11th September 2025
1. First Overseas Atal Innovation Centre: Recently, India’s
first overseas Atal Innovation Centre was inaugurated at the
IIT Delhi–Abu Dhabi campus during the Union Education Minister’s visit to the UAE.
- About First Overseas Atal Innovation Centre: The first international innovation hub established under the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM).
- Purpose: Encourage innovation, research, and entrepreneurship among students and young professionals.
- Strengthen India–UAE cooperation in education, sustainability, and technology solutions.
- Key Roles: Support and incubate start-ups with mentorship and resources.
- Provide state-of-the-art labs and infrastructure for advanced research.
- Facilitate student exchanges, teacher training, and skill-development programmes.
- Serve as a platform for global collaboration and innovation networking.
- About Atal Innovation Mission: A national flagship programme of the Government of India to foster a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Nodal Agency: Implemented by NITI Aayog.
- Goal: Build an innovation-driven ecosystem spanning schools, universities, research institutions, and industries.
2. Adi Sanskriti: Recently, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs launched the Beta Version of “
Adi Sanskriti,” bringing together tradition and technology.
- About Adi Sanskriti: A first-of-its-kind digital learning platform designed to preserve, promote, and empower India’s tribal artforms and communities.
- Vision: Envisioned as the world’s first Digital University for tribal culture, knowledge, and livelihoods.
- Components: Adi Vishwavidyalaya (Digital Tribal Art Academy): 45 immersive courses on dance, painting, crafts, music, and folklore.
- Adi Sampada (Socio-Cultural Repository): Over 5,000 curated documents on paintings, dance, clothing & textiles, artefacts, and livelihood.
- Adi Haat (Online Marketplace): Linked with TRIFED; evolving into a dedicated marketplace for tribal artisans.
- Partnership: Built with State Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs) from 15 states including Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Meghalaya, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Earlier Initiative Link: Follows the launch of Adi Vaani, an AI-based translator for tribal languages.
3. Regional Testing Laboratory: Recently, the state-of-the-art
Regional Testing Laboratory (RTL) of the Central Power Research Institute (CPRI) was inaugurated at Nashik to strengthen India’s power sector.
- About RTL: Testing and certification of electrical and power equipment including:
- Transformers
- Energy Meters
- Smart Meters
- Transformer Oil
- Benefits: Reduces turnaround time for testing and certification.
- Strengthens quality assurance ecosystem.
- Facilitates faster procurement cycles for utilities.
- Significance: RTL Nashik will serve industry needs while also boosting research and development in power sector equipment testing.
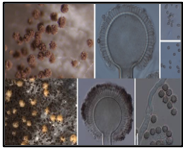
4. New Species of Aspergillus section Nigri: Recently, researchers from
MACS-ARI Pune discovered two new fungal species of
Aspergillus section Nigri, namely
Aspergillus dhakephalkarii and
Aspergillus patriciawiltshireae, in the Western Ghats.
- About Aspergillus Section Nigri: A group of black-coloured fungi, commonly called black aspergilli.
- Widely present in soil and plants.
- Play a major role in citric acid production, the food industry, fermentation, and agriculture.
- Often referred to as the “workhorses of biotechnology” because of their wide industrial applications.
- About Aspergillus dhakephalkarii : Rapidly growing species.
-
- Produces brown spores and orange sclerotia (resting structures).
- Characterised by smooth, oval-shaped spores, unlike many related species with rough, spiny spores.
- About Aspergillus patriciawiltshireae: Also a fast-growing species with abundant sclerotia.
- Shows modest spore production.
- Features spiny spores and branching conidiophores that split into multiple columns.
- First Indian Records: aculeatinus and A. brunneoviolaceus were reported for the first time in India. Confirms that the Western Ghats are a hotspot of hidden fungal diversity.
5. Gyan Bharatam: Recently, the Ministry of Culture announced the launch of ‘
Gyan Bharatam’, which will be marked by the first-ever Gyan Bharatam International Conference on ‘Reclaiming India’s Knowledge Legacy through Manuscript Heritage’.
- About Gyan Bharatam: A landmark national initiative for preserving, digitising, and disseminating India’s manuscript heritage.
- Objectives: Nationwide identification and documentation of manuscripts.
- Conservation and restoration of fragile texts.
- Large-scale digitisation using AI-driven tools.
- Creation of a National Digital Repository.
- Research, translation, and publication of rare manuscripts.
- Capacity building for scholars and conservators.
- Development of digital platforms for accessibility.
- Public participation via collaborative programmes.
- Global partnerships and integration of manuscript wisdom into education.
- Implementation: Through a broad alliance of libraries, religious institutions, and private custodians.
6. Melioidosis: Recently, a case of
melioidosis was confirmed by health authorities in a patient from Turakapalem village, Andhra Pradesh.
- About Melioidosis: An infectious disease caused by the environmental Gram-negative bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei.
- Seasonality: The disease shows a seasonal pattern, with about 75–85% of cases reported during the rainy season.
- Fatality: It carries a high case fatality rate (CFR), ranging between 16% and 50% in endemic areas.
- Geographic Distribution: Endemic in Southeast Asia, northern Australia, much of the Indian subcontinent, southern China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan.
- Risk Groups: More common among individuals with diabetes, alcohol use disorder, chronic kidney disease, or chronic lung conditions (such as cystic fibrosis or COPD).
- Symptoms: May include fever, headache, breathing difficulties, abdominal or chest pain, and other flu-like signs.
- No vaccine is currently available against melioidosis.
7. Swachh Vayu Survekshan: Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change conducted the
Swachh Vayu Survekshan under the
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
- Million-Plus Population Cities: Indore ranked 1st, followed by Jabalpur (2nd) and Agra/Surat (3rd).
- Top 10 Rankings: Navi Mumbai (4), Kanpur (5), Bhopal (6), Allahabad (7), Chandigarh (8), Ahmedabad/Pune/Nagpur (10).
- Cities with 3–10 Lakh Population: Amravati (1), Jhansi & Moradabad (joint 2nd), Alwar (3rd).
- Cities with Population under 3 Lakh: Dewas (Madhya Pradesh) ranked 1st.
- Parwanoo (Himachal Pradesh) 2nd, Angul (Odisha)
- PM10 Decline: Out of 130 NCAP cities, 103 cities recorded a decline in PM10 levels.
- Metro Performance: Mumbai achieved the highest reduction (44%) in PM10 (2024–25 vs 2017–18).
- NAAQS Achievement: 22 cities met the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for PM10 (<60 µg/m³).Chennai was the only major metro to meet the limit, with an annual average of 58 µg/m³.
8. Decentralised Finance (DeFi): Recently, the boom in
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) has raised national security concerns, with experts warning about its potential misuse for terror financing and money laundering.
- About DeFi: A blockchain-based financial system that enables saving, borrowing, investing, and transacting without traditional banks or intermediaries.
- Technology Base: Operates through smart contracts, decentralised applications (DApps), and peer-to-peer networks.
- Origin: Inspired by the Bitcoin (2009) philosophy of decentralisation and transparency.
- Objectives: Democratising finance by eliminating intermediaries. Offering inclusive, low-cost, borderless financial services to anyone with internet access.
- Risks: Susceptible to hacking, fraud, money laundering, and terror financing due to anonymity and lack of regulation.
9. Huangyan Island: Recently,
China declared the creation of a national nature reserve on
Huangyan Island (Scarborough Shoal) in the South China Sea.
- About Huangyan Island: A coral atoll under dispute in the South China Sea.
- Known by different names: Scarborough Shoal (English), Huangyan Island (China), and Panatag Shoal (Philippines).
- Geography: Located about 220 km west of Luzon (Philippines), close to the Manila Trench.
- Historical Context: Included under the Treaty of Washington (1900). The name “Scarborough” comes from a British ship that ran aground in 1748.
- Current Dispute: Claimed by China, Taiwan, and the Philippines.
- Important for fisheries, energy resources, and military positioning.
10. Bonda Tribe: Recently, the Governor of Odisha stressed the need for comprehensive development in
Bondaghati, home to the Bonda tribe, a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- About the Bonda Tribe: Found only in Malkangiri district, Odisha, mainly concentrated in the Khairaput block.
- One of the oldest tribes in India and listed as a PVTG.
- Also known as Bondo, Bondas, Bonda Paraja, and Bhonda.
- Believed to be among the earliest settlers in India, tracing their roots to the Austroasiatic race.
- Language: Speak Remo, part of the Austroasiatic language family.
- Religion: Animistic, centered on nature worship and ancestral spirits.
- Occupation: Depend on subsistence agriculture, hunting, and gathering.