Explore the evolution of the Indian Constitution, its historical roots, key British Acts, Constituent Assembly, landmark amendments, and unique features shaping modern India’s democratic framework.


Indian Constitution: A constitution is a comprehensive framework of laws and regulations that establishes the structure of a state's government. It delineates the roles and interactions of various governmental institutions.
The Constitution of India is a product of a historical process that draws upon a rich array of constitutional antecedents.
|
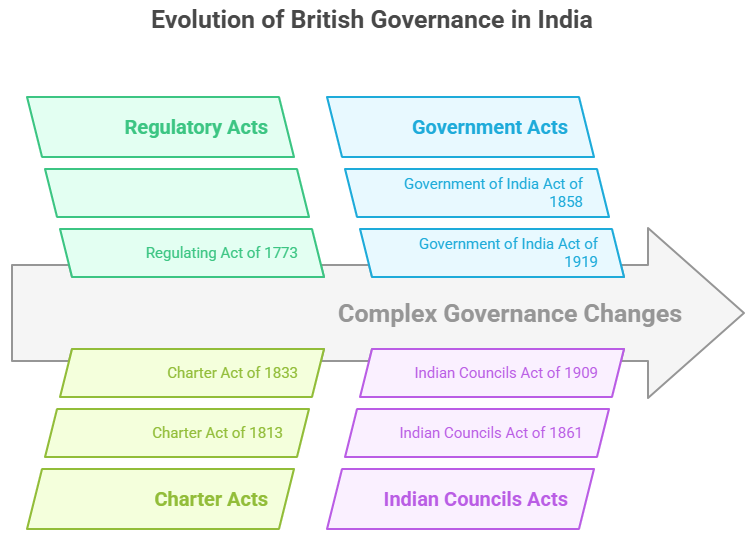
Important British Acts during colonial time |
Regulating Act of 1773, Charter Act of 1833, Indian Councils Act of 1861, Government of India Act of 1919, Government of India Act of 1935 etc. |
|
Constituent Assembly |
Formation: December 9, 1946 Duration: From December 1946 to November 1949 Adoption of Constitution: November 26, 1949 |
|
Amendments |
Provide flexibility, address deficiencies, reflect social change, enhance democracy, protect fundamental rights, meet international obligations, and ensure constitutional stability. |
|
Basic Structure Doctrine |
Originated: Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala case in 1973. |
|
Current Role |
The Constitution has been amended to address evolving needs, but its core principles remain intact. |
British colonial rule in India shaped the bedrock of the Indian Constitution:
Critics have raised several concerns about the Constituent Assembly, highlighting the following issues:
|
Samvidhan Divas: Celebrating India's Constitution Samvidhan Divas, observed on 26th November annually, honors the adoption of the Constitution of India, representing the nation's dedication to its fundamental principles and values. |
The Indian Constitution is not merely a rulebook for governing the nation, but a visionary blueprint that sought to uphold the ideals of dignity and Swaraj (self-rule) that emerged during the Indian national movement.
The Indian Constitution is a remarkable blend of various constitutional frameworks from over 60 countries.
Convention, judicial interpretation, and the written portion of the composition from a variety of sources mainly from the Government of India Act, 1935.
|
Countries |
Features taken |
|
Ireland |
Directive Principles of State Policy, Ability Representation in the Rajya Sabha, and the process for electing the Indian President |
|
USA |
Fundamental Rights |
|
UK |
Parliamentary system of Government |
|
Germany |
Emergency provision |
|
South Africa |
Two-thirds majority amendment procedure in Parliament and election of Rajya Sabha members |
The Constituent Assembly drafted the Constitution for Independent India, creating a legal framework and India-specific systems that granted dignity to millions of people. We can conclude that even though indirectly elected, the Constituent Assembly was representative in the sense that it consisted of the people from all sections of the Indian society. Although with some limitations, constituent assembly drafted a comprehensive constitution.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.