India's Fintech sector has experienced rapid growth over the past decade and is currently at the forefront of the Fintech Revolution. The traditional cash-dependent Indian economy has undergone a significant transformation due to the convenience and efficiency of digital services.
What are Fintechs?
- Fintech is a combination of "financial technology" and refers to new technologies that aim to enhance and automate the delivery and use of financial services.
- At its core, fintech utilizes specialized software and algorithms to assist companies, business owners, and consumers in managing their financial operations and processes more effectively.
Key Fintech Products
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): DPI refers to digital solutions that facilitate essential functions such as collaboration, commerce, and governance, which are crucial for public and private service delivery.
- Digital Public Goods (DPGs): DPGs encompass open-source software, open data, open AI models, open standards, and open content that adhere to privacy and best practices.
Current State of the Fintech Sector in India
- Rapid Growth and Valuation of India's Fintech Market: India is one of the fastest-growing fintech markets globally, with a valuation of 50-60 billion USD in FY20, expected to reach 150 billion USD by 2025.
- Increasing Number of Fintech Companies in India: The number of fintech companies in India has surpassed 2,100, with over 67% established in the last five years alone.
- Diverse Sub-Segments in India's Fintech Sector: The sector comprises various sub-segments, including payments, lending, WealthTech, personal finance management, InsurTech, RegTech, and more.
- Shift in Investment Focus within the Fintech Sector: Initially, the majority of investment inflow in the fintech sector focused on payments and alternative finance. However, there is now a more equitable distribution of investments across other segments, such as InsurTech and RegTech.
- Significant Growth in Digital Payments Segment: The digital payments segment has experienced significant growth, with monthly transaction volumes exceeding 5.7 billion and a value of around 2 trillion USD in 2021.
- India's Leadership in Digital Payment Adoption: India leads in real-time online transactions, surpassing the combined numbers of the USA, UK, and China, making it a global leader in digital payment adoption.
- Widely Accepted Fintech Services in India: Fintech services such as mobile banking, mobile wallets, paperless lending, and secure payment
|
Significance of Fintech in India
- Enabling Financial Inclusion
- Fintech has reached under-banked and unserved segments, where traditional banks struggled to penetrate.
- Increased transparency through adaptable, multilingual options and a robust interface has expanded the consumer base.
- Reduced friction between financial institutions and retail customers.
- Attracting Capital Flows
- Fintech has drawn capital flows into the Indian economy.
- Bridging Gender and Accessibility Gap
- Fintech has addressed challenges faced by women during the pandemic, such as mobility restrictions and loss of employment.
- The ease of signing up, making transactions, and obtaining credit offered by fintech services has resonated with women.
- Fintech Unicorn and Soonicorn Valuations
- The Indian market has witnessed a rise in fintech unicorn and soonicorn valuations.
- This is attributed to the regulatory sandbox regime introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 2019, paving the way towards a $5 trillion economy.

Government Initiatives Driving Fintech Growth
- Jan Dhan Yojana
- It has facilitated financial inclusion with over 450 million beneficiaries gaining access to various financial services.
- Fintech players have leveraged this initiative to develop technology products for the large consumer base in India.
- India Stack
- India Stack, a collection of APIs, has empowered governments, businesses, startups, and developers to address India's challenges through digital solutions.
- The India Stack has been a catalyst for the rapid evolution of fintech in India.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- UPI, a mobile app-based payment system, enables fund transfers between bank accounts.
- Digital Rupee
- India recently introduced the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), known as the digital rupee or e-rupee.
- The digital rupee, an electronic version of cash, is expected to accelerate the growth of the fintech market in India.
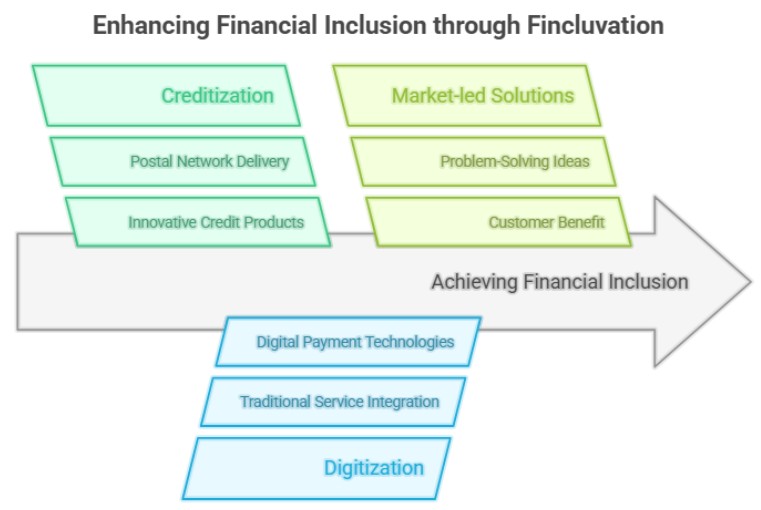
India Post Payments Bank Launches 'Fincluvation'
- India Post Payments Bank (IPPB), a government-owned entity under the Department of Posts (DoP), has introduced Fincluvation, a collaborative initiative with the Fintech Startup community.
- Aim: To co-create and innovate financial inclusion solutions.
- Startups are encouraged to develop solutions aligned with the following tracks:
- Creditization: Create innovative and inclusive credit products that cater to the needs of target customers and deliver them through the Postal network.
- Digitization: Enhance convenience by merging traditional services with Digital Payment Technologies. For example, transforming the traditional Money Order service into an Interoperable Banking service.
- Market-led Solutions: Propose problem-solving ideas related to IPPB and/or DoP, benefiting the target customers.
Associated Challenges
- Cyber-Attacks:
- Recent incidents of hacks targeting debit card companies and banks highlight the ease with which hackers can access systems and cause irreparable harm.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Consumers are primarily concerned about the responsibility for cyber-attacks and the misuse of personal and financial information.
- Regulatory Difficulties: Regulation poses challenges in the emerging realm of FinTech, particularly in relation to cryptocurrencies.
Regulating Fintech: Finding the Right Approach
- To address these risks, regulators have begun examining the operations of fintech firms and implementing supervisory measures.
Steps Taken by India for Fintech Regulation
India has implemented following measures to regulate fintech activities:
- Zero-MDR Guidelines: These guidelines aim to promote small ticket debit card merchant transactions.
- Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) Criticism: The Reserve Bank of India's decision to prohibit prepaid instruments with credit lines related to BNPL has faced criticism for potentially hindering fintech growth and innovation.
- Cryptocurrency Transactions: The RBI's strict stance on cryptocurrency transactions has also drawn criticism from fintech firms. X.
Way Forward
- Guarding Against Cybercriminals: Strict law and monitoring tools to be brought
- Educating Consumers: Consumer awareness regarding using of Apps, software to be raised
- Data Protection Law: Thorough debate and deliberation are necessary for the passage of the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019
- Increase in Domestic capability: Further increase in manufacturing and software development within India boost Fintech development
Conclusion
While the Indian fintech sector holds immense growth potential and promises to bring about positive changes in the economy, it is crucial to approach its expansion with caution. The accompanying regulatory challenges must be acknowledged and addressed effectively to ensure a secure and sustainable fintech ecosystem.