic Significance: Reflects the deepening Special Strategic and Global Partnership between India and Japan, established in 2014.
- Reinforces shared commitment to a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- Highlights robust navy-to-navy cooperation promoting regional peace and stability.
3. Sinapic Acid: Recently, researchers at Nagaland University identified a naturally occurring plant compound,
Sinapic acid that can significantly accelerate wound healing under diabetic conditions.
- About Sinapic Acid: A natural phenolic acid and derivative of cinnamic acid.
- Properties: Exhibits antioxidant, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and neuroprotective
- Sources: Abundantly present in spices, citrus fruits, berries, vegetables, cereals, and oilseed crops.
- Mechanism of Action: Works by activating the SIRT1 pathway, which plays a vital role in tissue repair, angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and inflammation control.
- Significance: The finding represents a scientific breakthrough in treating diabetic wounds naturally and effectively.
- Diabetic wounds, commonly seen as foot ulcers, heal slowly due to nerve damage, poor circulation, and infections, often leading to severe complications or amputation.
- Sinapic acid offers a promising, non-toxic approach to promote faster recovery and restore skin health in diabetic patients.
4. NESTS: Recently, National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) showcased educational and cultural innovations by launching a GI-tagged painting album and academic diaries.
- Key Highlights: To showcase NESTS’ Knowledge Management, Capacity Building, Educational and Cultural Initiatives.
- Major Releases & Initiatives: Launch of GI-Tagged Tribal Painting Compilation and Academic Diaries for Teachers, Students, and Class Monitors.
- Release of “Canvas of Tribal Culture” — a GI-Tagged Painting Album celebrating tribal art forms.
- Teacher Diary: Promotes reflective teaching and professional growth.
- Student Diary: Encourages daily academic tracking, reflection, and discipline.
- Class Monitor Diary: Builds leadership, accountability, and teamwork.
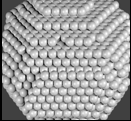
5. Atomic Stencilling: Recently, scientists from the US and South Korea developed a novel technique called
“atomic stencilling” to precisely design and pattern nanoparticles.
- Key Highlights: The idea was inspired by artistic stenciling, adapted to the nanoscale
- Core concept: Iodide atoms act as a microscopic stencil, selectively adhering to certain faces of gold nanoparticles.
- Polymers are then applied like paint, attaching only to unmasked regions.
- Result: Controlled creation of polymer “patches” on nanoparticles — allowing precise design of size, shape, and pattern.
- Scale: The method can create nanoparticles about 2 nanometres wide — thousands of times smaller than a human hair.
- Outcome: Over 20 types of patchy nanoparticles were produced, featuring corner, face, and web-like patch designs.
- Self-assembly achievement: These patchy nanoparticles spontaneously formed ordered 3D crystals (superlattices) — a long-sought goal in nanomaterials science.
- Applications: Metamaterials with properties not found in nature, Targeted drug delivery, Ultra-efficient catalysts, Next-generation electronics and smart materials.
6. 3D Sensors: Recently, the
National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) announced plans to deploy vehicles equipped with advanced
3D sensors and data acquisition systems across 23 States.
- Key Highlights: Coverage: Over 20,000 km of highways across 23 States, including two- to eight-lane projects.
- Objective: To identify potholes, cracks, and surface defects for timely corrective action and improved commuter experience.
- Technology & Method: Deployment of vehicles equipped with advanced sensors and data acquisition systems, including:
- 3D laser-based systems
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Inertial Measurement Devices (to measure acceleration and angular velocity)
- Data Storage & Analysis: Collected data will be uploaded to NHAI’s AI-based portal “Data Lake.”
- Additional Road Safety Efforts: NHAI identifying “black spots” (accident-prone areas) based on State-reported accident data.
- Electronic Detailed Accident Report (e-DAR) project: Serves as a central repository for recording and managing road accident data.
7. Kerala: Recently,
Kerala is set to achieve a historic milestone by officially declaring the
State free from extreme poverty at a public function at the Central Stadium in Thiruvananthapuram.
- Key Highlights: The extreme poverty eradication programme was launched in 2021, as one of the first decisions of the Left Democratic Front (LDF)
- According to NITI Aayog (2021), Kerala already had India’s lowest poverty rate — 0.7% of its population.
- The government aimed to reach and rehabilitate this remaining population through targeted interventions.
- Survey & Implementation: 64,006 families identified as extremely poor based on criteria such as food, health, livelihood, and shelter.
- Outcome: Out of 64,006 families, 59,277 have been successfully uplifted from extreme poverty.
- Governance & Monitoring: Integration of all existing welfare schemes and creation of special programmes ensured coverage.
- Geo-tagging of beneficiaries’ houses and completion of a social audit ensured transparency.
8. Sevilla Forum: Recently, a new international initiative — the
Sevilla Forum on Debt — was officially launched at the 16th United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD16) in Geneva.
- About Sevilla Forum: It is a Spanish-led initiative, supported by UNCTAD and the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA).
- The Forum provides an inclusive platform for dialogue and action on global sovereign debt reform.
- Purpose & Goals: To sustain political attention on commitments made in Sevilla, and to develop technical pathways for responsible borrowing and lending.
- Aims to reform the global debt architecture and translate commitments into institutional mechanisms for fairer debt governance.
- Forms part of the Sevilla Platform for Action and complements the Sevilla Commitment, which provides a roadmap for development financing and debt sustainability.
- Global Debt Context: As of 2024, global public debt reached $102 trillion.
- Significance: The Forum strengthens multilateral cooperation and aligns financial reform with development goals.
- Seeks to build a fairer, more development-oriented international debt system, reducing burdens on vulnerable economies.
9. SoGA 2025 Report: Recently, the
State of Global Air (SoGA) 2025 report warned that air pollution has become a major threat to brain health and a leading cause of chronic disease and early death in India.
- Key findings: India’s Health Impact: 2 million deaths in 2023 linked to air pollution-related diseases — a 43% rise from 1.4 million in 2000.
- Nearly 9 out of 10 deaths (89%) are due to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) — heart disease, lung cancer, diabetes, and dementia.
- Most affected States: Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, and West Bengal — each with over 100,000 deaths in 2023.
- 75% of India’s population lives in areas exceeding WHO’s PM2.5 target (35 µg/m³).
- Deaths from household air pollution are declining, but ambient PM2.5 and ozone-related deaths have increased.
- Firm evidence now shows air pollution as a major risk factor for dementia.
- Globally: 626,000 dementia deaths and 40 million healthy years of life lost in 2023.
- In India: Over 54,000 dementia deaths (2024) linked to pollution exposure.
10. ChatGPT Atlas: OpenAI unveiled
ChatGPT Atlas, an
AI-powered web browser built around its popular chatbot, marking a
direct challenge to Google Chrome.
- About ChatGPT Atlas: Aims to transform web browsing through AI-driven interaction, data synthesis, and task automation, potentially reshaping the future of search and information access.
- Key Features: AI Sidebar: Users can open a ChatGPT-powered sidebar to summarize webpages, compare products, and analyze data directly from any site.
- Agent Mode: (For paid users) ChatGPT can interact with websites autonomously — performing end-to-end tasks like shopping, trip planning, or research.
- Availability: Now live on Apple macOS; versions for Windows, iOS, and Android coming soon.