Explore how trade transformed into territorial conquest during the British Conquest of India and wider European expansion in South India. Understand key policies like the Doctrine of Lapse and how the spice trade, strategic ports, and political rivalries shaped colonial dominance in South India.

The British conquest of India marks a pivotal period in Indian history, characterized by the gradual expansion of British influence and control over Indian territories from the early 17th century until independence in 1947.
|
ASPECTS |
ACCIDENTAL |
INCIDENTAL |
|
Initial Arrival |
For trade purposes, with no initial intent for conquest. |
Arrived for trade, incidentally engaged in territorial conflicts. |
|
Early Actions |
Drawn into conflicts by the chaotic Indian political landscape. |
Involvement in politics grew as a byproduct of trade interests. |
|
Nature of East India Company |
Politically neutral, no initial expansion plans. |
Initially neutral, later their involvement in politics grew incidentally. |
|
Motivation |
Reluctant acquisition to secure commercial interests. |
Expansion was a byproduct of securing and promoting trade. |
|
Wars and Conflicts |
Engaged reluctantly to protect trade. |
Conflicts arose incidentally from involvement in local politics. |
|
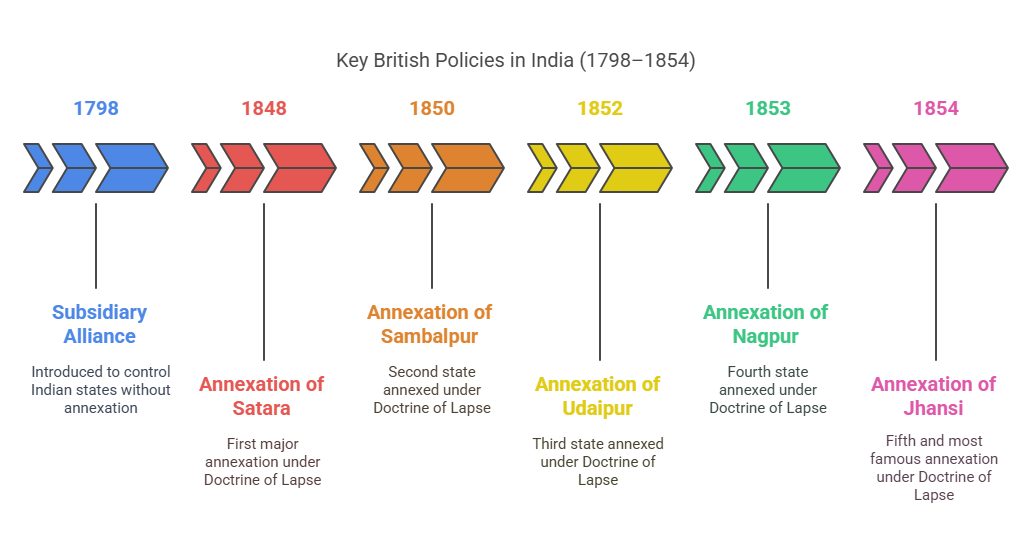
Imperial Policies (1798-1818) |
Reacting to external threats like France and Russia. |
Expansionist policies developed from geopolitical needs. |
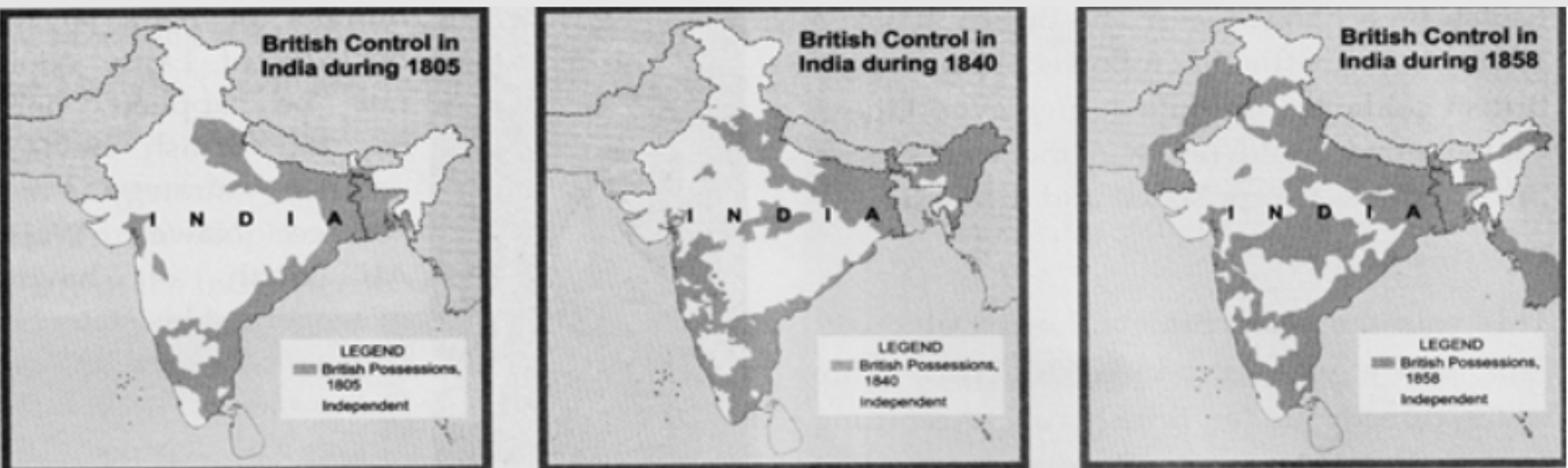
The strategic location, rich spice trade, and minimal Mughal influence made South India a prime target for European Expansion in South India, as European powers sought trade dominance and colonial expansion. Among these powers, the British played a leading role through the British Conquest of India, which gradually extended their control from trading posts to full colonial rule across the subcontinent, including key regions in the south.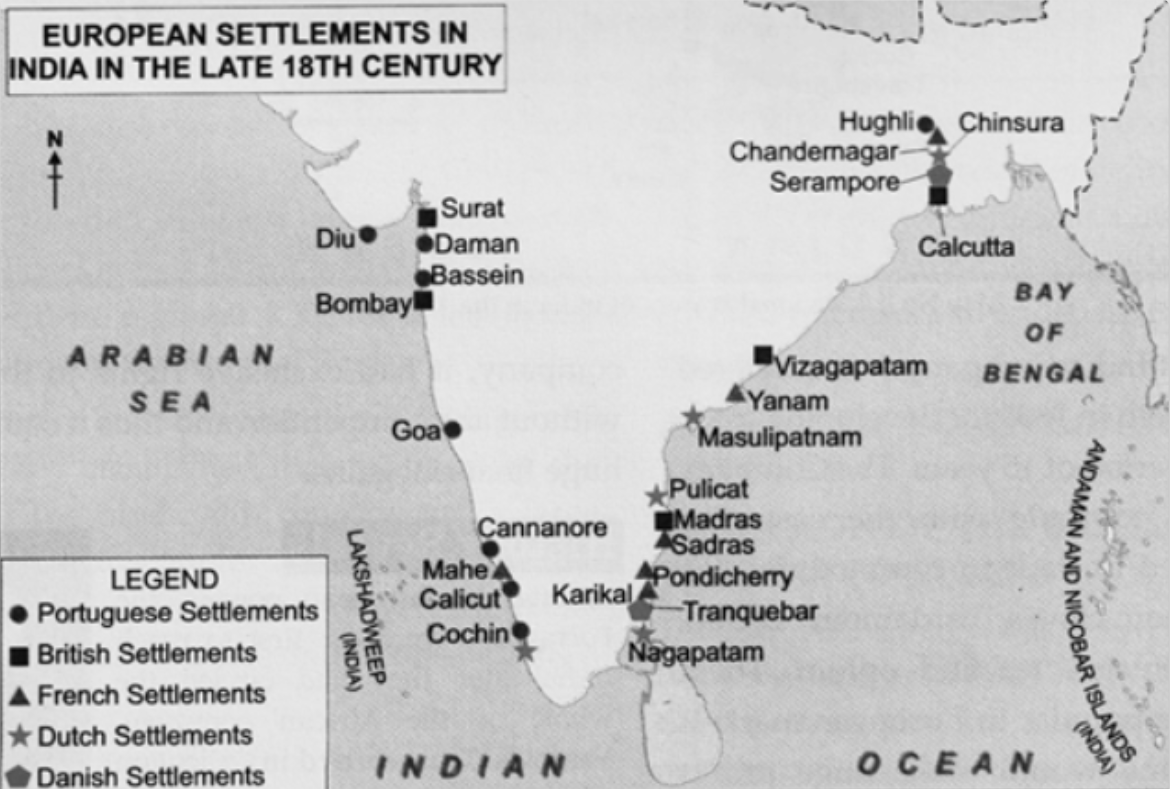
Among these powers, the British eventually played the dominant role through the British Conquest of India, transitioning from trade to territorial control, especially in South India.
|
KEY FACTS
|
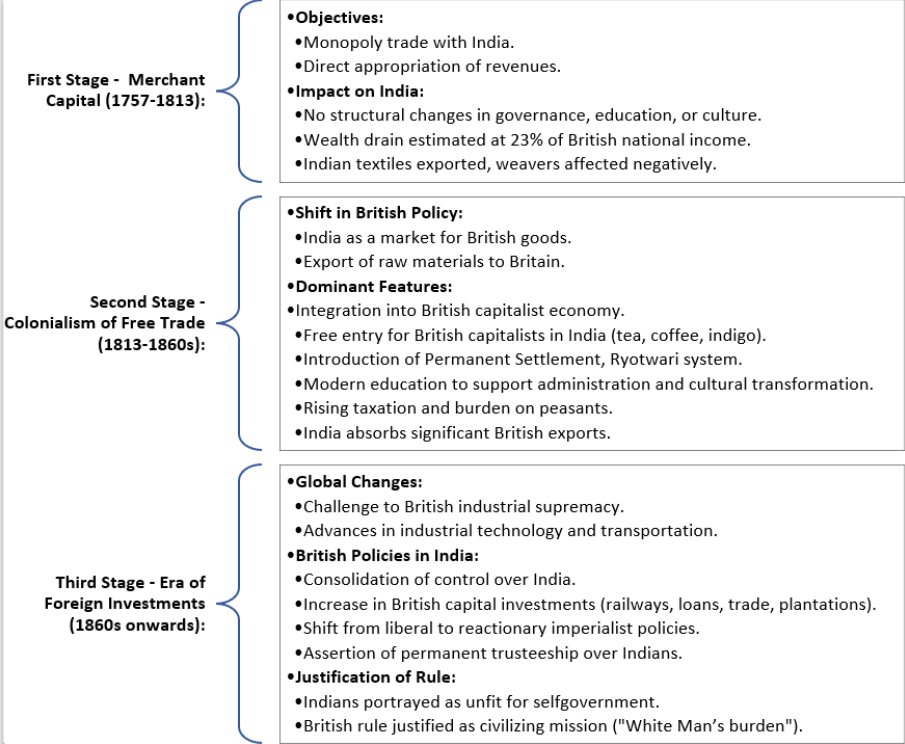
Each stage reflects a distinct phase of British economic strategy in India, marked by changing objectives, policies, and their impact on Indian society and economy.
Objectives
Impact on India


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.