Learn about Article 32 of the Indian Constitution, which ensures the right to constitutional remedies. Understand writ jurisdiction, PIL, Supreme Court rulings, and its significance in protecting fundamental rights.


Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) of the Indian Constitution provides a powerful mechanism for enforcing fundamental rights, ensuring that citizens can seek legal remedies if their rights are violated. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar famously called the Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) the "heart and soul" of the Constitution, as it guarantees the right to move the Supreme Court for fundamental rights protection. This article delves into the significance of Article 32, its role in issuing writs, its application during emergencies, and its impact on Public Interest Litigation (PIL).
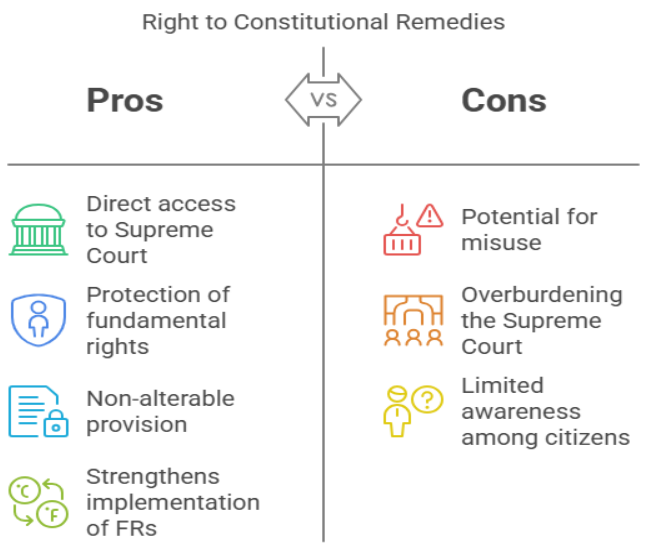
Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) grants individuals the right to seek remedies for the enforcement of their fundamental rights. This means that if any fundamental right is violated, the aggrieved person can directly approach the Supreme Court for justice. The provision itself is a fundamental right, making it a cornerstone of India's constitutional framework.
To enforce fundamental rights, Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) empowers the Supreme Court to issue five types of writs:
While Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) provides writ jurisdiction to the Supreme Court, Article 226 grants similar powers to High Courts. However, High Courts can issue writs not just for fundamental rights violations but also for other legal rights.
Under Article 32, Parliament has the authority to empower lower courts to issue writs, but this provision has not been widely implemented in India.
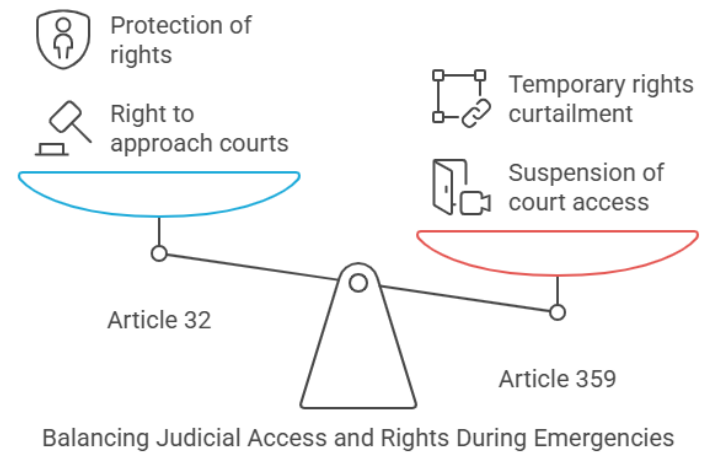
During a National Emergency, the President can suspend the right to move any court for the enforcement of fundamental rights under Article 359. However, Article 32 itself is not suspended—only the ability to enforce certain rights in courts is temporarily restricted.
Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) has played a crucial role in the evolution of Public Interest Litigation (PIL). PIL allows individuals, NGOs, and organizations to approach the Supreme Court on behalf of those whose rights have been violated but lack the means to seek legal recourse.
Through PILs, Article 32 has become an instrument of social justice, enabling the judiciary to protect vulnerable communities.
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar emphasized that without Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32), fundamental rights would be meaningless. It is the mechanism through which citizens can directly access the Supreme Court, making it one of the strongest guarantees of justice in India.
Due to the increasing number of PILs and individual petitions, the Supreme Court faces a significant backlog of cases, delaying justice.
Some individuals and organizations misuse PILs for personal or political gains, diverting attention from genuine rights violations.
Despite being a fundamental right, many citizens, especially in rural areas, lack awareness or resources to file petitions under Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32).
To ensure effective implementation of Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32), the following measures can be taken:
Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32) is a powerful constitutional safeguard that ensures the enforcement of fundamental rights. By allowing direct access to the Supreme Court, it serves as a guardian of justice and democracy in India. However, challenges like judicial delays and misuse of PILs must be addressed to strengthen its impact. As Dr. Ambedkar rightly said, it remains the "heart and soul" of the Indian Constitution, ensuring that fundamental rights are protected in their true spirit.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.