Explore the Districts of Uttar Pradesh, their area, unique cultural and historical significance, key economic contributions, and population density etc.
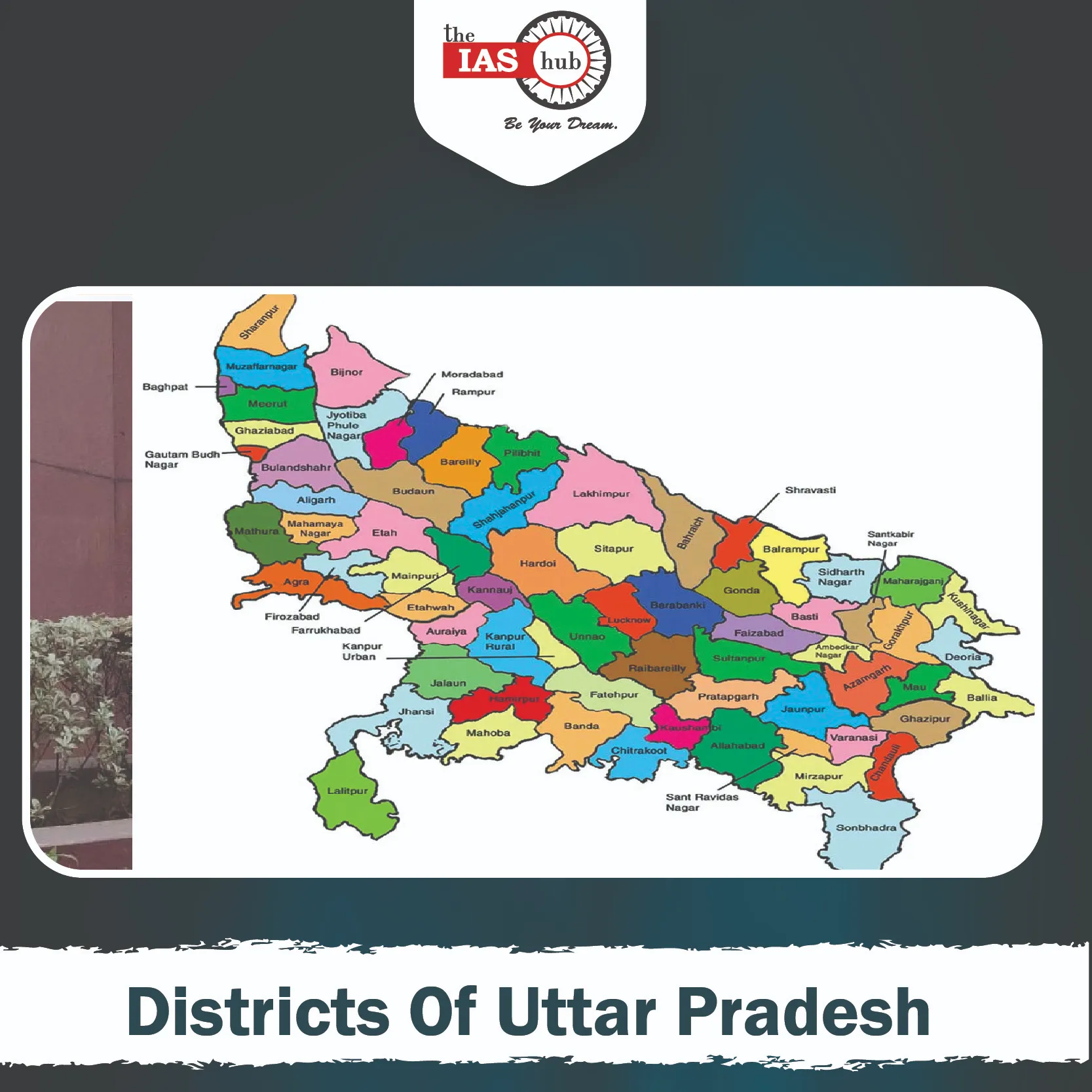

Uttar Pradesh, the most populous state in India, is divided into 75 districts. These districts serve as administrative units, each with distinct geographical, cultural, and economic characteristics. The state is a hub of history, agriculture, and industry, making its districts crucial for governance and development.

Uttar Pradesh has been a significant region in Indian history, shaping political, cultural, and economic developments over millennia. In ancient times, it was the center of Vedic civilization, with the Kuru and Panchala kingdoms playing key roles. During the Mahajanapada period (6th century BCE), prominent states like Kashi, Kosala, and Vatsa flourished here. The region later became a core part of the Maurya and Gupta empires, contributing to advancements in administration, economy, and culture. Buddhism and Jainism gained prominence, with cities like Sarnath and Kaushambi becoming major religious centers.
During the medieval period, Uttar Pradesh witnessed the rise of regional powers such as the Gurjara-Pratiharas and the Gahadavalas before coming under the control of the Delhi Sultanate in the 13th century. The Mughal Empire further strengthened the region’s significance, making Agra one of its capital cities. Under Akbar, the region saw extensive administrative and economic reforms. Cities like Varanasi, Allahabad, and Lucknow became important centers of culture, art, and trade. The weakening of Mughal authority led to the emergence of the Nawabs of Awadh, who maintained semi-autonomous rule until the British annexation in 1856.
British rule brought significant changes, with UP becoming a key center of resistance. The Revolt of 1857, which began in Meerut, saw major battles in Kanpur, Lucknow, and Jhansi. After the rebellion’s suppression, the British restructured governance, renaming the region the North-Western Provinces and later the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh. The introduction of railways, English education, and new land revenue policies disrupted traditional agrarian structures, leading to frequent peasant unrest. The region played a leading role in the nationalist movement, with leaders like Motilal Nehru, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Madan Mohan Malaviya emerging from here. The Non-Cooperation, Civil Disobedience, and Quit India movements saw significant participation from UP.
After independence in 1947, the United Provinces was renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950. The state remained politically dominant, producing many national leaders, including several prime ministers. Economic and social challenges such as population pressure, agrarian distress, and communal tensions have shaped its modern trajectory. Today, Uttar Pradesh is India’s most populous state and continues to be a crucial political and cultural hub.
Below is a table listing all the districts of Uttar Pradesh:
| S.No | District | Population (2011 Census) | Area (sq km) |
| 1 | Agra | 4,418,797 | 4,027 |
| 2 | Aligarh | 3,673,889 | 3,650 |
| 3 | Ambedkar Nagar | 2,397,888 | 2,350 |
| 4 | Amethi | 2,540,956 | 2,321 |
| 5 | Amroha | 1,840,221 | 2,321 |
| 6 | Auraiya | 1,379,545 | 2,054 |
| 7 | Azamgarh | 4,613,913 | 4,054 |
| 8 | Badaun | 3,681,896 | 5,168 |
| 9 | Bagpat | 1,303,048 | 1,321 |
| 10 | Bahraich | 3,487,731 | 5,967 |
| 11 | Ballia | 3,239,774 | 2,981 |
| 12 | Balrampur | 2,148,665 | 3,264 |
| 13 | Banda | 1,799,410 | 4,408 |
| 14 | Barabanki | 3,260,699 | 3,825 |
| 15 | Bareilly | 4,448,359 | 4,120 |
| 16 | Basti | 2,461,056 | 2,688 |
| 17 | Sant Ravidas Nagar | 1,554,203 | 1,015 |
| 18 | Bijnor | 3,682,713 | 4,561 |
| 19 | Bulandshahr | 3,499,171 | 4,512 |
| 20 | Chandauli | 1,952,756 | 2,484 |
| 21 | Chitrakoot | 991,730 | 3,216 |
| 22 | Deoria | 3,100,946 | 2,535 |
| 23 | Etah | 1,774,480 | 2,431 |
| 24 | Etawah | 1,581,810 | 2,311 |
| 25 | Ayodhya | 2,470,996 | 2,764 |
| 26 | Farrukhabad | 1,885,204 | 2,279 |
| 27 | Fatehpur | 2,632,733 | 4,152 |
| 28 | Firozabad | 2,498,156 | 2,362 |
| 29 | Gautam Buddha Nagar | 1,648,115 | 1,269 |
| 30 | Ghaziabad | 4,681,645 | 1,956 |
| 31 | Ghazipur | 3,622,727 | 3,377 |
| 32 | Gonda | 3,433,919 | 4,003 |
| 33 | Gorakhpur | 4,440,895 | 3,321 |
| 34 | Hamirpur | 1,104,285 | 4,121 |
| 35 | Hapur | 1,338,211 | 1,774 |
| 36 | Hardoi | 4,092,845 | 5,986 |
| 37 | Hathras | 1,564,708 | 1,800 |
| 38 | Jalaun | 1,689,974 | 4,565 |
| 39 | Jaunpur | 4,476,072 | 4,038 |
| 40 | Jhansi | 2,000,755 | 5,024 |
| 41 | Kannauj | 1,656,616 | 2,275 |
| 42 | Kanpur Dehat | 1,796,184 | 3,021 |
| 43 | Kanpur Nagar | 4,581,268 | 3,155 |
| 44 | Kasganj | 1,436,719 | 1,993 |
| 45 | Kaushambi | 1,599,596 | 1,901 |
| 46 | Kheri | 4,021,243 | 7,680 |
| 47 | Kushinagar | 3,564,544 | 2,873 |
| 48 | Lalitpur | 1,221,592 | 5,039 |
| 49 | Lucknow | 4,589,838 | 2,528 |
| 50 | Maharajganj | 2,684,703 | 2,951 |
| 51 | Mahoba | 875,958 | 2,884 |
| 52 | Mainpuri | 1,868,529 | 2,760 |
| 53 | Mathura | 2,541,894 | 3,340 |
| 54 | Mau | 2,205,968 | 1,713 |
| 55 | Meerut | 3,443,689 | 2,599 |
| 56 | Mirzapur | 2,496,970 | 4,405 |
| 57 | Moradabad | 4,772,006 | 3,648 |
| 58 | Muzaffarnagar | 4,143,512 | 4,008 |
| 59 | Pilibhit | 2,037,225 | 3,686 |
| 60 | Pratapgarh | 3,209,141 | 3,717 |
| 61 | Prayagraj | 5,954,391 | 5,482 |
| 62 | Rae Bareli | 3,405,559 | 4,609 |
| 63 | Rampur | 2,335,398 | 2,367 |
| 64 | Saharanpur | 3,466,382 | 3,860 |
| 65 | Sambhal | 2,219,331 | 2,457 |
| 66 | Sant Kabir Nagar | 1,715,183 | 1,624 |
| 67 | Shahjahanpur | 3,006,538 | 4,575 |
| 68 | Shamli | 1,271,780 | 1,271 |
| 69 | Shravasti | 1,117,361 | 1,126 |
| 70 | Siddharthnagar | 2,559,297 | 2,752 |
| 71 | Sitapur | 4,483,992 | 5,743 |
| 72 | Sonbhadra | 1,862,559 | 6,905 |
| 73 | Sultanpur | 3,797,117 | 4,436 |
| 74 | Unnao | 3,108,367 | 4,558 |
| 75 | Varanasi | 3,676,841 | 1,535 |

The largest districts in Uttar Pradesh by area are:
| Rank | District | |
| 1 | Lakhimpur Kheri | |
| 2 | Sonbhadra | |
| 3 | Hardoi | |
| 4 | Sitapur | |
| 5 | Bahraich |
| Rank | Districts | Description | Area (sq km) | Map |
| 1 | Lakhimpur Kheri | Located in the Terai region, Lakhimpur Kheri is the largest district in Uttar Pradesh by area. It shares a border with Nepal and is known for its sugarcane production, dense forests, and Dudhwa National Park, which is home to tigers, elephants, and rare swamp deer. The district has a strong agrarian economy, with sugar mills playing a vital role. | 7,680 |  |
| 2 | Sonbhadra | Situated in southeastern Uttar Pradesh, Sonbhadra is known as the “Energy Capital of India” due to its coal, thermal, and hydroelectric power plants. The district has rich mineral resources, including limestone, bauxite, and gold reserves. It also has historical and archaeological significance, with ancient cave paintings and temples. The Vindhya and Kaimur hills add to its geographical diversity. | 6,905 |  |
| 3 | Hardoi | Hardoi is an agricultural district in central Uttar Pradesh, known for its wheat, rice, and potato production. The district has historical relevance, with links to the Mahabharata and Mughal periods. It is also home to several religious and cultural sites, including temples and Sufi shrines. The Gomti River flows through the district, supporting irrigation and local livelihoods. | 5,986 |  |
| 4 | Sitapur | Located in the Awadh region, Sitapur has a mix of historical, cultural, and economic importance. It was a center of activity during the 1857 Revolt and has several temples dedicated to Hindu deities. Agriculture is the mainstay of the economy, with crops like sugarcane, wheat, and pulses being widely cultivated. The district also has religious significance, with Naimisharanya being a major pilgrimage site for Hindus. | 5,743 |  |
| 5 | Bahraich | Bordering Nepal, Bahraich is known for its historical significance and biodiversity. It was an important center during ancient and medieval times and played a role in the 1857 Revolt. The district has a diverse population, including a significant tribal presence. Agriculture dominates the economy, and Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary is a key ecological site, home to rare species like the Gangetic dolphin and swamp deer. | 5,967 |  |
The smallest district in Uttar Pradesh by area is Hapur, covering approximately 660 sq km. Carved out of Ghaziabad in 2011, it is known for its agricultural economy, particularly wheat, sugarcane, and dairy farming. The district is also a hub for brass and paper manufacturing industries. Its proximity to Delhi makes it an important part of the National Capital Region (NCR).

The state government manages the districts of Uttar Pradesh through a well-defined administrative framework. Each district is led by a District Magistrate (DM), responsible for law and order, revenue collection, and development programs. The Superintendent of Police (SP) oversees law enforcement, ensuring public safety.
Each district is further divided into tehsils or sub-divisions, managed by a Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM). These tehsils contain blocks, which govern villages and towns. This hierarchical structure allows for efficient governance and local administration.
| Division | Headquarters | Districts |
| Aligarh Division | Aligarh | Aligarh, Etah, Hathras, Kasganj |
| Agra Division | Agra | Agra, Mathura, Mainpuri, Firozabad |
| Azamgarh Division | Azamgarh | Azamgarh, Ballia, Mau |
| Ayodhya Division | Ayodhya | Ayodhya, Ambedkar Nagar, Barabanki, Sultanpur, Amethi |
| Basti Division | Basti | Basti, Sant Kabir Nagar, Siddharthnagar |
| Bareilly Division | Bareilly | Bareilly, Pilibhit, Shahjahanpur, Budaun |
| Chitrakoot Division | Banda | Banda, Chitrakoot, Hamirpur, Mahoba |
| Devipatan Division | Gonda | Bahraich, Balrampur, Gonda, Shravasti |
| Gorakhpur Division | Gorakhpur | Deoria, Gorakhpur, Kushinagar, Maharajganj |
| Jhansi Division | Jhansi | Jalaun, Jhansi, Lalitpur |
| Kanpur Division | Kanpur | Auraiya, Etawah, Farrukhabad, Kannauj, Kanpur Dehat, Kanpur Nagar |
| Lucknow Division | Lucknow | Hardoi, Lakhimpur Kheri, Lucknow, Raebareli, Sitapur, Unnao |
| Meerut Division | Meerut | Baghpat, Bulandshahr, Gautam Buddha Nagar, Ghaziabad, Meerut, Hapur |
| Mirzapur Division | Mirzapur | Mirzapur, Sant Ravidas Nagar (Bhadohi), Sonbhadra |
| Moradabad Division | Moradabad | Bijnor, Amroha, Moradabad, Rampur, Sambhal |
| Prayagraj Division | Prayagraj | Prayagraj, Fatehpur, Kaushambi, Pratapgarh |
| Varanasi Division | Varanasi | Chandauli, Ghazipur, Jaunpur, Varanasi |
| Saharanpur Division | Saharanpur | Muzaffarnagar, Saharanpur, Shamli |
The districts of Uttar Pradesh span a diverse landscape. The northern districts, including Saharanpur and Bijnor, have fertile lands due to the Himalayan foothills. The Gangetic plains, covering districts like Kanpur, Allahabad, and Varanasi, are known for their agricultural productivity. The Bundelkhand region, with districts like Jhansi and Banda, experiences a drier climate, affecting its agricultural output. The Terai belt, near districts such as Lakhimpur Kheri and Bahraich, is rich in biodiversity, with lush forests and wildlife reserves.
Several districts of Uttar Pradesh have deep-rooted cultural and historical importance. Varanasi, one of the world’s oldest cities, is a spiritual hub. Agra, home to the Taj Mahal, attracts millions of tourists. Ayodhya, believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama, holds immense religious significance. Mathura and Vrindavan, associated with Lord Krishna, see heavy pilgrim footfall.
The state has played a major role in India’s history, from the Mughal era to the freedom movement. Districts like Meerut and Lucknow were central to the 1857 Revolt, shaping India’s independence struggle.
Below is a table highlighting unique characteristics of select districts of Uttar Pradesh:
| S.No | District | Importance |
| 1 | Agra | Famous for the Taj Mahal, leather goods, textiles, handicrafts, and petha sweet. |
| 2 | Aligarh | Known for lock industry, Aligarh Muslim University, cuisine, and cultural heritage. |
| 3 | Prayagraj (Allahabad) | Major pilgrimage site, Kumbh Mela, traditional arts, chikankari embroidery, glass bangles. |
| 4 | Ambedkar Nagar | Named after B.R. Ambedkar, agriculture, temples, historical sites. |
| 5 | Amethi | Parliamentary constituency of Rajiv Gandhi, agriculture, educational institutions. |
| 6 | Amroha | Handcrafted wooden toys, historical sites, Dargah of Shah Wilayat. |
| 7 | Auraiya | Textile industry, historical sites, Pali Temple. |
| 8 | Azamgarh | Historical legacy, literary heritage, pilgrimage sites. |
| 9 | Baghpat | Agriculture, historical sites, ancient town of Agroha. |
| 10 | Bahraich | Wildlife, national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, agriculture. |
| 11 | Ballia | Cultural heritage, historical sites, agriculture. |
| 12 | Balrampur | Rich history, temples, agriculture. |
| 13 | Banda | Natural beauty, waterfalls, temples, weaving, embroidery. |
| 14 | Barabanki | Historical figures, scenic beauty, agriculture. |
| 15 | Bareilly | Unique cuisine, historical and cultural heritage, handicrafts. |
| 16 | Basti | History, temples, natural attractions, agriculture. |
| 17 | Sant Ravidas Nagar (Bhadohi) | Carpet industry, cultural heritage, ancient temples. |
| 18 | Bijnor | Natural beauty, unique cuisine, agriculture. |
| 19 | Budaun | History, ancient monuments, natural beauty, agriculture. |
| 20 | Bulandshahr | Blend of cultures, historical monuments, scenic beauty, agriculture. |
| 21 | Chandauli | Cultural heritage, natural beauty, scenic spots, industrial center. |
| 22 | Chitrakoot | Religious significance, temples, natural beauty, pilgrimage center. |
| 23 | Deoria | Religious significance, temples, natural beauty, agriculture. |
| 24 | Etah | Unique cuisine, cultural heritage, agriculture. |
| 25 | Etawah | Cultural heritage, natural beauty, industrial center. |
| 26 | Ayodhya | Rich history, religious significance, pilgrimage center. |
| 27 | Farrukhabad | Blend of cultures, historical monuments, scenic beauty, agriculture. |
| 28 | Fatehpur | Cultural heritage, natural beauty, agriculture. |
| 29 | Firozabad | Glass industry, cultural heritage, temples, monuments. |
| 30 | Gautam Buddha Nagar (Noida) | Modern infrastructure, multinational companies, education, IT industry. |
| 31 | Ghaziabad | Strategic location, cultural heritage, industrial center. |
| 32 | Ghazipur | Agricultural contributions, mango orchards, folk traditions. |
| 33 | Gonda | Natural beauty, monuments, rice, wheat, sugarcane production. |
| 34 | Gorakhpur | Historical significance, educational institutions, commercial center. |
| 35 | Hamirpur | Ancient temples, cultural heritage, traditional handicrafts. |
| 36 | Hapur | Strategic location, handicrafts, industrial center. |
| 37 | Hardoi | Eco-tourist destinations, Gomati River, educational centers. |
| 38 | Hathras | Agricultural production, spice “hing,” Desi Ghee products, cultural heritage. |
| 39 | Jalaun | Rich history, historical sites, mineral resources, handicrafts. |
| 40 | Jaunpur | Tourist attractions, agriculture, emerging industries. |
| 41 | Jhansi | Historical significance, railway junction, architecture, agriculture. |
| 42 | Kannauj | Perfume capital, rose water, fairs and festivals. |
| 43 | Kanpur Dehat | Agricultural economy, dairy farming, small-scale industries. |
| 44 | Kanpur Nagar | Industrial city, educational institutions, historical landmarks. |
| 45 | Kasganj | Rich history, buffalo milk ghee, export industry. |
| 46 | Kaushambi | Historical sites, religious center, Hindu deities. |
| 47 | Lakhimpur Kheri | Sugar production, wildlife, Sikh population. |
| 48 | Kushinagar | Major Buddhist pilgrimage site, fragrances, handloom industry. |
| 49 | Lalitpur | Ceramic and terracotta handicrafts, folk culture, temples. |
| 50 | Lucknow | Architecture, cuisine, education, cultural heritage. |
| 51 | Maharajganj | Protected forests, wildlife sanctuaries, agriculture. |
| 52 | Mahoba | Sun temple, rock-cut images, mineral resources. |
| 53 | Mainpuri | Industries including cotton ginning, oilseed milling, and handicrafts. |
| 54 | Mathura | Birthplace of Lord Krishna, cultural and religious significance, Mathura Peda sweet. |
| 55 | Mau | Handloom industry, Banarasi sarees, dress materials. |
| 56 | Mirzapur | Brass industry, carpets, handicrafts, cultural heritage. |
| 57 | Meerut | Industrial hub, historical significance, cuisine. |
| 58 | Moradabad | Brass industry, cultural heritage, exports. |
| 59 | Muzaffarnagar | Sugar industry, wrestling, Haiderpur wetland. |
| 60 | Pilibhit | Pilibhit Tiger Reserve, mining, agriculture. |
| 61 | Pratapgarh | Agrarian district, Kisan Devta Mandir, Ganga dolphins. |
| 62 | Rae Bareli | Industries like NTPC and Modern Coach Factory, AIIMS. |
| 63 | Rampur | Cuisine, Rampur knife, poetry. |
| 64 | Saharanpur | Cottage industries, wood carving, historical significance. |
| 65 | Sambhal | Brass industry, cottage crafts, agriculture. |
| 66 | Sant Kabir Nagar | Cultural heritage, Samadhi sthal of Sant Kabir. |
| 67 | Shahjahanpur | Education, mangoes, historical sites. |
| 68 | Shamli | Sugarcane, jaggery production, paper mills. |
| 69 | Shravasti | Ancient city ruins, Stupas, Jain temples, historical significance. |
| 70 | Siddharthnagar | Historical and cultural heritage, wildlife, agriculture. |
| 71 | Sitapur | Traditional crafts, mangoes, cultural heritage. |
| 72 | Sonbhadra | Obra Dam, industries, historical sites, Rihand Dam. |
| 73 | Sultanpur | Shri Dudhnath Baba Ji Maharaj Temple, historical significance. |
| 74 | Unnao | Leather industries, historical sites, archaeology. |
| 75 | Varanasi | Spiritual significance, temples, Banarasi sarees, silk industry, Ghats along the Ganges. |
The economy of Uttar Pradesh thrives on agriculture, industry, and tourism. Districts like Bareilly, Gorakhpur, and Moradabad contribute significantly through their unique industries.
The districts of Uttar Pradesh reflect India’s rich heritage, economic strength, and administrative efficiency. From the cultural landmarks of Varanasi and Agra to the industrial growth in Noida and Kanpur, each district contributes uniquely to the state’s identity. With continued efforts in infrastructure, employment, and governance, Uttar Pradesh’s districts will play an even greater role in India’s progress.
Are you preparing for UPSC 2025? Join IAShub’s UPSC coaching batches to boost your preparation. Enroll now!
Lakhimpur Kheri is the largest district in Uttar Pradesh, covering an area of 7,680 square kilometers. It is known for its vast agricultural lands and the Dudhwa National Park.
Hapur is the smallest district in Uttar Pradesh, covering approximately 660 square kilometers. Despite its small size, it plays a significant role in industry and trade.
A complete list of all 75 districts in Uttar Pradesh, along with their population and area, is available in the article. The list includes key details such as historical significance, economic contributions, and cultural heritage.
Varanasi, Agra, Ayodhya, Mathura, and Meerut are among the most historically significant districts in Uttar Pradesh. Varanasi is one of the world's oldest cities, Agra is home to the Taj Mahal, Ayodhya is believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama, Mathura is associated with Lord Krishna, and Meerut played a key role in India's First War of Independence in 1857.


Refine your answer writing skills and elevate your UPSC preparation with personalized support and expert feedback.
Fill out the form to get started with the program or any other enquiries !








Are you dreaming of becoming an IAS officer? Then, IAShub can be your best guide. It is one of the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi. Many students who want to clear the UPSC exam join IAShub for learning. The institute gives both online and offline classes. Their teachers are experienced and helpful. They easily explain every topic. Students also get notes, tests, and tips to do well in the exam.
IAShub is in Delhi and is trusted by many UPSC students. It offers coaching for every part of the UPSC exam – Prelims, Mains, and Interview. The classes are simple and easy to understand. The teachers are experts and guide students in the right way. IAShub is also known for its helpful notes, test series, and answer-writing practice. IAShub is the best coaching in Delhi and also gives UPSC Online Classes. This helps students from any place in India to learn. The online classes are live and also recorded. So, students can watch them anytime. These classes cover the full UPSC syllabus.
Here are some important services provided by IAShub:
The UPSC Civil Services Exam has three parts:
This exam is tough, but with the right guidance, it becomes easy to manage. Students must study smart and stay regular.
IAShub supports students from the beginning to the end. It gives the right books, tests, and notes. The classes are easy to follow, and the teachers are always ready to help. Students get personal doubt sessions too. The test series and answer checking help students learn where they need to do better. Also, free study materials save time and money.
IAShub also guides students during the final stage – the interview. Experts take mock interviews and give useful tips. This full support makes IAShub one of the best IAS coaching in Delhi.
