Explore key issues faced by Scheduled Castes in India, including caste discrimination, poverty, and violence. Learn about major government initiatives for their socio-economic upliftment, education, employment, and legal protection.


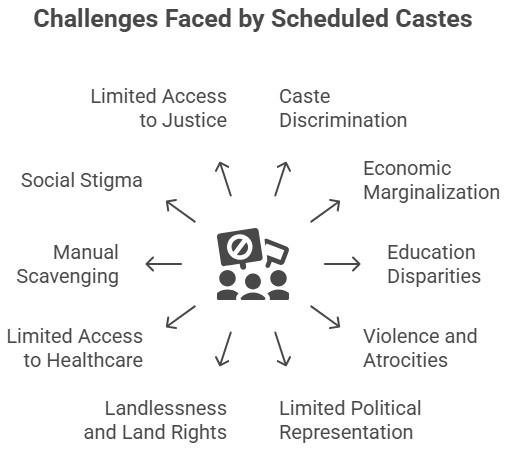
Scheduled Castes (SCs), historically marginalized under India's rigid caste system, continue to face deep-rooted social and economic challenges. Despite constitutional safeguards, issues like discrimination, poverty, and limited access to education and justice persist.
|
Initiative |
Objective |
|
Educational |
|
|
Upgradation of Merit of SC Students |
Provide facilities for education in residential/non-residential schools for SC students |
|
Dr Ambedkar Foundation |
Promote Dr Ambedkar's ideology and administer schemes emerging from Centenary Celebration |
|
Post Matric Scholarship for Scheduled Caste Students (PMS-SC) |
Empower SC students through education as the largest intervention by the central government |
|
Pre-Matric Scholarships to SC students |
Support parents of SC children in educating their wards to minimize dropouts |
|
Dr Ambedkar National Centre at Janpath |
Establish a world-class library and e-learning centre |
|
Scholarships for higher education and coaching |
Multiple schemes for SC students, including fellowships and overseas study |
|
Social |
|
|
The Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955 |
Enacted to prevent untouchability and promote civil rights |
|
SC and ST (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 |
Provide financial assistance to states/UTs for implementing these acts |
|
Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 |
Promote eradication of dry latrines, manual scavenging, and rehabilitation of manual scavengers |
|
Economic |
|
|
National Scheduled Castes Finance and Development Corporation (NSFDC) |
Finance income-generating activities of SCs below the poverty line limits |
|
National Safai Karmachari Finance and Development Council (NSKFDC) |
Provide credit facilities to Safai Karmacharis, manual scavengers, and their dependents |
|
Babu Jagjivan Ram Chatrawas Yojana |
Construction of hostels for SC students under the PM Anusuchit Jati Abhyuday Yojana |
|
Self-employment scheme for Rehab of Manual Scavengers |
Support self-employment opportunities for rehabilitating manual scavengers |
|
Credit Enhancement Guarantee Scheme for SC |
Provide credit guarantee facility to young and start-up entrepreneurs belonging to the SC community |
|
PM-DAKSH |
Provide long and short-term skills training to target youth |
|
PM AJAY |
Merger of centrally sponsored schemes: Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP) and Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY) |
Addressing the issues requires a multi-dimensional approach, including effective law enforcement, intelligence gathering, community engagement, socio-economic development, political stability, diplomatic efforts, and international cooperation in combating transnational threats.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.