Russia has been an enduring and trusted partner for India, and the development of their bilateral relations has been a cornerstone of India's foreign policy. Since the signing of the "Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership" in October 2000, the relationship between India and Russia has taken on a new dimension, marked by increased levels of cooperation across various domains.
Historical Background of India-Russia Relations
Soviet Legacy

- The historical roots of this relationship can be traced back to the early 20th century, with Indian freedom fighters drawing inspiration from the Russian Revolution.
- During the Cold War, India and the Soviet Union formed a strong alliance in strategic, military, economic, and diplomatic spheres.
- After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia continued this close relationship, resulting in a Special Strategic Relation between the two countries.
The Indo-Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation, along with Soviet support, aided India's successful operations in 1971.
India-Russia Strategic Partnership
- India and Russia maintain various institutionalized dialogue mechanisms, operating at both political and official levels, to ensure regular interaction and follow-up on cooperation initiatives.
- This partnership was further elevated to a "Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership" in 2010.
Challenges and the Post-Covid Scenario
- Recent years have seen challenges in the India-Russia relationship, exacerbated by Russia's close ties with China and Pakistan. The post-Covid scenario has further impacted the partnership.
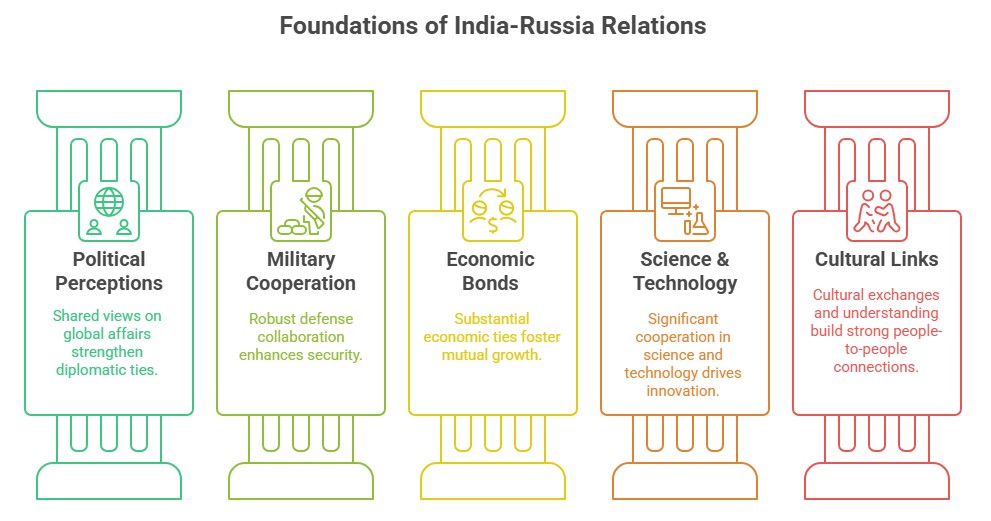
Five Pillars of India-Russia Relations
The India-Russia relationship has evolved and gained strength based on five key pillars:
- Similar political and strategic perceptions: India and Russia share common perspectives on global affairs.
- Intensive military-technical cooperation: Defense collaboration between the two nations has been robust.
- Strong economic bonds: Economic ties between India and Russia have been substantial.
- Deep ties in science and technology: India and Russia have fostered significant cooperation in the fields of science and technology.
- People-to-people and cultural links: The relationship between the people of India and Russia has been characterized by cultural exchanges and mutual understanding.
Areas of Cooperation in India-Russia Relations
Political Cooperation
- Annual Summit: The meeting between the Prime Minister of India and the President of the Russian Federation stands as the pinnacle of institutionalized dialogue, solidifying the Strategic Partnership between the two nations.
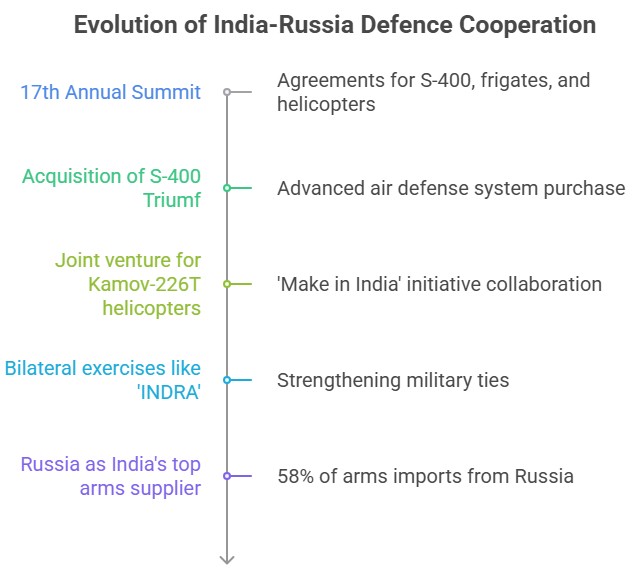
- 17th Annual Summit: Adoption of a Joint Statement titled 'Partnership for Global Peace and Stability' and a 'Roadmap of Events' to commemorate the 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations established in 2017.
- 19th Annual Summit in 2018: It welcomed the India-Russia Business Summit in New Delhi and the conclusion of a contract for the supply of the S-400 Long Range Surface to Air Missile system to India.
- President Putin's Executive Order (2019): Awarding PM Narendra Modi Russia's highest state decoration, The Order of St. Andrew the Apostle, for his significant contribution to the development of the privileged strategic partnership and friendly ties between Russia and India.
- Support for UNSC seat to India: Russia has also supported India’s claim for a permanent seat in UNSC and stood by India on the J & K issue thereby blocking Pakistan’s attempt to internationalize the issue.
Levels of Political Interactions
- BRICS Summit & SCO Summit: It provide platforms for bilateral interaction and discussion of regional issues.
- Regular high-level interactions: Occur between India and Russia through the Intergovernmental Commissions on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC) and on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC-MTC).
Economic Cooperation
- Trade: India-Russia trade hit a record $39.8 billion in 2022–23. The surge in bilateral trade came in the backdrop of India’s huge purchase of discounted Russian oil.
- Mutual goals by 2025: Both countries aim to increase bilateral investment to US$50 billion and bilateral trade to US$30 billion by 2025.
- India's Participation in the Eastern Economic Forum: Extending $1 Billion Line of Credit for the Development of Far-Right Region of Russia
- Collaboration in the diamond industry: The Gem & Jewellery Export Promotion Council of India struck a deal with Alrosa, the world's largest diamond mining company, for direct sourcing of rough diamonds.
- Investment projects: They include Imperial Energy Tomsk, Sakhalin I, Volzhsky Abrasive Works Volgograd, Commercial Indo Bank, Kamaz Vectra, Shyam Sistema Telecom Ltd, Sberbank, and VTB.
Diaspora and Cultural Exchanges in India-Russia Relations
- Indian Student Enrolment: Approximately 4,500 Indian students are currently enrolled in medical and technical institutions in the Russian Federation.
- Hindustani Samaj: The oldest Indian organization in Russia, functioning since 1957.
- Russian students learning Hindi: Around 1500 Russian students are regularly taught Hindi in approximately 20 Russian institutions, including prominent universities and schools.
- Programmes like 'Namaste Russia': It promote educational collaboration between India and Russia, facilitated through institutes like Jawaharlal Nehru Cultural Centre.
- Festival of India in Russia: Held from September 2018 to March 2019 in 22 cities, featuring 34 performances by 10 groups. Showcased the finest Indian music, dance, cuisine, and spiritual traditions.
- Exhibition honoring Mahatma Gandhi: The State Duma of the Russian Federation inaugurated an exhibition on October 2, commemorating Mahatma Gandhi's 150th birth anniversary and his connection with Russian writer Leo Tolstoy.
Defence Cooperation in India-Russia Relations
- Evolution of Cooperation: India-Russia defence cooperation has transitioned from a buyer-seller framework to joint research, development, and production.
- Notable Defence Equipment: Examples include the BrahMos Missile System, Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft, SU-30 aircraft, T-90 tanks, and frigates.
- Agreements: During the 17th Annual Summit, agreements were concluded for the supply of S-400 air defence systems, construction of frigates (Krivak Class), and joint venture manufacturing of Kamov-226T helicopters under the 'Make in India' initiative.
- Military Hardware: India has acquired advanced military hardware from Russia, such as the S-400 Triumf, Kamov Ka-226 helicopters, T-90S Bhishma tanks, and INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier.
- Bilateral Exercises: Joint military exercises, including the 'INDRA' exercise, play a significant role in defence cooperation.
- Arms imports: Russia is responsible for 58% of India's total arms imports, followed by Israel (15%) and the USA (12%).
Nuclear Cooperation in India-Russia Relations
- Strategic Vision: The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) of India and Russia's Rosatom signed a strategic vision document in December 2014 to strengthen cooperation in peaceful atomic energy applications.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Russia has constructed two nuclear power plants at Kudankulam, and agreements have been signed for the construction of additional units.
Energy and Infrastructure
- Indian Investments: Indian companies have invested close to $5.5 billion in Russia's Oil and Gas sector.
- Transport Corridor: The North South International Transport Corridor (INSTC) aims to reduce transportation time and costs between the two countries, boosting economic ties.
- Natural gas: Russia possesses one of the largest reserves of natural gas globally. ONGC Videsh, an Indian company, has acquired a 20% stake in the Sakhalin oil and gas plant.
- St. Petersburg Declaration: Both countries agreed to jointly explore hydrocarbons in the Arctic area. Russia's "Pivot to Asia" strategy and India's Draft Arctic Policy demonstrate the convergence between the two nations. The development of resources in the region will be facilitated by the Northern Sea Route.
Space, Science, and Technology
- Framework Agreement: In 2007, India and Russia signed a framework agreement on cooperation in peaceful uses of outer space, including satellite launches, GLONASS navigation, remote sensing, and societal applications.
- New Initiatives: Recent initiatives include the India-Russia Bridge to Innovation, cooperation in telemedicine, creation of a Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL), and the Russia India Network (RIN) of universities.
Terrorism
- Cooperation against Terrorism: The Agreement on Cooperation in Combating Terrorism and Organized Crime, signed during a visit by an Indian delegation to Russia in November 2017, aims to jointly fight evolving risks and threats.
- Exchange of Information: The agreement reinforces the relationship between India and Russia through the exchange and sharing of information, expertise, and best practices.
- Support for CCIT: Russia supports India's proposal for the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT).
Cyber Security
- International Information Security Agreement: India has an Agreement on Cooperation in International Information Security with Russia.
- Combating Radicalization: India and Russia collaborate closely to combat radicalization through social media platforms.
- Quantum Technology Collaboration: The Russian Quantum Center (RQC) has shown interest in collaborating with India to offer quantum technology, specifically quantum cryptography, to enhance cybersecurity in sectors like banking and national security.

Significance of India-Russia Relations to India
Strategic Advantage
- Russia's Strategic Assets: Russia possesses strategic bombers and has veto power in the UNSC, acting as a counterweight against global hegemony.
- Countering Threats: Russia has effectively countered China and Pakistan's attempts to undermine India's territorial integrity in the past.
- Historical Support: The Soviet Union and Russia have historically supported India on the Kashmir issue, while India has maintained a balanced position on Ukraine.
- International Support: Russia's support is crucial for India's aspirations for permanent membership in the UN Security Council, inclusion in the Nuclear Suppliers Group, technology control regimes, and the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
- Access to Resources: Russia can provide access to Central Asian Republics rich in resources like Uranium, Oil & Gas.
- Contributions to India: Russia has contributed to the development of India's nuclear, defense, space, and heavy industry sectors and has been a friend during critical moments, such as the 1971 Indo-Pakistan war.
Defence Procurement
- Major Arms Supplier: India has imported over $36 billion worth of arms from Russia, accounting for more than 70% of its total imports between 1992 and 2015.
- Nuclear Submarine Lease: India's only nuclear submarine, INS Chakra, is leased from Russia, and negotiations for leasing another Akula class nuclear submarine are in the final stages.
- Building Indigenous Defense Sector: Russia supports India in building an indigenous defense sector through technology transfer and joint R&D.
- Technology Transfer Advantage: Russia remains a better source for easier technology transfer than the USA in terms of material technologies and strategic raw materials inheritance.
Energy
- Meeting Energy Demands: India's relations with Russia are important to meet its increasing energy demands, as it lacks direct access to energy-rich Central Asian Republics.
- Investments in Energy Projects: India has made investments in energy projects like Sakhalin I to increase its energy imports from Russia.
- Nuclear Technology: Russia's nuclear technology is essential for India to achieve its renewable energy targets.
Recent Developments and Challenges
- Growing Ties with Other Countries: India's growing ties with the US, France, and Israel, and the emergence of the Indo-US collaboration pose a challenge to the relevance of Russia for India.
- Uneasiness with Russia-Pakistan Cooperation: Russia's increasing military cooperation and sale of military equipment to Pakistan create uneasiness for India.
- Russia-China Axis: Russia's deepening relations with China and their joint military exercises and economic partnerships affect India's maneuvering space in the region.
- Shifting Approach on Regional Issues: Shifts in Russia's approach towards regional issues, such as the AfPak issue, and its changing policies raise concerns for India.
- Diversification of Defense Equipment: India's defense equipment diversification, including deals with France and Israel, reduces its reliance on Russia.
Way Forward
- Visible Defence Deals: India should conclude visible, high-value defense deals with Russia and maintain a strong military relationship.
- Participation in Eurasian Economic Union: India's potential participation in the Eurasian Economic Union can benefit all members of the grouping.
- Establishing Rupee-Rouble Payment Mechanism: A new rupee-rouble payment mechanism should be established to facilitate trade in local currencies, bypass US sanctions, and enhance competitiveness.
- Promoting Trilateral Cooperation: Mutually beneficial trilateral cooperation between Russia, China, and India (RIC) should be promoted to reduce mistrust between India and China.
- Ensuring Stability in Afghanistan: India and Russia should work together to achieve stability and security in Afghanistan through an Afghan-led and Afghan-owned peace process.
- Seizing Defence Market Opportunities: Russia should seize the opportunity to become a major player in India's defence market as part of the "Make in India" initiative.
Conclusion
India and Russia share a long-standing relationship that is crucial for India's economic, energy, and geopolitical interests. Strengthening this relationship and finding a new logic for the "special relationship" should be pursued with energy and enthusiasm by both sides.