Discover the causes, key leaders, and impact of the Revolt of 1857, a crucial chapter in India’s fight for independence. Learn about the political, economic, and socio-religious factors that led to the uprising, along with the courage of leaders like Rani Laxmibai, Nana Saheb, and General Bakht Khan.

The Revolt of 1857, also known as the First War of Indian Independence, was a widespread uprising against the British East India Company's rule in India. It was a watershed moment in Indian history. It emerged as a spontaneous uprising against various grievances and injustices inflicted by the British East India Company.
|
Interesting Facts:
|
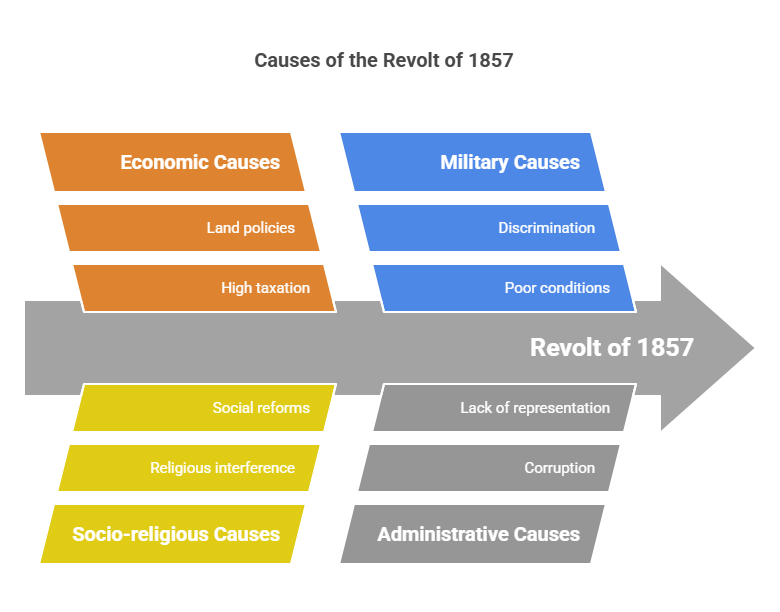
The Revolt of 1857 was driven by political annexations, economic exploitation, socio-religious discontent, military grievances, and administrative misrule by the British.
|
Interesting Facts: Doctrine of Lapse:
|
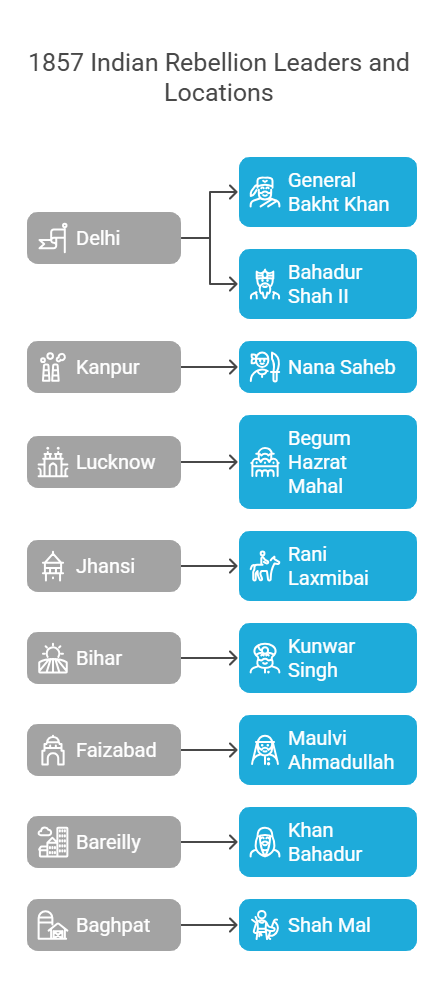
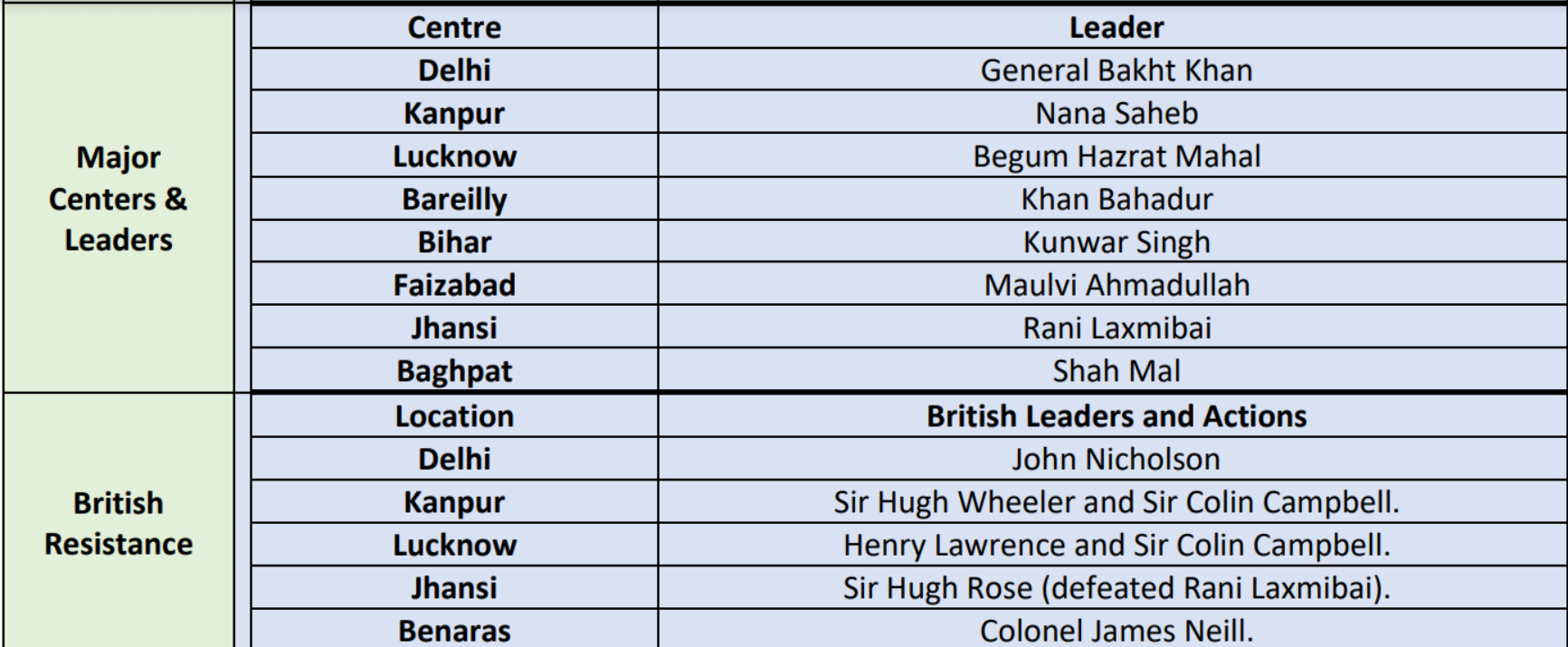
The Revolt of 1857, or India's First War of Independence, saw bitter opposition in most major centers of revolt of 1857 in North India. Indian leaders like General Bakht Khan at Delhi, Nana Saheb at Kanpur, and Rani Laxmibai at Jhansi led the resistance against British domination. But the British, led by officers such as John Nicholson, Sir Colin Campbell, and Sir Hugh Rose, made harsh counterattacks to quell the rebellion. The Delhi, Kanpur, Lucknow, and Jhansi battles are still key milestones in India's fight for independence.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !






Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.