1. India–Philippines Upgrade Ties to Strategic Partnership | Key Highlights of State Visit
For Prelims:
-
India–Philippines Strategic Partnership
-
75 years of diplomatic ties (est. 1949) Look East Policy (1992) Act East Policy (2014)
-
BrahMos Missile Deal ($375 million, 2022)
-
BIMSTEC (Observer – Philippines)
-
UPI–PHLink (digital payments)
For Mains:
-
Strategic Convergence in Indo-Pacific
-
Defence Diplomacy in Act East Policy
-
India’s Maritime Outreach
-
Role of Digital Diplomacy (UPI, fintech)India’s Role in ASEAN Centrality
-
Trilateral exercises (India–Philippines–US/Japan)
-
Maritime Joint R&D (drones, sonar)
Context
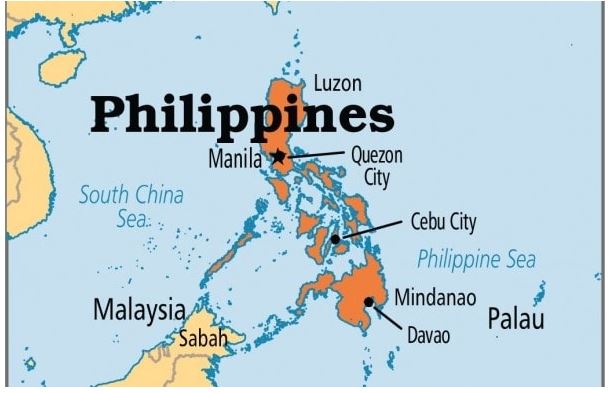
- The President of the Philippines is on a State Visit to India for the first time since assuming office in 2022.
About the Visit
- At a joint press briefing along with Marcos who is in India on a five-day visit, Modi said, "India and the Philippines are friends by choice and partners by destiny. From the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, we are united by shared values.
- Ours is not just a friendship of the past, it is a promise to the future." He said the Philippines is an important partner in India's Act East Policу.
- India and the Philippines have decided to boost their defence and maritime links, begin direct flights and start negotiating a new trade deal as they upgrade their ties to the level of a strategic partnership.
- India becomes only the fifth strategic partner for the Philippines. This new apex attests as much to the remarkably rapid growth, broadening and deepening of our 75-year-old bilateral relationship,
- India also invited the Philippines to participate in its Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region.
Other Developments
- Condemning the Pahalgam terror attack, The President Said, "I carry the message of our solidarity with India both over the tragic attack in Pahalgam earlier this year and in the broader fight against terrorism."
- The two countries have also agreed to establish mechanisms for service-to-service talks for information sharing and training exchanges among the militaries.
About India - Philippines Relations
- Historical Background: Established diplomatic relations in 1949.
- Rooted in shared colonial history, democratic values, and mutual interests across defence, trade, investment, and cultural exchange.
- 75th Anniversary of diplomatic ties celebrated in 2024–25.
- Look East and Act East Policy: When India launched the Look East Policy and intensified partnership with ASEAN in 1992, this also resulted in stronger relations with countries in the region including the Philippines.
- With the Act East Policy initiated in 2014, the relationship with the Philippines has diversified further into political-security; trade and industry and people-to-people realms.
- Defence and Security Cooperation: Defence Cooperation Agreement was signed in 2006.
- BrahMos Supersonic Missile Deal: $375 million contract signed in 2022, India delivered the first batch of BrahMos missile system in 2024, making Philippines the first foreign nation to acquire the missile weapon system.
- Maritime Security: Joint patrols, capacity building, and hydrographic cooperation.
- Regular dialogues: Joint Defence Cooperation Committee (JDCC) and Service-to-Service Staff Talks.
- Bilateral Trade: Bilateral trade between the two countries had grown steadily to reach US$ 3.5 billion in 2023-24.
- To facilitate bilateral trade, both countries signed an Agreement on Cooperation and Mutual Assistance in Custom Matters ratified in 2023.
- Negotiations on the Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) were revived in 2023.
- Indian Diaspora: It is estimated to be more than 70,000 in the Philippines.
- There has been a growing number of Indian professionals, estimated around 800, who are working in Indian and multinational corporations in the Philippines.
- Multilateral and Regional Cooperation Both countries are members of: ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF), East Asia Summit (EAS), India-ASEAN Dialogue Mechanism and BIMSTEC (Observer status by Philippines).

Other Facets of Relations
- Joint Military Exercises- Regular navy drills (e.g.,Sama Lahi-Lahi), coast guard exercises, and increased port visits. Discussions on expanding to army/air force collaborations.
- China Factor-Both nations face Chinese territorial pressure (South China Sea/Ladakh), driving alignment on upholding UNCLOS and a"free, open Indo-Pacific."
- ASEAN Centrality- Both support ASEAN-led regional architecture. India's "Act East Policy" aligns with Philippines' "AmBisyon 2040."
- Digital Partnership- Collaboration on fintech, digital payments (UPIPHLink), and IT skilling. The Philippines is a key market for Indian IT giants (TCS, Infosys).
Challenges in Relations
- Limited Economic Engagement: Despite growth, bilateral trade remains modest considering the size of both economies.
- Progress on the Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) is slow, with negotiations still in early stages.
- Maritime Security Gaps: Although MoUs exist, real-time maritime collaboration and joint patrols are limited.
- South China Sea tensions constrain deeper military cooperation, especially due to Philippines sensitivity to external involvement.
- Regional Geopolitics and China Factor: The Philippines’ complex ties with China and its dependency on US defence support limit its willingness to openly align with India in strategic domains.
Way Forward
- Enhance Connectivity & Soft Power : Launch direct flights (e.g., Manila-Mumbai/Delhi) and prioritize shipping routes (e.g., Visakhapatnam-Subic Bay).
- Align positions on UNSC reform (Philippines supports India's bid) and climate financing.
- Fast-track additional Brahmos missile batteries and explore Akash SAM systems, torpedoes, and naval vessels.Establish joint R&D in maritime tech (e.g., drones, sonar systems).
- Formalize Philippines as a "Quad Plus" partner for IndoPacific maritime security.
- Conduct trilateral drills (e.g., India-Philippines-US/ Japan) focusing on SCS patrols and disaster response.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS 2015, QUESTION
"Consider the following countries:
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the 'Dialogue Partners' of ASEAN?"_
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 6
(d) 1, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans:
Mains:
Q. UPSC GS PAPER 2, MAINS
"‘Act East Policy’ of India has led to the emergence of India as a leader in the Indo-Pacific. Discuss the key features and significance of this policy."
Ans:
2. NITI Aayog Evaluates MGNREGA for Continuation Beyond 2026 | Key Insights & Challenges
For Prelims:
-
MGNREGA, MGNREGA Act 2005
-
MGNREGA Act 2005
-
NITI Aayog
-
Development Monitoring and Evaluation Office
-
Expenditure Finance Committee
-
Ministry of Rural Development
For Mains:
-
Flood Control
-
Water Harvesting
-
Poverty Alleviation
-
Vulnerable Groups
-
Scheduled
-
Castes
-
Scheduled Tribes
-
16th Finance Commission
-
Evidence-Based Policy
-
Third-Party Evaluation
-
Scheme Continuation
Context
- NITI Aayog is currently evaluating the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).Government has informed Lok Sabha.
About the News
- The Development Monitoring and Evaluation Office (DMEO) under NITI Aayog is currently evaluating the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
- This evaluation is crucial for obtaining approval from the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) for the scheme’s continuation and budget allocation.
- The Ministry of Rural Development has circulated a proposal seeking an outlay of ₹5.23 lakh crore for MGNREGS till FY 2029–30, aligning with the 16th Finance Commission cycle.
- The Ministry of Finance mandates third-party evaluations for all Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes for continuation beyond March 31, 2026.
About Expenditure Finance Committee
- EFC, under the Ministry of Finance, appraises the financial viability of government schemes.
- Its approval is a procedural requirement for MGNREGS continuation, even though the scheme is legally backed under the MGNREGA Act.
- The evaluation and EFC approval process is part of the Centre’s larger strategy to assess and rationalize welfare schemes ahead of the next Finance Commission period.
Significance of Evaluation
- Improves Design & Implementation: Process evaluations identify bottlenecks, enabling midcourse corrections for better efficiency.
- Ensures Accountability & Transparency: Independent assessments build public trust in government spending.
- Enables Evidence-Based Decisions: Datadriven insights guide policy reforms, resource allocation, and planning.
- Promotes Learning & Improvement: Lessons from evaluations help replicate success and avoid past mistakes.
- Tracks and Achieves Outcomes: Evaluations assess impact, guiding adjustments to meet intended objectives
About MGNREGA
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005, is a legislation that provides a legal guarantee of up to 100 days of unskilled manual work per financial year to adult members of rural households willing to work.
- MGNREGA is to be implemented mainly by gram panchayats (GPs). The involvement of contractors is banned.
- Labour-intensive tasks like creating infrastructure for water harvesting, drought relief, and flood control are preferred.
Features Of MGNREGA
- Guaranteed Wage Employment: Provides 100 days of unskilled manual work annually to rural households.
- Legal Entitlement: Employment is a legal right with provision for unemployment allowance if work isn’t provided within 15 days.
- Gender Equality: Promotes equal wages for men and women; a large proportion of workers are women.
- Universal Coverage : Applicable to all rural households that volunteer for work, promoting inclusive development.
- Decentralized Planning: Empowers Gram Panchayats to plan and implement works.
- Accountability Mechanisms: Ensures social audits, grievance redressal, and DBT for transparency.
Significance
- Provides guaranteed employment to rural households, reducing seasonal unemployment and distress migration.
- Ensures minimum wages, improving the financial stability of rural workers.
- MGNREGA promotes gender equality by ensuring equal wages for men and women.
- A significant percentage of beneficiaries are women, leading to greater financial independence.
- Benefits marginalized communities, including Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and other vulnerable groups.
Challenges
- Delayed Wage Payments: Regular delays demotivate workers.
- Insufficient Funding: Budget constraints lead to reduced workdays and incomplete projects.
- Corruption & Leakages: Issues like fake job cards and misuse of funds persist.
- Poor Asset Quality: Some projects fail to create sustainable infrastructure.
Prelims:
Q. 2011 UPSC PRELIMS QUESTION
Among the following who are eligible to benefit from the ‘Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act.
(a) Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes women only
(b) Persons below the poverty line in rural areas
(c) Adult members of only the scheduled caste and scheduled tribe households
(d) Adult members of any household
Ans:
Mains:
Q. UPSC MAINS, 2022, GS PAPER 2
MGNREGA is a powerful instrument for inclusive growth in India, but it faces multiple implementation challenges." Discuss.
Ans:
3. Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF): Projects, Benefits & Challenges in India
For Prelims:
-
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)
-
Dairy Infrastructure Development Fund (DIDF)
-
Ministry of Fisheries
-
Animal Husbandry and Dairying
-
3% interest subvention
-
Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs)
-
Primary Wool Processing Infrastructure
For Mains:
-
Livestock-based Integrated Farming Systems (IFS)
-
Value Chains in Animal Husbandry
-
Livestock Market Access
-
Animal Health Infrastructure Development Fund
-
National Animal
-
Disease Control Programme (NADCP)
-
Livestock Health and Disease Control Scheme
-
Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS)
-
National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD)
Context
- Recently the Government informed the Parliament about the initiatives taken for the Animal Husbandry Sector in India.
About the News
- Through the Infrastructure development in the livestock sector, Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying is supporting individual entrepreneurs, private companies,
- The Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs), MSMEs, companies under Section 8 and dairy cooperatives, with benefits of 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, with 2 years moratorium.
- Under Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund, projects are being approved to establish dairy and meat processing units, animal feed plants, veterinary vaccine and drug manufacturing facilities, technologically assisted breed improvement farms (cattle/Buffalo/Sheep/Goat/Pig/ Poultry) animal waste to wealth management units, and primary wool processing infrastructure.
Projects approved under the Fund
- Since the inception of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF), 402 projects have been approved with a total project cost of ₹14,413.88 crore and term loan of ₹10,095.23 crore.
- Additionally, 37 projects with the project cost of Rs. 6776.80 crores and term loan of Rs. 4575.25 crores have also been approved under the Dairy Infrastructure Development Fund (DIDF) which has now been subsumed in AHIDF vide cabinet approval
Implementation stage
- These AHIDF-approved projects are at various stages of implementation and have the potential to generate employment for 43,372 personnel, benefiting approximately 25 lakh farmers.
Livestock Sector in India
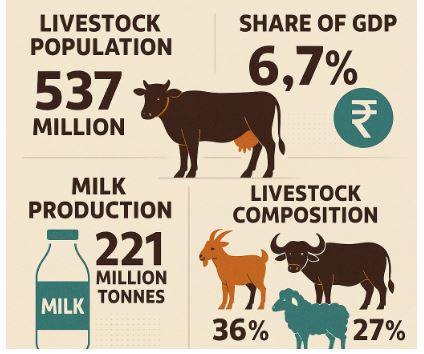
- India has the world's largest population of livestock.
- India is the largest producer of buffalo meat and 2nd largest producer of goat meat.
Significance of the Sector
- Contribution to GDP: Contribution to total Livestock GVA (at constant prices) was 30.19% of Agricultural and Allied Sector GVA and 5.73% of Total GVA in 2021-22.
- Employment Generation: Livestock rearing is a major source of livelihood for over 70% of rural households in India, with a significant proportion being small and marginal farmers and landless laborers.
- Interlinkages with Agri-activities: The livestock sector is crucial for production of organic inputs like manure and agricultural waste is used as fodder for animals.
- Food and Nutritional Security: Livestock products such as milk, meat, and eggs are rich in essential nutrients, playing a crucial role in combating malnutrition, especially among children and women.
- India is ranked 1st in milk production contributing 23% of global milk production.
Issues Faced by the Sector
- High economic losses due to animal diseases: E.g., Haemorrhagic Septicaemia, Foot and Mouth Disease, Brucellosis, etc.
- Also, zoonotic diseases can be transmitted between animals and humans, as evidenced by recent outbreaks like COVID-19, Ebola, and avian influenza
- Inadequate infrastructure and human resources: India has less than 60 recognized veterinary colleges in India, which are inadequate to turn out the required number of vets.
- Rise of Anti-Microbial Resistance: India ranks 4th in antibiotics use in animals, wherein the poultry sector is the largest reservoir of antibiotics.
- Economic Issues:
- Low Productivity: Due to inadequate nutrition, poor management practices, and low genetic potential of local breeds.
- Unorganized Sector: About half of total meat production comes from un-registered, make-shift slaughterhouses.
- High Marketing and transaction costs: of livestock products at around 15-20% of sale price.
- Low insurance cover: Only 15.47% of animals are under insurance cover.
- Shortage of fodder: India has only 5% of its cultivable land under fodder production while having 11% of livestock, creating a huge pressure on land, water and other resources.
- Inadequate attention towards extension services: There is no exclusive livestock extension program, and most services are animal health-focused, not extension-focused.
- Green House Gas emissions: Enteric methane emission from Indian livestock contributed 15.1% total global enteric methane emissions.
Way Forward
- National Animal Disease Reporting System (NADRS) requires to be strengthened with infrastructural support and digitalization for real-time reporting of disease outbreaks.
- Mobile veterinary services for remote areas to provide first aid, artificial insemination, deworming, and vaccination services at farmers' doorstep.
- To set up a national working group to review staff levels and training needs at DADF and state AHDs.
- Promote Livestock-based integrated farming system (IFS) to integrate crop cultivation, livestock rearing, and other agricultural activities to optimize resource use, enhance productivity, and ensure sustainability.
- Facilitating access to markets, establishing efficient value chains, and promoting digital platforms for marketing and information dissemination.
- Increase insurance Coverage in the Livestock Sector to shift the livestock owners' risk to insurance companies.
- Formulating Area-specific policy. E.g. policy focus in rain-fed areas should be on livestock rearing or livestock-based integrated farming systems.
Initiatives for India's Livestock Sector
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission: Focuses on the development and conservation of indigenous breeds through selective breeding and genetic upgradation.
- National Livestock Mission: Aims to ensure quantitative and qualitative improvement in livestock production systems and capacity building of all stakeholders.
- Extension of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) to the sector and establishment of Animal Health Infrastructure Development Fund etc.
- Dairy Development Programs: Schemes like the National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) and Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS) aim to modernize the dairy sector and promote entrepreneurship.
- Livestock Health and Disease Control Programs: Include the National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP) for FMD and Brucellosis, and the Livestock Health and Disease Control Scheme to strengthen disease surveillance and diagnostic services.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC 2013, PRELIMS
Consider the following livestock species:
- Buffalo
- Sheep
- Goat
- Pig
Which of the above contributes significantly to rural livelihood and nutrition in dryland India?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans:
Mains:
Q. UPSC GS MAINS 3, 2020
How can the livestock sector contribute to doubling farmers’ income?
Ans:
4. PAHAL Scheme: Aadhaar-Based LPG Subsidy Transfer & DBT Reform
For Prelims:
-
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)
-
LPG Subsidy
-
Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
-
Aadhaar-Based Authentication
-
Fake LPG Connections
For Mains:
-
Social Welfare Delivery
-
Transparency in Subsidy Transfer
-
Digital Governance Financial Inclusion
-
E-Governance
-
Fuel Subsidy Rationalization
-
Good Governance Initiative JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile)
Context
- Recently, the government has strengthened LPG subsidy transfers by enhancing the PAHAL scheme through Aadhaar-based authentication, leading to the identification and blocking of over 4 crore fake LPG connections.
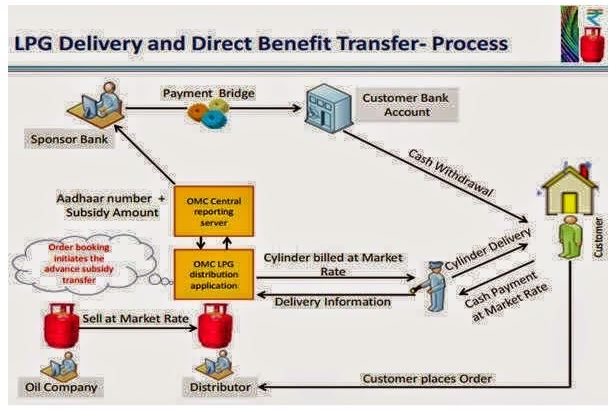
About PAHAL Scheme
- Launched by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, PAHAL is India's Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system for LPG subsidies.
- Under this scheme, consumers pay the market price for LPG cylinders, and the subsidy is directly transferred to their linked bank accounts.
- With coverage of over 17 crore LPG users, it is the world's largest cash transfer program.
Eligibility Criteria
- Must be a registered LPG consumer.
- The combined annual taxable income of the consumer and spouse should be below *10 lakh, as per the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS 2018, GS PAPER 1
Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana is aimed at:
A. providing free housing to Below Poverty Line (BPL) families
B. providing LPG connections to women from BPL households
C. providing employment to rural youth
D. providing free education to girl children
Ans:
5. Sea Star Wasting Disease: Cause Identified After 12 Years | Impact on Marine Ecosystems
For Prelims:
-
Sea Star Wasting Disease
-
North America Pacific Coast
-
2013 Epidemic
-
5 Billion Sea Stars Affected
-
20+ Sea Star Species
-
Sunflower Sea Star
For Mains:
-
Ecological Imbalance
-
Keystone Species
-
Marine Ecosystems
-
Biodiversity Loss Marine Habitat Degradation
-
Environmental Microbiology
-
Climate-linked Outbreaks Marine Conservation
Context
- Recently, after 12 years of extensive research, scientists have uncovered the cause of the devastating sea star wasting disease that has led to the death of over 5 billion sea stars along North America's Pacific coast since 2013.
Key Findings
- The epidemic devastated more than 20 sea star species, with the sunflower sea star (Pycnopodia helianthoides) being hit the hardest. Ο Ο
- Symptoms: White lesions, twisted limbs, and rapid disintegration of body tissue.
- Causal Agent: The bacterium Vibrio pectenicida was identified as the cause of the epidemic. •
- Detection Method: The bacterium was present in high concentrations in the coelomic fluid (sea star's internal fluid) of infected individuals but absent in healthy ones.
- Ecological Disruption: The collapse of predatory sea star populations allowed sea urchins to proliferate, leading to destruction of kelp forests, critical marine habitats.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS, 2011
What is the difference between a starfish and a jellyfish?
A. Starfish is an echinoderm, whereas jellyfish is a coelenterate.
B. Both are vertebrates.
C. Starfish moves by swimming, whereas jellyfish crawls.
D. Jellyfish causes water pollution but starfish does not.
Ans:
6. LEAP-1 Mission by Dhruva Space: India’s First Commercial AI-Powered Satellite Launch
For Prelims:
-
Dhruva Space – private Indian space startup
-
First commercial satellite mission of Dhruva Space
-
Launch Vehicle: SpaceX Falcon 9
-
Collaboration: Akula Tech & Esper Satellites (Australia)
-
Nexus-01 – AI/ML module with self-retraining capability
-
OTR-2 – Hyperspectral imaging sensor
For Mains:
-
Dhruva Space – private Indian space startup
-
First commercial satellite mission of Dhruva Space
-
Launch Vehicle: SpaceX Falcon 9
-
International Collaboration: Akula Tech & Esper Satellites (Australia)
-
Nexus-01 – AI/ML module with self-retraining capability
-
OTR-2 – Hyperspectral imaging sensor
Context
- Recently, Dhruva Space, an emerging Indian space-tech startup, unveiled plans for its first commercial satellite mission, LEAP-1.
About Leap - 1 Mission
- Stands for Launch, Experiment, Analyze, Progress.
- It is Dhruva Space's first commercial satellite mission, launched aboard SpaceX's Falcon 9.
- The mission carries international payloads focused on Al and Earth observation.
- Developed in collaboration with Akula Tech and Esper Satellites (both Australia)
Objectives
- Demonstrate real-time geospatial Al processing in space.
- Enable affordable hosted payloads for sectors like defense, agriculture, and disaster management.
- Exhibit Dhruva's P-30 satellite platform for commercial applications.
Payloads
- Nexus-01 (Akula Tech): An Al/ML module with onboard self-retraining capabilities.
- OTR-2 (Esper Satellites): A hyperspectral imaging sensor for high-resolution Earth observation.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTIONS, 2025
Consider the following space missions:
- Axiom‑4
- SpaDeX
- Gaganyaan
a) - ONLY ONE
b) - ONLY TWO
c) - ALL THREE
Ans:
7. Microplastic Pollution in India: Causes, Types & Coastal Impact
For Prelims:
-
Ministry of Earth Sciences
-
National Centre for Coastal Research
-
NCCR surveys
-
microplastic pollution
-
abandoned fishing gear
-
riverine discharges
For Mains:
-
UV radiation
-
wave action
-
marine pollution
-
coastal ecosystem impact
-
plastic waste sources
-
ocean microplastic monitoring
-
pollution mitigation India
Context
- Recently, surveys conducted by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), through the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR), have revealed that abandoned fishing gear and riverine discharges are the major contributors to microplastic pollution along India's coasts.
- These studies spanned 19 transects along the west coast, from Porbandar (Gujarat) to Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu), and 25 transects on the east coast, from Puri (Odisha) to Thoothukudi (Tamil Nadu).
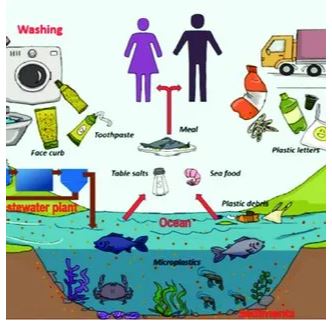
About Microplastics
- They are tiny plastic fragments, typically less than 5 mm in size. They are persistent in the environment, highly mobile, and difficult to remove once released into nature.
Types
- Primary in Microplastics: Intentionally manufactured small plastic particles. Found products like cosmetics, or released from synthetic textiles (e.g., clothes, fishing nets) during use or washing. Enter the environment through direct release, such as spills during production, abrasion, or consumer use.
- Secondary Microplastics: Formed when larger plastic items (e.g., bottles, bags) break down due to environmental exposure. Breakdown is caused by factors like sunlight (UV radiation) and ocean wave action.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION, 2018
Consider the following statements:
- Most of the world's coral reefs are in tropical waters.
- More than one-third of the world's coral reefs are located in the territories of Australia, Indonesia, and the Philippines.
- Coral reefs host far more animal phyla than those hosted by a tropical rainforest.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
8. Restitutionary Damages: Supreme Court on Pollution Control Powers in India
For Prelims:
-
Supreme Court judgment
-
Pollution Control Boards
-
restitutionary damages
-
Section 33A
-
Water Act 1974
-
Section 31A Air Act 1981
For Mains:
-
Polluter Pays Principle
-
Precautionary Principle
-
ecological recovery
-
Article 48A
-
Article 51A(g)
-
environmental governance
-
sustainable development
-
environmental jurisprudence
-
environmental accountability
Context
- Recently, the Supreme Court affirmed that Pollution Control Boards (PCBs) have the authority to impose restitutionary damages. The judgment clarified that under Section 33A of the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and Section 31A of the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, PCBs are empowered to:
- Levy fixed monetary penalties for environmental degradation, and
- Demand bank guarantees as precautionary measures to avert potential environmental harm.
About Restitutionary Damages
- Financial compensations or guarantees required from polluters to either restore damaged ecosystems or prevent potential environmental harm, even before any actual damage occurs.
Objective
- To restore air, water, and ecosystems to their original state, focusing not just on penalizing polluters but on promoting ecological recovery and long-term sustainability.
- Grounded in the "Polluter Pays" principle and the Precautionary Principle.
- Reinforces constitutional duties:
- Article 48A: Obligation of the State to protect and improve the environment.
- Article 51A(g): Fundamental duty of every citizen to protect and improve the natural environment.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION 2019
In India, ‘extended producer responsibility’ was introduced as an important feature in which of the following?
(a) Bio-medical Waste Rules, 1998
(b) Recycled Plastic Rules, 1999
(c) e‑Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011
(d) Food Safety Regulations, 2011
Ans:
9. District Flood Severity Index (DFSI): Measuring Flood Impact in Indian Districts
For Prelims:
-
District Flood Severity Index
-
IIT Delhi
-
IIT Gandhinagar
-
India Flood Inventory with Impacts (IFI-Impacts)
-
Flood severity indicators
-
Flood impact assessment
For Mains:
-
Flood-related deaths and injuries
-
District-level flood vulnerability
-
Disaster impact database
-
Population-based flood analysis
-
Disaster resilience
-
Geographic spread of floodsHydrological disasters in India
-
Climate-resilient infrastructure
-
Disaster management policies
-
Early warning systems
Context
- Recently, researchers from IIT Delhi and IIT Gandhinagar introduced a District Flood Severity Index (DFSI), which assesses the severity of floods using a range of indicators.
About
- Evaluates the historical severity of floods in Indian districts based on population impact, geographic spread, and flood duration.
- Based on the India Flood Inventory with Impacts (IFI-Impacts) database.
- Parameters Used in DFSI: Mean duration (in days) of all flooding events in a district.
- Percentage of area historically affected by floods.
- Total number of deaths and injuries caused by floods.
- Population size of the district.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION, 2017
With reference to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), consider the following statements:
- IMD is the nodal agency for issuing warnings on cyclones, storms, and earthquakes.
- IMD functions under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Ans:
10. India–Philippines Naval Exercise in South China Sea: Strategic Significance Explained
For Prelims:
-
INS Delhi
-
INS Shakti
-
INS Kiltan
-
Nine-Dash Line
-
China maritime claims
For Mains:
-
Defence diplomacy
-
FONOPs
-
Maritime security
-
Geostrategic significance
-
Indo-Pacific
-
Naval interoperability
-
ASEAN relations
-
UNCLOS compliance
Context
- Recently, India and the Philippines conducted their first-ever joint sail and naval exercises in the disputed South China Sea
About Exercise
- Purpose: To enhance maritime cooperation and interoperability between the two navies
- (Duration: Two days)
- To reinforce freedom of navigation in disputed waters. ° 이
- Location: Within the Philippine Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) in the South China Sea.
- Indian Naval Assets Involved: INS Delhi - Guided missile destroyer
- INS Shakti - Fleet replenishment tanker
- INS Kiltan - Anti-submarine warfare corvette
Strategic Significance
- A symbolic move against China's "Nine-Dash Line" claims.
- Supports India's Act East Policy and maritime cooperation through the "Necklace Diamonds" strategy.
- Strengthens defence diplomacy and freedom of navigation operations (FONOPs).
Prelims:
Q. UPSC PRELIMS 2017
“Consider the following statements:**
- The India-Australia Strategic Dialogue is a ministerial-level dialogue.
- The India-Australia naval exercise AUSINDEX is part of a broader effort to ensure freedom of navigation in the Indo-Pacific region.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Ans:
11. Biochar in India: Carbon Removal, Soil Health & Waste Management
For Prelims:
-
India
-
Carbon Removal Technologies
-
Biochar
-
National Carbon Market 2026
-
Pyrolysis
-
Agricultural Residues
-
Organic Municipal Solid Waste
For Mains:
-
Climate Mitigation
-
Sustainable Agriculture
-
Low-oxygen Combustion
-
Carbon Neutrality Target
-
India’s Climate Goals
-
Decarbonisation Pathways
-
Green Technology Innovation
Context
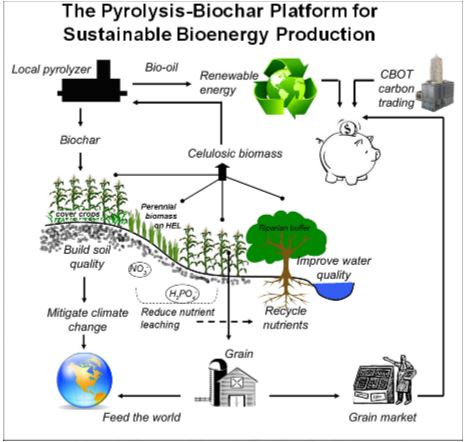
- Recently, India has turned its focus to carbon removal technologies such as biochar, recognising their potential in addressing climate challenges. This shift comes as the country prepares to launch its national carbon market in 2026.
About Biochar
- A carbon-rich, granular charcoal produced by pyrolysis (heating organic material in low-oxygen conditions). Made from agricultural residues and organic municipal solid waste. Produced at 400-600°C in kiln-like structures.
Key Benefits
- Acts as a long-term carbon sink (stores carbon in soil for 100-1,000 years).
- Improves soil health and fertility. Manages organic waste sustainably.
- Produces valuable byproducts: bio-oil and syngas.
- India can convert 30-50% of its agri and urban waste into 15-26 million tonnes of biochar, removing 0.1 gigatonnes of CO2-equivalent annually.
Prelims:
Q. PRELIMS QUESTION, 2020
What is the use of biochar in farming?
Consider the following statements:
- Biochar can be used as a part of the growing medium in vertical farming.
- When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it promotes the growth of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.
- When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it enables the medium to retain water for a longer time.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans:
12. Hepatitis D Virus (HDV): WHO Declares It Carcinogenic to Humans
For Prelims:
-
Hepatitis D Virus (HDV)
-
Carcinogenic virus (IARC classification)
-
Co-infection vs. Superinfection (HBV + HDV)
-
Transmission routes: blood
-
sex
-
injections
-
childbirth
-
Liver cancer – HDV contribution
-
WHO and IARC classification
For Mains:
-
Public health challenges in blood-borne infections
-
Role of WHO and IARC in disease classification
-
Co-infections and their health burden
-
Preventive healthcare and vaccination
-
Oncogenic viruses and cancer control
-
Early diagnosis and awareness of viral diseases
Context
- Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) officially classified the Hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic to humans. With this, HDV joins Hepatitis B and C as a major contributor to liver cancer.
About Hepatitis D
- A serious blood-borne viral infection that depends entirely on the presence of the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) to replicate. It cannot infect or multiply on its own and occurs in two forms: Co-infection: Simultaneous infection with both HBV and HDV.
Superinfection
- HDV infects a person already chronically infected with HBV.
- Common Symptoms of Hepatitis D, often misdiagnosed, include fatigue, jaundice, nausea, abdominal pain, and dark-colored urine.
- Transmission: Through infected blood, unprotected sex, unsafe injections, and from mother to child during birth.
Why Is HDV Considered Cancer-Causing:
- Aggravates HBV infection: Increases the risk of liver cancer by 2 to 6 times compared to HBV alone.
- Rapid liver damage: Up to 75% of co-infected individuals develop cirrhosis within 15 years, vs. ~50% in HBV-only cases.
- Faster progression: Leads to early onset of fibrosis and liver failure, especially among younger patients.
- Mechanism: HDV hijacks HBV's replication system, dramatically increasing viral load and oncogenic risk.
Prelims:
Q. UPSC Prelims 2019
Consider the following statements:
- Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
- Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
- Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses are several times more than those infected with HIV.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Ans: