Know about minorities in India under Section 2(c) of the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992. Learn their challenges, discrimination, government schemes, empowerment programs, and recent proposals like "Migrated Minority" status.


Minorities in India, as defined under the National Commission for Minorities (NCM) Act, 1992, include six notified communities. Their protection and empowerment are vital to ensure equality, social justice, and inclusive growth in the country.
Government Steps for Empowerment of Minorities in India are;
|
Schemes and Other Initiatives |
Description |
|
Pre and post-matric scholarship schemes for minorities (2007 and 2012) |
Scholarships provided to minorities for pre- and post-matric education |
|
Nai Roshni scheme (2013) |
Leadership development program for women of minority communities |
|
Learn and Earn scheme (2014) |
Skill upgradation scheme for minorities |
|
Minority Cyber Gram (MCG) (2014) |
Introducing digital literacy skills in identified minority clusters |
|
Nai Manzil scheme (2015) |
Education and skill development program for youth from the minority community |
|
Upgrading The Skills and Training In Traditional Arts/Crafts For Development (USTAAD) (2015) |
Upgrading skills and training in the preservation of traditional arts and crafts of minorities |
|
Hamari Dharohar (2015) |
Preserving the rich and diverse heritage of the minority community in India |
|
PM Jan Vikas Karyakram (2018) |
Improving basic needs and socio-economic conditions in minority concentration areas |
|
Naya Savera (2019) |
Free coaching and allied scheme for minorities |
|
Nai Udaan |
Support for minority students after clearing prelims of UPSC, State PSC, and SSC |
|
Strengthening of State Waqf Boards |
Support provided for training and administrative costs for State Waqf Boards |
|
Khwaja Garib Nawaz Senior Secondary School |
School established at Ajmer by Maulana Azad Education Foundation to boost minority education |
|
Maulana Azad fellowship scheme for minority students |
Fellowship scheme for minority students |
Delhi Government’s Proposal on Migrated Minorities in India
|
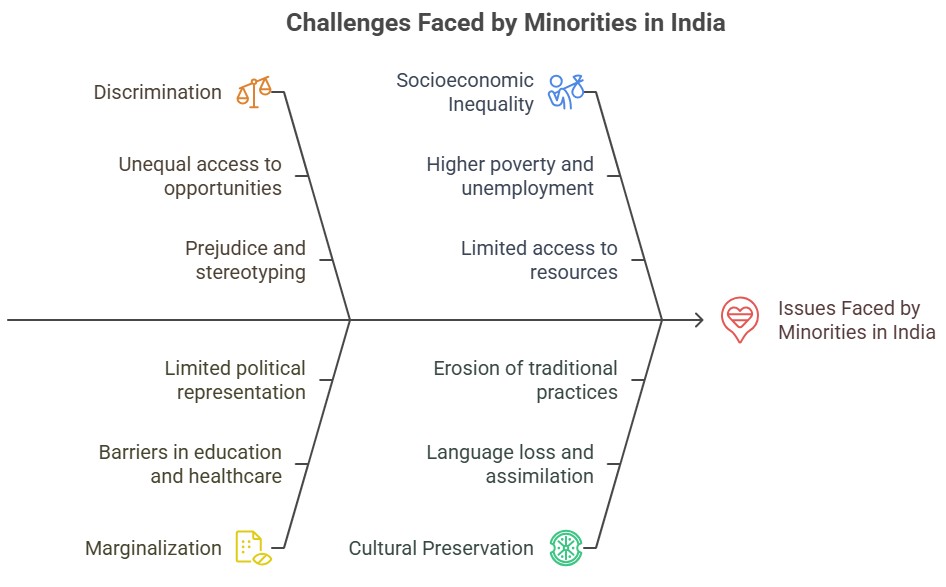
It is important to note that the specific issues faced by minorities can vary greatly depending on the cultural, social, and political context. Additionally, intersectionality should be considered, as individuals belonging to multiple minority groups may face compounded forms of discrimination and disadvantage.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.