30th August 2025
1. Achook Prahar: Recently, the drill named
Achook Prahar was carried out under simulated battlefield conditions to evaluate and strengthen operational readiness.
- About Achook Prahar: The exercise aimed to validate combat readiness under high-altitude and difficult terrain conditions.
o Soldiers tested a variety of weapons, including mortars, machine guns, rockets, and grenades.
o Focus was on assessing accuracy, battlefield effectiveness, and coordinated response capabilities.
o Enhancing Interoperability between Forces: Demonstrated strong coordination between the Indian Army and ITBP. The drill ensured seamless operational cooperation in high-altitude environments along the northeastern borders.
- Strategic Significance: Joint exercises like Achook Prahar strengthen India’s border defence capabilities. They help maintain a robust security posture along sensitive frontiers with China.
- The drills enhance readiness to respond swiftly to threats in challenging mountainous terrain.
2. Crocothemis Erythraea: Recently, odonatologists have reconfirmed the presence of the rare dragonfly species
Crocothemis erythraea in the high-elevation areas of the southern Western Ghats.
o Earlier, this species was frequently misidentified or overlooked because of its close resemblance to the more common lowland species,
Crocothemis servilia.
- About Crocothemis erythraea: Its common names include broad scarlet, common scarlet-darter, and scarlet darter.
o India hosts two Crocothemis species: servilia: Common in lowland areas (<600 m) and C. erythraea: Restricted to high-elevation habitats (>550 m)
o Findings: High-elevation specimens matched erythraea from the Himalayas
- C. servilia confirmed in lowland areas of both southern India and the Himalayas
o Ecological Insight: erythraea inhabits cool montane habitats like Sholas and grasslands, surviving in isolation.
o Significance: The confirmation of C. erythraea in the Western Ghats highlights the region’s ecological importance as a refuge for high-altitude and temperate species.
3. Nanjangud Rasabale Banana: Recently, the Union Minister for Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare stated that the Indian Council for Agricultural Research (ICAR) plans to start a research initiative focused on protecting the
Nanjangud Rasabale banana from various diseases.
- About Nanjangud Rasabale Banana: Grown primarily in the Mysore and Chamarajanagar districts of Karnataka.
- GI Tag: Received a Geographical Indication (GI) in 2006 for its thick pulp, unique taste, and distinct aroma.
- Soil Requirement: Thrives in black clay alluvial saline soil, which contributes to its special aroma.
- Medicinal Value: Believed to have neurological health benefits.
- Threats: Vulnerable to Panama Wilt disease, a fungal infection caused by theFusarium Wilt pathogen, which poses a major challenge to farmers.
4. Coal and Energy Transition: Recently, a report by
Carbon Brief, using data from the Global Coal Plant Tracker, revealed that China and India together accounted for
nearly 87–88% of the world’s proposed coal power projects in the first half of 2025.
- China’s Coal Expansion: Added 21 GW of new coal capacity in six months—the highest in almost a decade.
- Proposed
7 GW of new coal capacity in H1 2025.
- Many new plants serve as
standby capacity, running only during peak demand.
- Coal use growth limited due to rapid expansion of
renewables; CO₂ emissions fell ~1% in H1 2025.
- India’s Dual Strategy: Commissioned 1 GW of new coal plants in H1 2025; 92 GW in proposals.
- Renewable energy capacity surpassed 220 GW by March 2025, aiming for 500 GW by 2030.
- Coal still provides ~70% of electricity, making India reliant on a “dual track” of coal + renewables.
- Coal plant retirements remain slow; only 8 GW shut down in 2025.
- Coal expansion in China and India driven by energy security, baseload needs, and industrial growth, not just carbon emissions.
- Decisions by China and India in the next decade will significantly influence global emissions trajectories.
5. Daruma Doll: Recently, during a two-day visit to Japan aimed at strengthening civilisational and cultural ties, the Indian Prime Minister was presented with a traditional
Daruma doll.
- About Daruma Doll: Traditional Japanese wish doll, typically made of papier-mâché, with a rounded bottom allowing it to pop back up when tipped.

- Symbolism: Represents perseverance, good luck, and goal achievement.
- Usage Tradition: One eye coloured when setting a goal.
- Second eye coloured once the goal is achieved, symbolising not giving up.
- Inspired by the saying: “Fall seven times, stand up eight.”
- Origin & Inspiration: Modeled after Bodhidharma, a 5th-century Indian monk from Kancheepuram (Daruma Daishi in Japan).
- Shape Significance: Rounded shape, no limbs, and blank eyes reflect Bodhidharma’s nine-year meditation in China after travelling from India.
- Name Meaning: “Daruma” derives from the Sanskrit word Dharma, meaning cosmic law or duty, with no direct Japanese or Chinese equivalent.
6. SPNIWCD: Recently,
the Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development (SPNIWCD) launched its official website. This marks a significant step toward the digitalisation of training and improved access to resources.
- Key Features: The SPNIWCD website offers a wide array of features aimed at enhancing accessibility, transparency, and user experience:
- E-Learning Modules: Enables users to enhance their skills and knowledge at their own pace.
- E-Archive and Digital Library: Provides secure storage, quick retrieval, and easy access to research materials and important documents.
- Real-Time Dashboard: Live updates on training programmes, schemes, and institutional activities.
- Online Registration & Appointment System: Simplifies access to services including Child Guidance Centre (CGC), Advanced Diploma in Child Guidance and Counselling (AGSC), National Communal Harmony, and NCF.
- Interactive Feedback Mechanism: Captures user suggestions for continuous improvement.
- Resource Repository: Comprehensive coverage of Mission Shakti, Mission Vatsalya, Mission Saksham Anganwadi, Poshan 2.0, and sections on child protection, women empowerment, safety, nutrition, and statistical data.
- User-Friendly Design: Ensures seamless navigation for all users.
7. SCOPE Eminence Awards: Recently, the President of India presented the
SCOPE Eminence Awards for 2022–23, recognizing the exceptional contributions of Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs) to the country’s socio-economic development. The awards ceremony took place in New Delhi.
- About SCOPE Eminence Awards: Recognises the significant contributions of Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs) across social, economic, environmental, technological, and ethical dimensions.
- Holistic Development: Awards highlight achievements in sustainable development, corporate governance, corporate social responsibility, and innovation.
- Role of Public Sector: Since independence, PSEs have been key drivers of industrialisation, infrastructure, social upliftment, and regional development.
- Support to National Campaigns: CPSEs contribute to initiatives like Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India; e.g., Akashteer Air Defence System developed during Operation Sindoor.
- Technological and Self-Reliance Contributions: PSEs aid in national security, technological self-reliance, and sectors like agriculture, mining, manufacturing, processing, and services.
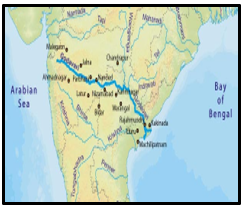
8. Godavari River: Recently, the
Godavari river at Bhadrachalam crossed the first flood warning level of 43 feet, reaching 43.90 feet. It was carrying 9.71 lakh cusecs of floodwater downstream.
- About Godavari River: India’s second-longest river after the Ganga and the third-largest by basin area, draining about 10% of India’s total geographical area. Also known as Dakshina Ganga or South Ganges River.
- Origin: Brahmagiri Mountain at Trimbakeshwar, Nashik district, Maharashtra.
- Length: Approximately 1,465 km.
- Mouth: Empties into the Bay of Bengal at Narasapuram, West Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh.
- States and Basin: Mainstem Flows Through: Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh.
- Basin Extends Into: Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, parts of Chhattisgarh and Odisha.
- Basin Area: Around 121,000 sq mi (313,000 sq km).
- Boundaries: North – Satmala hills, Ajanta range, Mahadeo hills; South & East – Eastern Ghats; West – Western Ghats.
- Rainfall: Receives maximum rainfall during the Southwest monsoon.
- Major tributaries include: Pravara, Purna, Manjra, Penganga, Wardha, Wainganga, Pranhita (combined flow of Wainganga, Penganga, Wardha), Indravati, Maner, Sabri.
9. Study on Global Warming Impact on Aircraft Turbulence: Recently, a study by researchers at the
University of Reading,
UK, found that ongoing global warming could increase turbulence at typical aircraft cruising altitudes, making the atmosphere less stable and raising risks to aviation safety.
- Key Findings: Wind Shear Increase: Jet stream wind shear projected to rise by 16–27% between 2015 and 2100.
- Reduced Stability: Atmospheric stability expected to decline by 10–20%, affecting both hemispheres.
- Clear-Air Turbulence (CAT): Increased wind shear and lower stability favor the occurrence of CAT, which is invisible on radar and difficult for pilots to predict.
- Impact on Aviation: Greater turbulence could lead to: Longer periods with seatbelt signs on
- Suspension of cabin service more frequently
- Increased risk of passenger injuries and fatalities
- Need for Technology: Airlines may require new detection systems to spot turbulence in advance.
10. LUPEX Mission: Recently, the Prime Minister of India welcomed the agreement between ISRO and JAXA for the Chandrayaan-5 mission under the
Lunar Polar Exploration (LUPEX) programme.
- About LUPEX Mission: Jointly developed by ISRO and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
- Objective: Explore the Moon’s southern polar region, focusing on the presence of water and other elements, potentially as surface ice.
- Technological Focus: Showcase innovative surface exploration technologies, with emphasis on vehicular transport and survival during lunar night.
- Mission Components: Features both a lander (developed and operated by ISRO) and a rover (developed and operated by JAXA).
- International Participation: The rover will also carry instruments from NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), alongside ISRO and JAXA instruments.